Collecting Logs for Google Workspace (Legacy)

For the newer method of collecting logs from Google Workspace Alert Center, configure a Google Alert Workspace Alert Center Source.
This section explains how to collect logs from Google Workspace Alert Center and ingest them into Sumo Logic for use with the Google Workspace App predefined dashboards and searches.
Google Workspace Alert Center: Provides full visibility into alerts from Google Workspace apps, allowing you to investigate and correlate alerts and monitor potential threats. You can configure the list alerts to be collected. The alerts are forwarded to Sumo Logic’s HTTP endpoint in JSON format.
Alert types
All the alerts are in JSON format. Most of the alerts have few common fields like alertId, customerId, createTime, source, type and data. The differences are in the data section of the JSON where the alert type specific details are recorded. For more information about different alert types refer this Google Workspace Alert document.
Sample log messages
This section provides a sample Google Workspace Alert Center log message.
{
"alertId": "2b49ec18-2f92-4d58-acca-45994b740848",
"createTime": "TIMESTAMP",
"customerId": "03gm7p8e",
"data": {
"@type": "type.googleapis.com/google.apps.alertcenter.type.DomainWideTakeoutInitiated",
"takeoutRequestId": "unique9gfd87ss",
"email": "john@alertcenter1.bigr.name"
},
"deleteTime": "TIMESTAMP",
"endTime": "TIMESTAMP",
"metadata": {
"alertId": "2b49ec18-2f92-4d58-acca-45994b740848",
"customerId": "03gm7p8e",
"status": "NOT_STARTED",
"updateTime": "TIMESTAMP"
},
"source": "Domain wide takeout",
"startTime": "TIMESTAMP",
"type": "Customer takeout initiated"
}
Sample queries
The query sample provided in this section is from the Google Workspace Activity by Users with Compromised Credentials panel of the Google Workspace - Alert Center - Investigations Dashboard.
_sourceCategory=googleworkspace_google_apps
| json "actor", "events", "id" nodrop
| json field=actor "email"
| json field=id "applicationName"
| where [subquery:_sourceCategory=googleworkspace_alerts "Leaked password"
| json "alertId","customerId","source","type","data", "data.email" as alert_id, customer_id, source, type, data, email
| where type="Leaked password"
| count by email
| compose email
]
| parse regex field=events "\"name\":\"(?<event_name>[^\"]+)\",\"type\":\"(?<event_type>[^\"]+)\"" multi
| formatDate(_messageTime,"MM-dd-yyyy HH:mm:ss:SSS") as event_time
| count by event_time, event_name, event_type, email, applicationName
| fields -_count
| sort by event_time
Collection overview
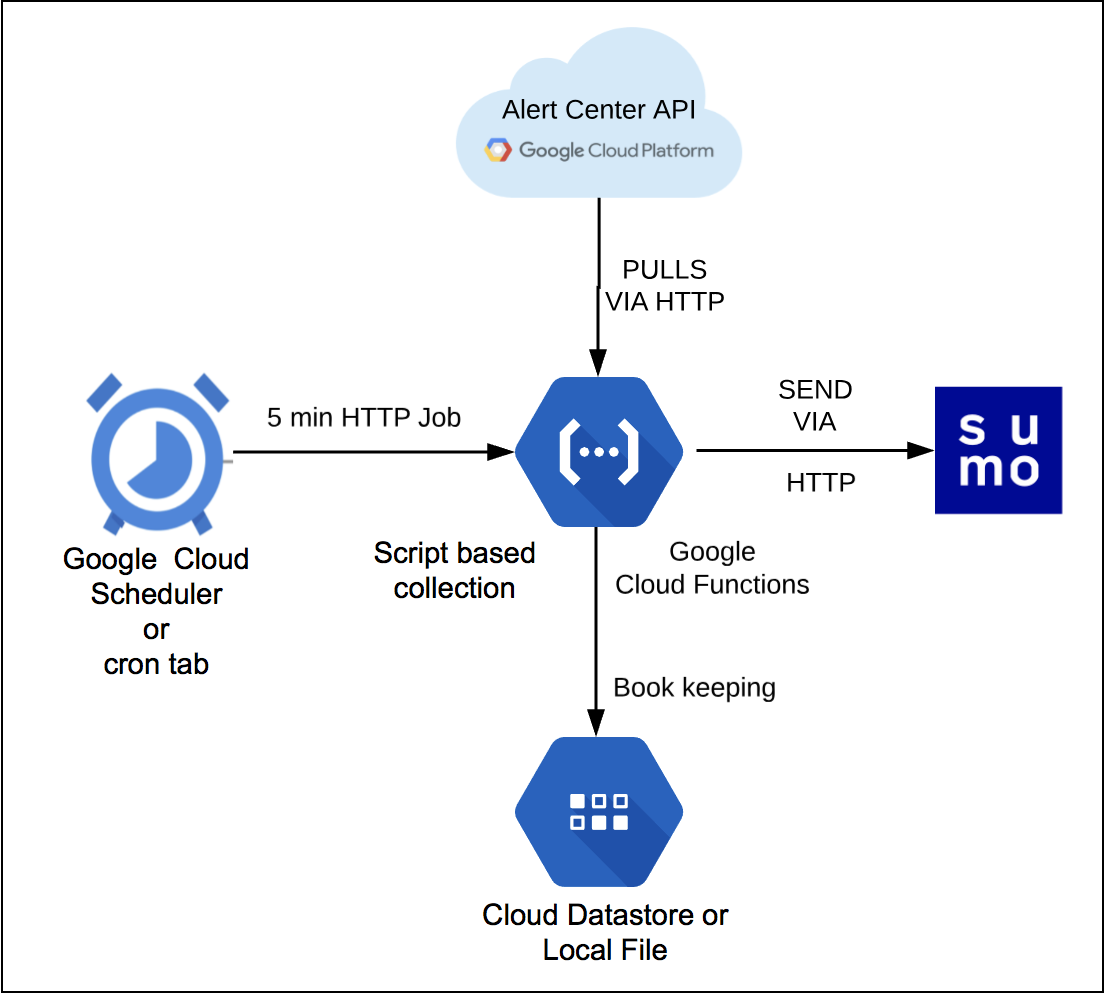
Sumo Logic provides a serverless solution which pulls logs from Google Workspace with API calls. You can configure the list alerts to be collected, but by default all alerts are collected. The alerts are then forwarded to Sumo Logic’s HTTP endpoint in JSON format. By default the collection starts from the current date and time, but this setting is also configurable as detailed in the Advanced configuration section.
