Save to Index
When you create a Scheduled Search, you can save the results to an Index. This way, your data can be searched at a later time using _index=index_name with increased search performance.
For example, you could use the following query to find successful logins on a Linux system, then save the results to an Index using the Save to Index alert type for your Scheduled Search.
_sourceCategory=OS/Linux* ("su:" or "sudo:" or "sshd:" or "sshd[" or "pam:") (("Accepted" and "pam") or "session" or ("to" and "on")) !"closed"
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<dest_host>\S*)\s(?:\w*):\s+(?<message>.*)$" nodrop
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<dest_host>\S*)\s(?:\S*)\[\d+\]:\s+(?<message>.*)$" nodrop
| parse "session * for user * by *(uid=" as (action,dest_user,src_user) nodrop
| parse regex "session (?<action>\w*) for user (?<dest_user>\S*)" nodrop
| parse "Accepted keyboard-interactive/pam for * from * port * *" as (dest_user,src_host,src_port,protocol)
| parse "rhost=* " as src_host nodrop
| where dest_user!="" | "Login/Success" as classification | "Low" as Severity | "Linux" as Device_Vendor | "OS" as Device_Type
When naming your index, use a name that's descriptive and easy to remember. Names can be comprised of alphanumeric characters; underscores( _ ) are the only special characters allowed.
Should I create a Scheduled View or use Save to Index?
In most cases, if you can use a Scheduled View for your use case, this may be a better option, as Scheduled Views include many built in safeguards, as well as management features. If your search query needs to use operators that are restricted for Scheduled Views, saving your Scheduled Search results to an Index allows you to do this.
Limitations
- When you use Save to Index, metadata fields from the Collector (for example, _collector) will be dropped.
- Role filters may not work. If the filter depends on any field that doesn't exist in the Index (or has been altered like _collector), then it won't work.
- No more than 512 results can be saved each time the Scheduled Search completes.
Save the results of a scheduled search as an Index
- Save a search.
- Click Schedule this search.
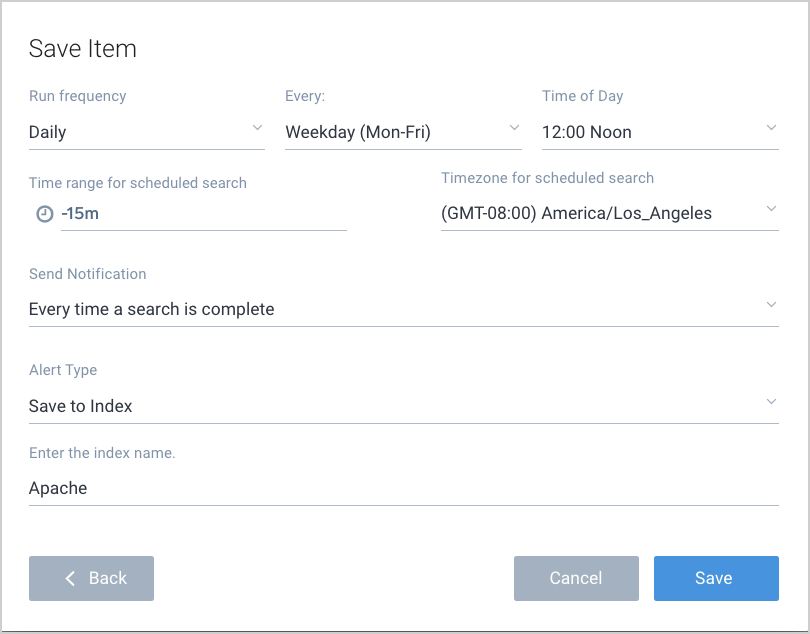
- For all configuration options, see Schedule a Search.
- Alert Type. Select Save to Index.
- Index Name. Enter a name that you'll use to search the data in a query. Use a name that's descriptive and easy to remember. Names can be comprised of alphanumeric characters; underscores (
_) are the only special characters allowed. - Click Save.
Once you have saved your Scheduled Search as an Index, you can cancel or edit the Scheduled Search, but you cannot delete an Index.