Suppressed Lists
This topic has information about suppressed lists and how to create them.
About suppressed lists
Cloud SIEM supports several types of signal suppression: suppression of redundant signals, suppression of signals on particular entities, suppression of signals on blocks of IP addresses, and finally the suppressed lists feature, which enables you to suppress signals that contain a particular indicator value in any of the signals’ records.
You can create suppressed lists from the Cloud SIEM UI or using the Cloud SIEM API. A suppressed list can contain a set of indicators—IPs, hostnames, or any other type that you can use in a match list—and then any signal that has a record containing a listed indicator will be suppressed.
Here are some sample suppressed lists:
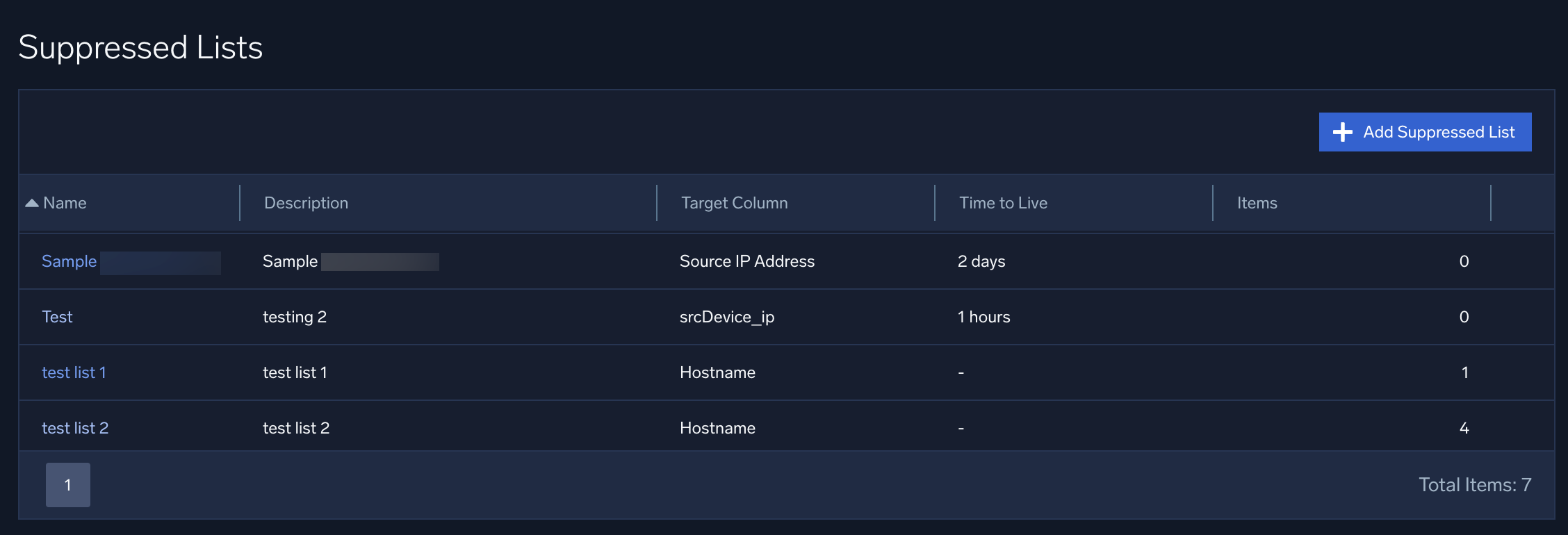
Note that each suppressed list has a Target Column, which you define when you create the list. The target column indicates what type of record fields should be compared to the suppressed list, for example, hostnames, URLs, domains, IP addresses, usernames, and so on. For more information, see How are suppressed lists used.
When you create a suppressed list, you can choose one of the following as its target column.
- Hostname
- File Hash
- URL
- Domain
- Username
- IP Address
- IP ASN
- IP ISP
- IP Organization
- Source IP Address
- Source IP ASN
- Source IP ISP
- Source IP Organization
- Destination IP Address
- Destination IP ASN
- Destination IP ISP
- Destination IP Organization
Suppressed list or match list?
When deciding whether to put an indicator on a suppressed list or a match list, consider the following.
Suppressed lists are intended for situations in which you want to suppress any signal with a record that contains a suppressed indicator. You don’t need to reference a suppressed list in a rule expression for suppression to occur.
Match lists are for when you want to use the existence or absence of an indicator to determine whether a specific rule or set of rules should fire a signal. So, a match list only has an effect when referenced by a rule expression.
How are suppressed lists used?
Cloud SIEM uses suppressed lists similar to how it uses match lists. When Cloud SIEM processes an incoming record, it compares the entries in each suppressed list to record fields of the same type as the target column of the suppressed list. For example, given a suppressed list whose target column is Domain, Cloud SIEM will compare items on that list only to record fields that contain domains.