Add a Hosted Collector and HTTP Source
This section demonstrates how to add a hosted Sumo Logic collector and HTTP Logs and Metrics source, to collect alerts for Google Workspace Alert Center.
- Identify the Sumo Logic Hosted Collector you want to use, or create a new Hosted Collector as described in the following task.When you configure the HTTP Source, make sure to save the HTTP Source Address URL. You will need this to configure in configuration file.
- Create a new Sumo Logic Hosted Collector by performing the steps in Configure a Hosted Collector.
- Add an HTTP Logs and Metrics Source.
- In the Advanced Options for Logs, under Timestamp Format, click Specify a format and enter the following information in the respective fields:
- Format:
yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS'Z' - Timestamp locator:
\"createTime\":(.*),
- Format:
- Click Test and paste in a test log line when prompted to do so.
- If the test is successful, click Save.
- Make a note of the URL of the new source.
Configure collection for Google Workspace Alert Center
In this section, we explore various mechanisms to collect findings from Google Workspace Alert Center and send them to Sumo Logic, where they are shown in dashboards as part of the Google Workspace App. You can configure your Google Workspace Alert Center collector in Google Cloud Platform (GCP) or by deploying script-based collection on a Linux machine.
Using GCP Collection
This section provides instructions for configuring Google Workspace Alert Center collection in your GCP environment. The Google Workspace Alert Center collector function fetches the findings from Google Workspace and sends them to Sumo Logic.
To configure Google Workspace Alert Center collection in your GCP environment, do the following:
- Go to the Cloud Shell Editor.
- Run the following command:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SumoLogic/sumologic-gsuitealertcenter/master/sumo_gsuite_alerts_collector_deploy.sh
- Edit the
sumo_gsuite_alerts_collector_deploy.shbash script to configure following variables:region: The Region where the Google function will be deployed. For example: "us-central1"project_id: The project id of the project where the collector and all its resources will be deployeddelegated_email: The valid email address of one of your org's G Suite super admin users.Sumo_endpoint: The Sumo Logic HTTP endpoint created in Step 1
- Run the following script:
sh sumo_gsuite_alerts_collector_deploy.sh
- In the command prompt, enter
Nfor the following question:Allow unauthenticated invocations of new function. - Copy the Client ID displayed at the end of the script output. You will use the Client Name field when you configure Google Workspace Alert Center to allow client API access in the following task.
- Go to the Cloud Datastore page of the project, with the Project ID you configured in the previous steps of this procedure, and create a database instance with the Cloud Firestore in Datastore Mode option. For more information, refer to the Google Cloud Datastore documentation.
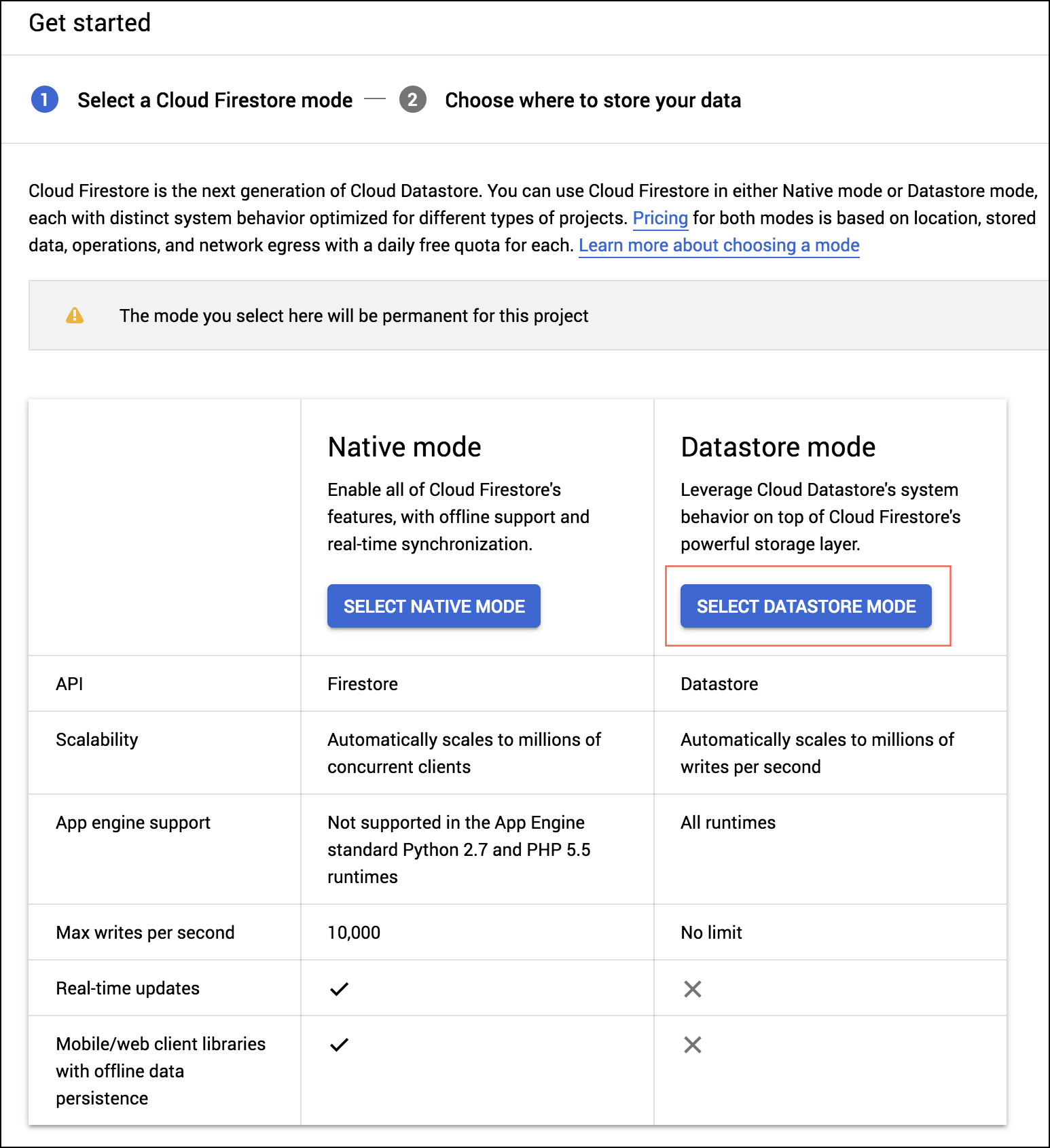
The script you used in this procedure configured the environment variables in the config file. You can update the variables by following the instructions Google's Updating environment variables documentation.
Configure Google Workspace Alert Center to allow client API access
This section explains how to configure Google Workspace Alert Center to allow API access.
Follow the step 2 and step 3 under “Set up the Alert Center API” docs to enable alert center API and grant domain-wide access to the application.
To configure GCP Collection for Google Workspace Alert Center, use the Client ID for the service account copied in Step 6 here.
If you're using the Configure Script-Based Collection for Google Workspace Alert Center use the Client ID present in the JSON generated after adding the key in the service account.
To configure Google Workspace Alert Center:
- Go to your G Suite domain's Admin console (see instructions on signing in to your Admin console), go to Security > Access and data control > API Controls.
- In the newly opened window, click Manage Domain-wide Delegation at the bottom.
- Click Add new button on the top.
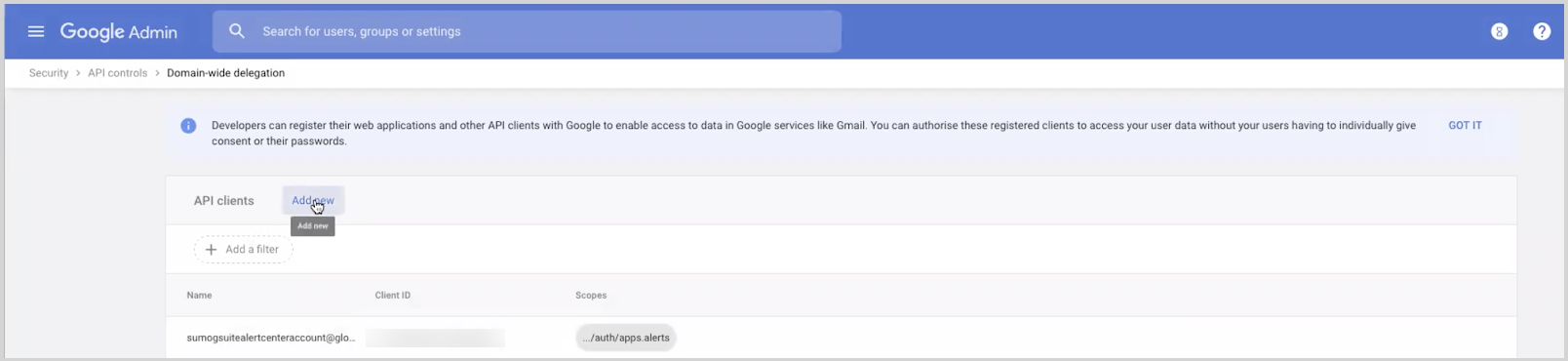
- Enter the Client ID for the service account copied in Step 2, then in the OAuth Scopes field enter the following: https://www.googleapis.com/auth/apps.alerts.
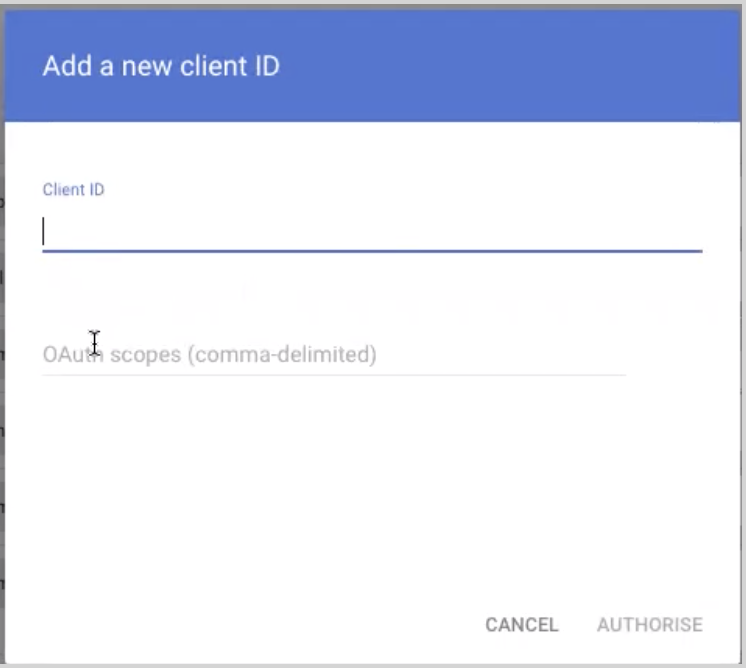
- Click Authorise.
Adding new Alert types
In the future, if Google adds a new alert type do the following to add new alert types:
- Go to the gsuitealertcenterfunc google cloud function console.
- Click Edit at the top and then click Next.