Keep in mind:
- Suppression lists will suppress any signal where the suppressed indicator is present, regardless of the primary entity in the signal.
- Entity suppression will only suppress the signal if the suppressed entity is the primary signal.
- If any entities within the record match items listed in a suppressed list, suppressed signals will be generated for those entities across all rules. Consequently, these signals will not affect the entity's Activity Score or contribute to insight generation.
When a record contains a value that matches one or more suppressed lists, two fields in the record get populated:
listMatches. Cloud SIEM adds the names of the suppressed lists that the record matched, and the column values of those lists. For example, if an IP address in a record matches the SourceIP address in the “vuln_scanners” suppressed list, thelistMatchesfield would look like this:listMatches: ['vuln_scanners', 'column:SourceIp']matchedItems. Cloud SIEM adds the actual key-value pairs that were matched. For example, continuing the example above, if “vuln_scanners” match list contained an entry “5.6.7.8”, and the record’s SourceIp is also “5.6.7.8”, the assuming the SourceIP address in the “vuln_scanners” suppressed list, thematchedItemsfield would look like this:matchedItems: [ { value: '5.6.7.8', …other metadata about list item } ]
Because the information about list matches gets persisted within records, you can reference it downstream in both rules and search.
For more information about signal Suppression mechanisms, see About Signal Suppression.
Suppressed list limitations
A suppressed list can contain up to 50,000 items.
Create a suppressed list from the UI
Perform the steps below to create a suppressed list and add an indicator to it using the Cloud SIEM UI.
- New UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu, select Cloud SIEM > Suppressed Lists. You can also click the Go To... menu at the top of the screen and select Suppressed Lists.
Classic UI. In the top menu select Content > Suppressed Lists. - Click Add Suppressed List.
- On the Add Suppressed List popup, enter the following:
- Name. Name of the suppressed list.
- Description. Enter a description for the list.
- Target Column. The type of record field to which items on the list should be compared.
note
If you want to create a custom target column, click Manage Custom Columns. For more information, see Custom Match List Columns.
- Time to Live (hours). (Optional) Enter the number of hours after which the entries on the list should expire.
- Click Save.
- The suppressed list now appears on the Suppressed Lists page.
- Click the name of the suppressed list to open it.
- On the Suppressed List > Details page, click Add Suppressed List Item.

- On the Add Suppressed List Item popup, enter:
- Value. The value of the entity. Make sure the value you enter is of the same type as the type you selected as the target column for the list. For example, if the target column is Domain, enter a domain.
- Description. (Optional) Enter a description of the list item.
- Expiration. (Optional) The date and time at which the list item should be removed from the list.
- Click Save to add the item to the list.
- The item now appears on the list.
Import a list of indicators
You can import list items by uploading a .csv file. This is convenient when you want to add many items to a list.
Create a CSV file
Create a .csv file. You can import up to three fields for an item.
- value (Required). The value of the list item. The item you supply should be of the same type as the target column defined for the suppressed list. For example, if the target column is IP Address, supply an IP address.
- description (Optional). A description of the list item.
- expires (Optional). Expiration date and time for the list item, in ISO 8601 format, for example: *2020-08-17 01:18:00 *
CSV file guidelines
Follow these guidelines when you create the .csv file:
- Use the first line of the file to identify the fields, and then add a line for each list item with the fields in the same order as the field names in the header. (Fields can be in any order, but the fields for each item must be in the same order as the field in the header.)
- If a field contains a comma, enclose it in double quotes (“).
- Save the file with a .csv extension.
Here is an example of a file in which all fields are supplied:
value,description,expires 10.99.19.9,test-desc,2020-08-17 01:18:00
Here is an example of a file in which only the required field, value, is specified:
value 10.99.19.9
Upload file
- On the Suppressed Lists page, click the name of the list.
- Click Import Items.
- On the import popup:
- Drag your file onto the import popup, or click to navigate to the file, and then click Import.
- Optionally, you can enter an expiration for the indicators on the list. If you do, it will override any expirations that are defined in the file. Enter the expiration in any ISO date format. For example:
2022-12-31
Manage suppressed lists with the Cloud SIEM API
You can use Cloud SIEM APIs to create and manage suppressed lists. For information about Cloud SIEM APIs and how to access the API documentation, see Cloud SIEM APIs.
Best Practices for using suppressed lists
When creating a custom suppressed list, consider directionality selecting the target column. In most cases, suppressed lists work fine with a directionless column type, like IP Address. However, in some cases, a suppressed list is best configured with a directional column type, such as Source IP Address or Destination IP Address. In some cases it works best to create multiple suppressed lists with the same items in each, but different target columns. For example, you can have the same IP addresses in three suppressed list: one whose target column is IP Address, one with Source IP Address, and one with Destination IP Address.