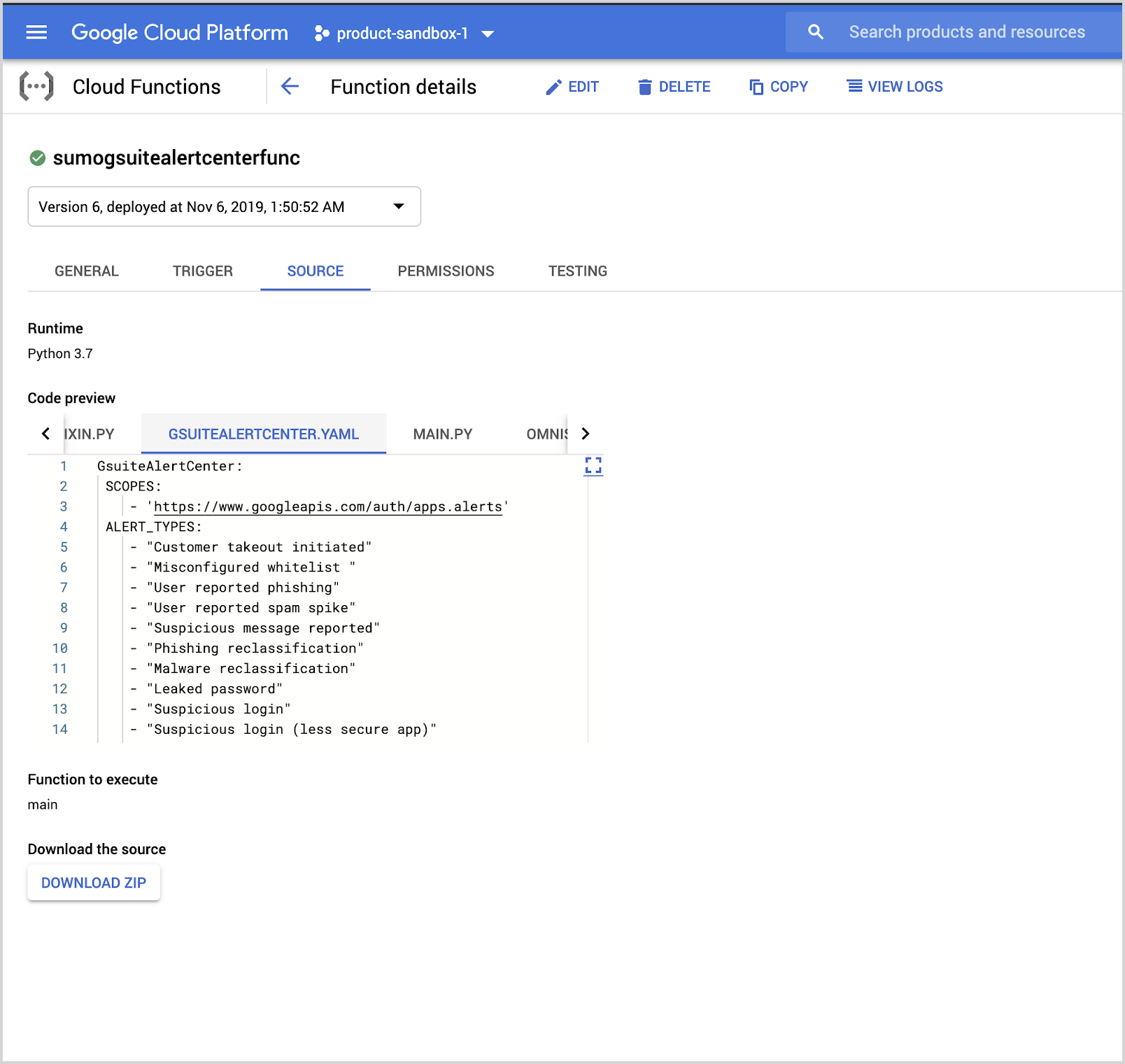
- In the editor, edit the gsuitealertcenter.yaml file and add the new alert types in
ALERT_TYPESparameter from the “Alert type” column present in Google Workspace Alert types documentation.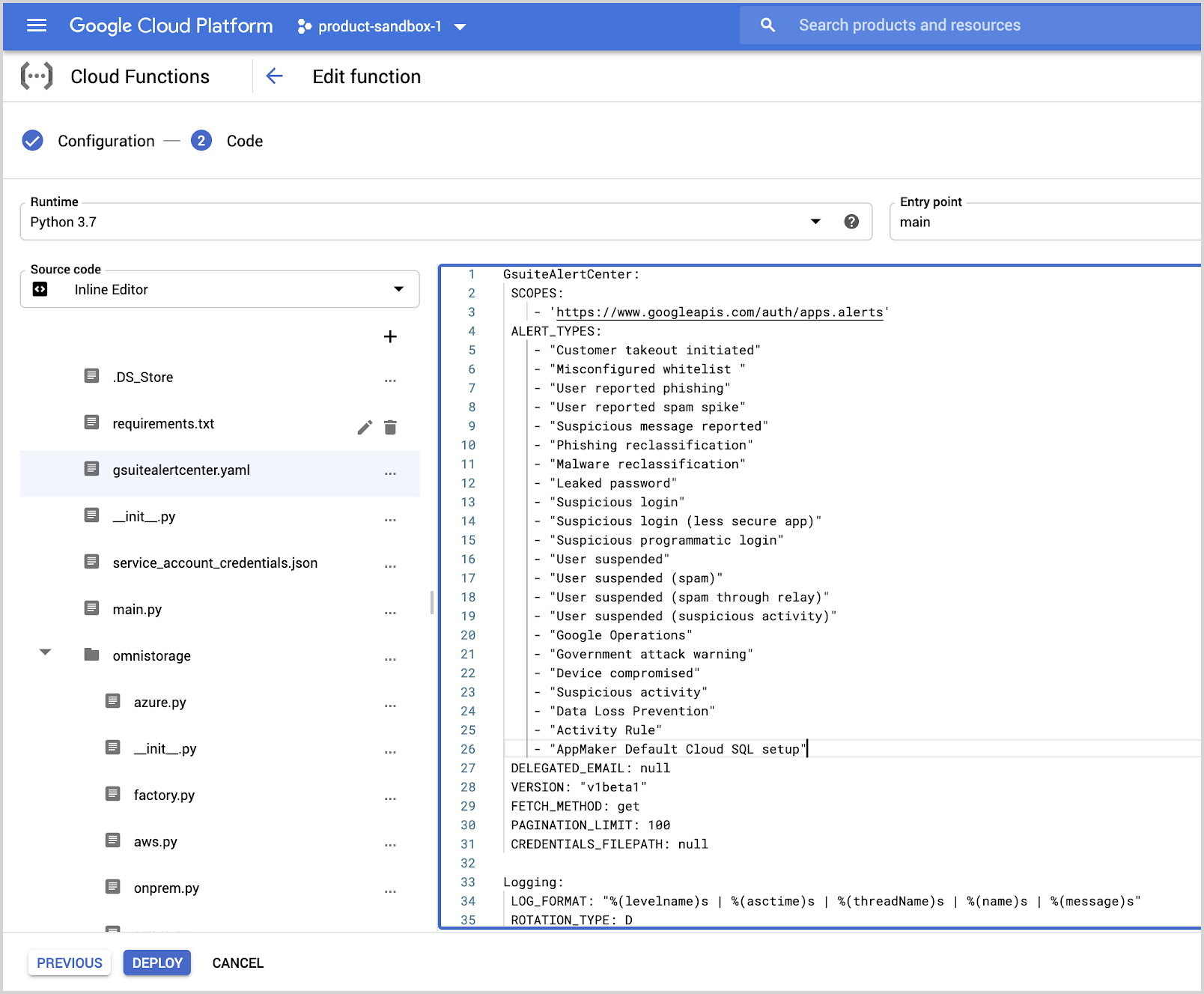
- Click Deploy.
Advanced Configuration
This section provides a list of environment variables for Google Workspace Alert Center and their usage. For information on how to set these environment variables, refer to this Google Cloud document.
| Environment Variable | Usage |
|---|---|
ALERT_TYPES | "Customer takeout initiated" "Misconfigured whitelist" "User reported phishing" "User reported spam spike" "Suspicious message reported" "Phishing reclassification" "Malware reclassification" "Leaked password" "Suspicious login" "Suspicious login (less secure app)" "Suspicious programmatic login" "User suspended" "User suspended (spam)" "User suspended (spam through relay)" "User suspended (suspicious activity)" "Google Operations" "Government attack warning" "Device compromised" "Suspicious activity" |
BACKFILL_DAYS | Number of days before the event collection will start. If the value is 1, then events are fetched from yesterday to today. |
PAGINATION_LIMIT | Number of events to fetch in a single API call. |
LOG_FORMAT | Log format used by the Python logging module to write logs in a file. |
ENABLE_LOGFILE | Set to TRUE to write all logs and errors to a log file. |
ENABLE_CONSOLE_LOG | Enables printing logs in a console. |
LOG_FILEPATH | Path of the log file used when ENABLE_LOGFILE is set to TRUE. |
NUM_WORKERS | Number of threads to spawn for API calls. |
MAX_RETRY | Number of retries to attempt in case of request failure. |
BACKOFF_FACTOR | A backoff factor to apply between attempts after the second try. If the backoff_factor is 0.1, then sleep() will sleep for [0.0s, 0.2s, 0.4s, ...] between retries. |
TIMEOUT | Request timeout used by the requests library. |
SUMO_ENDPOINT | HTTP source endpoint URL created in Sumo Logic. |
Troubleshooting the GCP Function
This section shows you how to troubleshoot the function and resolve errors you may have encountered.
To verify the function, do the following:
- Log in to your GCP account, navigate to the cloud function you created, and click Testing.
- Click the Test the function button.
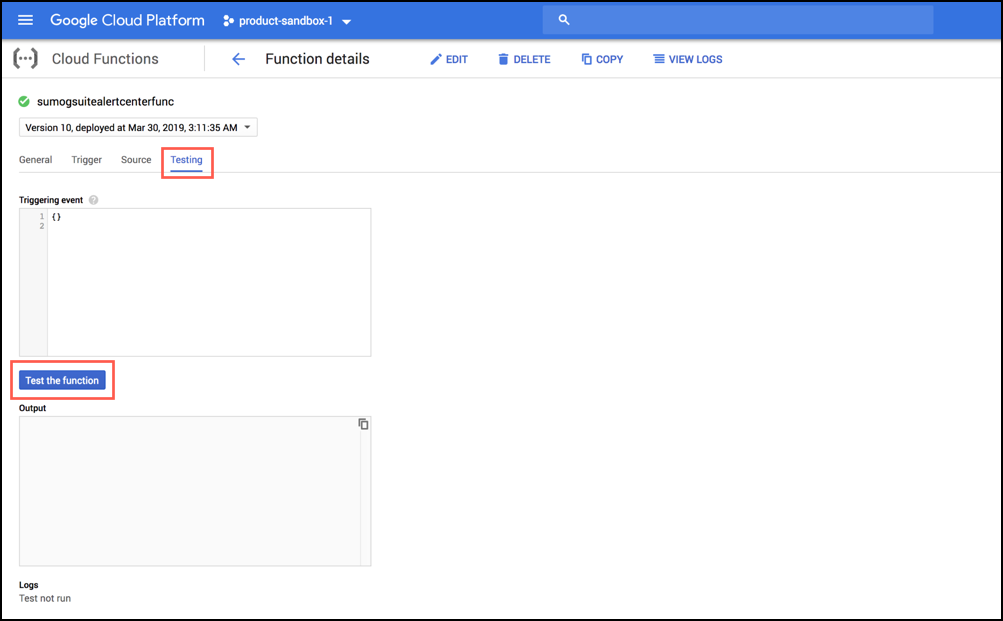
- Click the View Logs button to view the function logs. If an environment variable was not set, you will see error messages similar to the following.
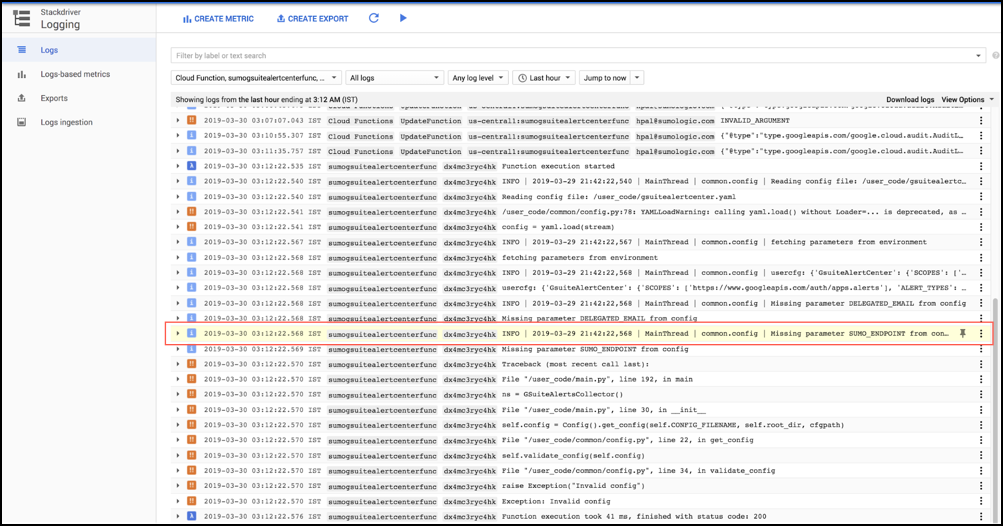
- Set the missing environment variable to resolve the issue.
To verify whether the cloud scheduler job is triggering the function:
- Enter Cloud Scheduler in the search bar and click.

- Click View button under Logs column corresponding to the Cloud Scheduler job starting with sumogsuite as show below.
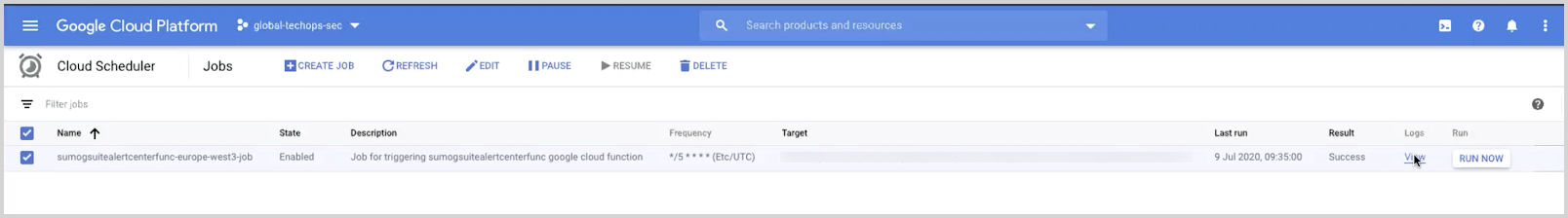
- In the newly opened window, you should be able to see logs with no errors seen under Severity. If there is an error, you can see more details by clicking on the Error section under Severity.
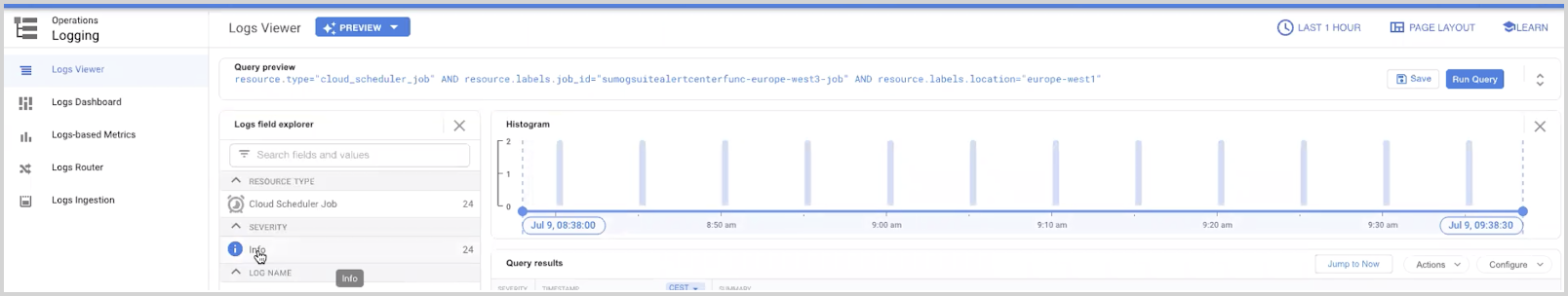
Using Script-Based Collection
This section provides instructions for deploying script-based collection for Google Workspace Alert Center. This script collects logs for the Sumo Logic Google Workspace Alert Center App.
The _sumologic-gsuite_alertcenter script is compatible with python 3.7 and python 2.7. This has been tested on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS and Debian 4.9.130.
Prerequisites
- This task assumes you have successfully added a Hosted Collector and HTTP source, as described in Configure Collection for Google Workspace Alert Center.
- The following tasks assume you are logged in to the user account with which you will install the collector. If you are not, use the following command to switch to that account:
sudo su <user_name>
Configure the script on a Linux machine
This task shows you how to install the script on a Linux machine.
For python 3, use pip3 install sumologic-gsuitealertcenter (step 3) and /usr/bin/python3 -m sumogsuitealertscollector.main (step 6) in operating systems where default python is not python3.
To deploy the script, do the following:
- Set up the Alert Center API as described in the following Google documentation. Assign the Cloud Datastore Owner role while creating a service account. Copy the Client ID present in the JSON generated after adding the key in the service account (it will be used further in step 3 while granting domain wide access).
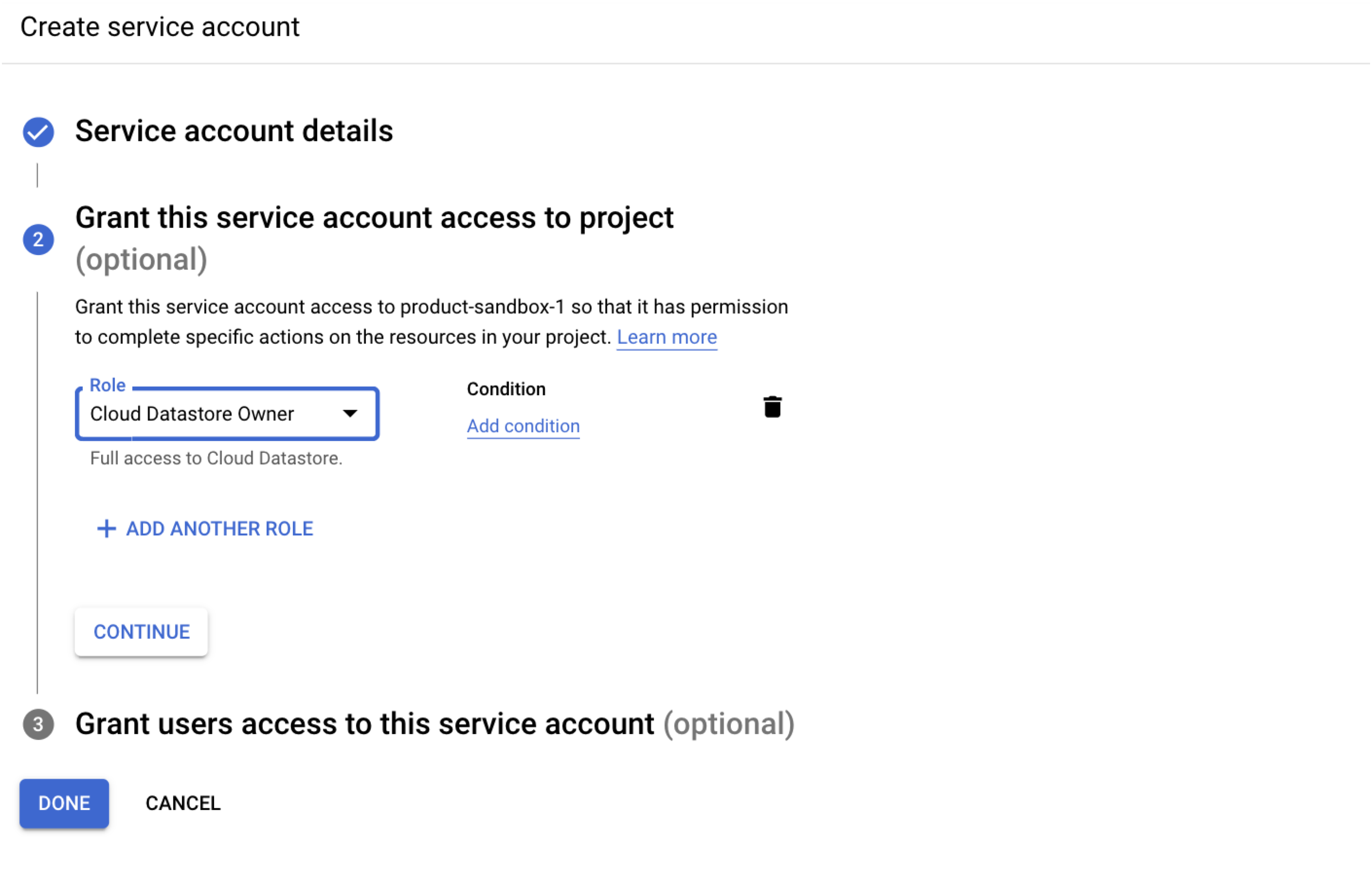 While creating the key in the service account, make a note of the location of the Service Account JSON file that has been downloaded to your computer. You will need this path later.
While creating the key in the service account, make a note of the location of the Service Account JSON file that has been downloaded to your computer. You will need this path later. - If pip is not already installed, follow the instructions in the pip documentation to download and install pip.
- Log in to a Linux machine (compatible with either Python 3.7 or Python 2.7) and install the script using the following command. For python 3, use pip3 install in the following command.
pip install sumologic-gsuitealertcenter
- Create a configuration file named gsuitealertcenter.yaml in home directory by copying the following snippet.
SumoLogic:
SUMO_ENDPOINT: <SUMO LOGIC HTTP URL>
GsuiteAlertCenter:
DELEGATED_EMAIL: "<email address of your org's Google Workspace super admin>"
CREDENTIALS_FILEPATH: "<path to json Service Account JSON file>"
Collection:
ENVIRONMENT: onprem
- Add the
SUMO_ENDPOINTandCREDENTIALS_FILEPATH(from step 1 above), andDELEGATED_EMAILparameters, then save the file. For theDELEGATED_EMAILparameter: if you do not have an email address of one of your super admins, you can use a service account email address instead if you delegate domain-wide authority to that account. - Create a cron job for running the collector every 5 minutes by using
crontab -eand adding the following line. If you're using python3, for operating systems where the default python is not python3, use/usr/bin/python3 -m sumogsuitealertscollector.mainin the following command.
*/5 * * * * /usr/bin/python -m sumogsuitealertscollector.main > /dev/null 2>&1
Advanced Configuration
This section provides a list of environment variables for Google Workspace Alert Center that you can define in the configuration file, as shown in this example. See the following table for explanations for each of the environment variables.
For information on how to set these environment variables, refer to this Google Cloud document.
| Environment Variable | Usage |
|---|---|
ALERT_TYPES | "Customer takeout initiated" "Misconfigured whitelist" "User reported phishing" "User reported spam spike" "Suspicious message reported" "Phishing reclassification" "Malware reclassification" "Leaked password" "Suspicious login" "Suspicious login (less secure app)" "Suspicious programmatic login" "User suspended" "User suspended (spam)" "User suspended (spam through relay)" "User suspended (suspicious activity)" "Google Operations" "Government attack warning" "Device compromised" "Suspicious activity" |
BACKFILL_DAYS | Number of days before the event collection will start. If the value is 1, then events are fetched from yesterday to today. |
PAGINATION_LIMIT | Number of events to fetch in a single API call. |
LOG_FORMAT | Log format used by the Python logging module to write logs in a file. |
ENABLE_LOGFILE | Set to TRUE to write all logs and errors to a log file. |
ENABLE_CONSOLE_LOG | Enables printing logs in a console. |
LOG_FILEPATH | Path of the log file used when ENABLE_LOGFILE is set to TRUE. |
NUM_WORKERS | Number of threads to spawn for API calls. |
MAX_RETRY | Number of retries to attempt in case of request failure. |
BACKOFF_FACTOR | A backoff factor to apply between attempts after the second try. If the backoff_factor is 0.1, then sleep() will sleep for [0.0s, 0.2s, 0.4s, ...] between retries. |
TIMEOUT | Request timeout used by the requests library. |
SUMO_ENDPOINT | HTTP source endpoint URL created in Sumo Logic. |
Troubleshooting
This section shows you how to run the function manually and then verify that log messages are being sent from Alert Center. To run the function manually, do the following:
- Enter one of the following commands:
- For python, use this command:
python -m sumogsuitealertscollector.main- For python3, use this command:
python3 -m sumogsuitealertscollector.main - The script generates logs in /tmp/sumoapiclient.log by default. Check these logs to verify whether it’s getting triggered or not.
- If you installed the collector as
rootuser and then run it as a normal user, you will see an error message similar to the following because the config is not present in the home directory of the user running the collector. Switch torootthe user and run the script again.
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sumogsuitealertscollector/main.py", line 190, in main
ns = GSuiteAlertsCollector()
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sumogsuitealertscollector/main.py", line 29, in __init__
self.config = Config().get_config(self.CONFIG_FILENAME, self.root_dir, cfgpath)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sumogsuitealertscollector/common/config.py", line 22, in get_config
self.validate_config(self.config)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sumogsuitealertscollector/common/config.py", line 34, in validate_config
raise Exception("Invalid config")
Exception: Invalid config
You can also avoid this error by running the script with config file path as first argument.
- To verify if there are new messages generated by Alert Center, go to Google Home > Security > Alert Center and then do the following:
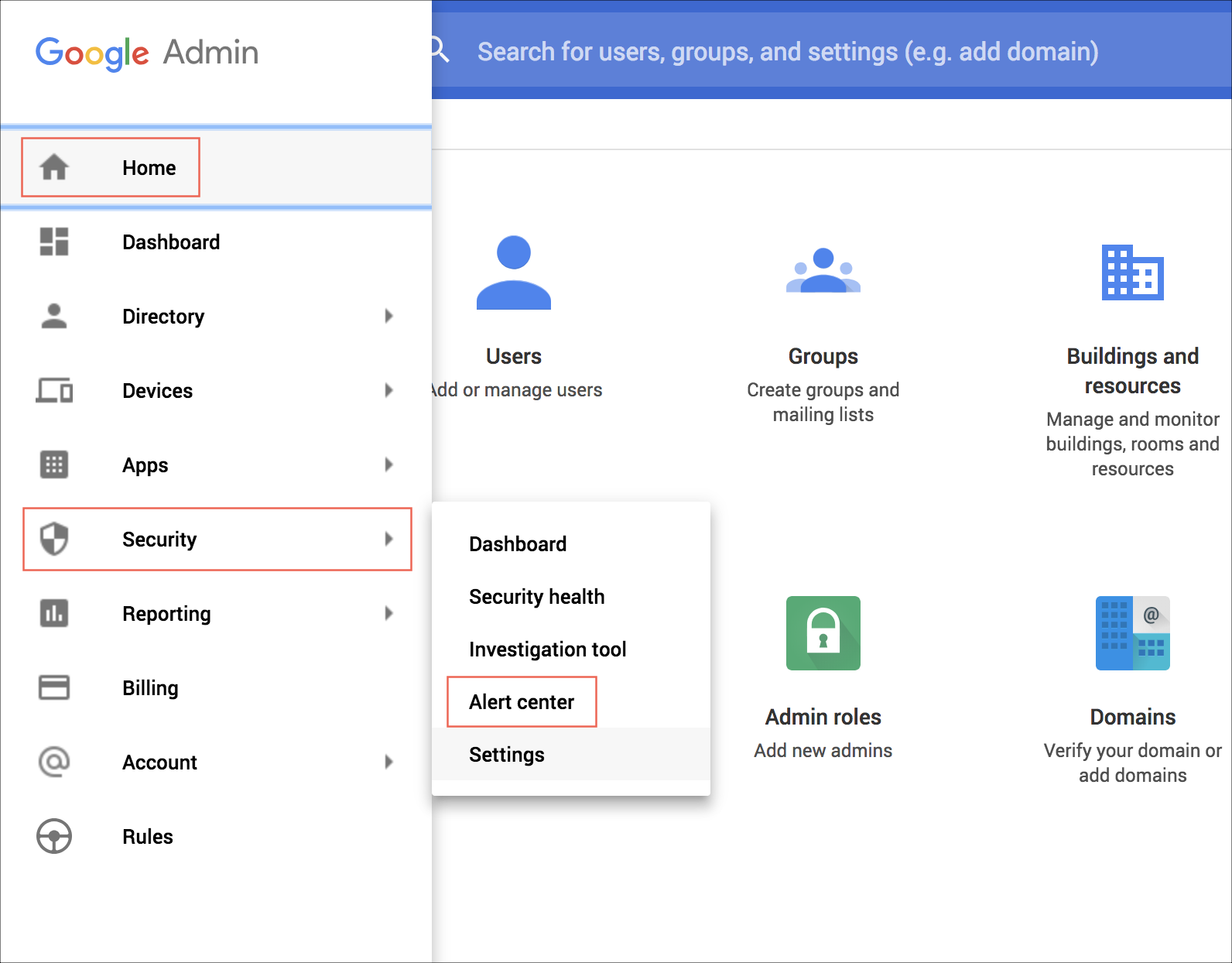
- Check for an error message similar to the following. If you see this, verify that the DELEGATED_EMAIL in your configuration belongs to a valid Google Workspace super admin user (or a service account that's been delegated domain-wide authority).
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/sumogsuitealertscollector/main.py", line 191, in main
ns.run()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/sumogsuitealertscollector/main.py", line 162, in run
task_params = self.build_task_params()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/sumogsuitealertscollector/main.py", line 152, in build_task_params
obj = self.set_new_end_epoch_time(alert_type, self.DEFAULT_START_TIME_EPOCH)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/sumogsuitealertscollector/main.py", line 81, in set_new_end_epoch_time
response = self.alertcli.alerts().list(**params).execute()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/googleapiclient/_helpers.py", line 130, in positional_wrapper
return wrapped(*args, **kwargs)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/googleapiclient/http.py", line 851, in execute
raise HttpError(resp, content, uri=self.uri)
googleapiclient.errors.HttpError: <HttpError 400 when requesting
https://alertcenter.googleapis.com/v1beta1/alerts?pageSize=1&filter=create_time+%3E%3D+%222019-04-17T16%3A29%3A14.061731Z%22+AND+create_time+%3C%3D+%222019-04-18T16%3A27%3A14.417915Z%22+AND+type+%3D+%22Customer+takeout+initiated%22&orderBy=create_time+desc&alt=json
returned "Request contains an invalid argument."> - If you installed the collector as
rootuser and then run it as a normal user, you will see an error message similar to the following because the config is not present in the home directory of user running the collector. Switch torootuser and run the script again.Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sumogsuitealertscollector/main.py", line 190, in main
ns = GSuiteAlertsCollector()
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sumogsuitealertscollector/main.py", line 29, in __init__
self.config = Config().get_config(self.CONFIG_FILENAME, self.root_dir, cfgpath)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sumogsuitealertscollector/common/config.py", line 22, in get_config
self.validate_config(self.config)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sumogsuitealertscollector/common/config.py", line 34, in validate_config
raise Exception("Invalid config")
Exception: Invalid config
You can also avoid this error by running the script with config file path as first argument.