Azure Storage

Azure Storage is Microsoft's cloud storage solution for modern data storage scenarios offering highly available, massively scalable, durable, and secure storage for a variety of data objects in the cloud. This integration helps in monitoring the transaction volume and read/write activity of all your storage accounts.
In Azure Storage, storage accounts allow you to create and manage the following storage services:
- Blob storage stores any type of text or binary data, such as a document, media file, or application installer. You can set Blob storage for private access or share contents publicly to the Internet. Blob storage serves the same purpose as both AWS S3 and EBS.
- Table storage. Stores structured datasets. Table storage is a NoSQL key-attribute data store that allows for rapid development and fast access to large quantities of data. Similar to AWS SimpleDB and DynamoDB services.
- Queue storage. Provides messaging for workflow processing and for communication between components of cloud services.
- File storage. Offers shared storage for legacy applications using the standard Server Message Block (SMB) protocol. File storage is used in a similar manner to EFS in the AWS platform.
Log and metric types
For Azure Storage, you can collect the following logs and metrics:
-
Resource logs, which provide an insight into operations that were performed within an Azure resource. For a complete schema for resource logs refer to the documentation below:
- Azure Blob Storage schema
- Azure File Storage schema
- Azure Queue Storage schema
- Azure File Storage schema
Requests made by the Blob storage service itself, such as log creation or deletion, aren't logged. For a complete list of the logged data, see Storage logged operations and status messages.
-
Activity logs provide insight into any subscription-level or management group-level events that have occurred in Azure. To learn more, refer to Azure documentation.
-
Metrics for Azure Storage are in the namespaces given below:
- Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts
- Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices
- Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/fileServices
- Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/queueServices
- Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/tableServices
noteOnly metrics with
category=Transactioncan be exported from the diagnostic settings export feature.Click on the above namespaces to learn more about the supported metrics. For a complete list of the dimensions that Azure Storage supports, refer to the documentation below:
- Azure Blob Storage Metrics dimensions
- Azure File Storage Metrics dimensions
- Azure Queue Storage Metrics dimensions
- Azure Table Storage Metrics dimensions
infoCapacity metrics are currently not supported via Diagnostic Settings.
Setup
Azure service sends monitoring data to Azure Monitor, which can then stream data to Eventhub. Sumo Logic supports:
- Logs collection from Azure Monitor using our Azure Event Hubs source.
- Activity Logs collection from Azure Monitor using our Azure Event Hubs source. It is recommended to create a separate source for activity logs. If you are already collecting these logs, you can skip this step.
- Metrics collection using our Azure Metrics Source.
You must explicitly enable diagnostic settings for each storage service (blob, queue, table, and file) and each storage account that you want to monitor. You can forward logs to the same event hub provided they satisfy the limitations and permissions as described here.
When you configure the event hubs source or HTTP source, plan your source category to ease the querying process. A hierarchical approach allows you to make use of wildcards. For example: Azure/Storage/Logs, Azure/Storage/Metrics.
Configure metrics collection
To set up the Azure Metrics source in Sumo Logic, refer to Azure Metrics Source.
The Sumo Logic Metrics source is currently in beta. To participate, contact your Sumo Logic account executive.
Configure logs collection
Diagnostic logs
In this section, you will configure a pipeline for shipping diagnostic logs from Azure Monitor to an Event Hub.
- To set up the Azure Event Hubs source in Sumo Logic, refer to Azure Event Hubs Source for Logs.
- To create the Diagnostic settings in the Azure portal, refer to the Azure documentation. Perform the steps below for each storage service (blob, queue, table, and file) and each storage account that you want to monitor.
- Choose
Stream to an event hubas the destination. - Select
allLogs. - Use the Event hub namespace and Event hub name configured in the previous step in the destination details section. You can use the default policy
RootManageSharedAccessKeyas the policy name.
- Choose
- Tag the location field in the source with the right location value.
Activity Logs
To collect activity logs, follow the instructions here. Do not perform this step in case you are already collecting activity logs for a subscription.
Since this source contains logs from multiple regions make sure that you do not tag this source with the location tag.
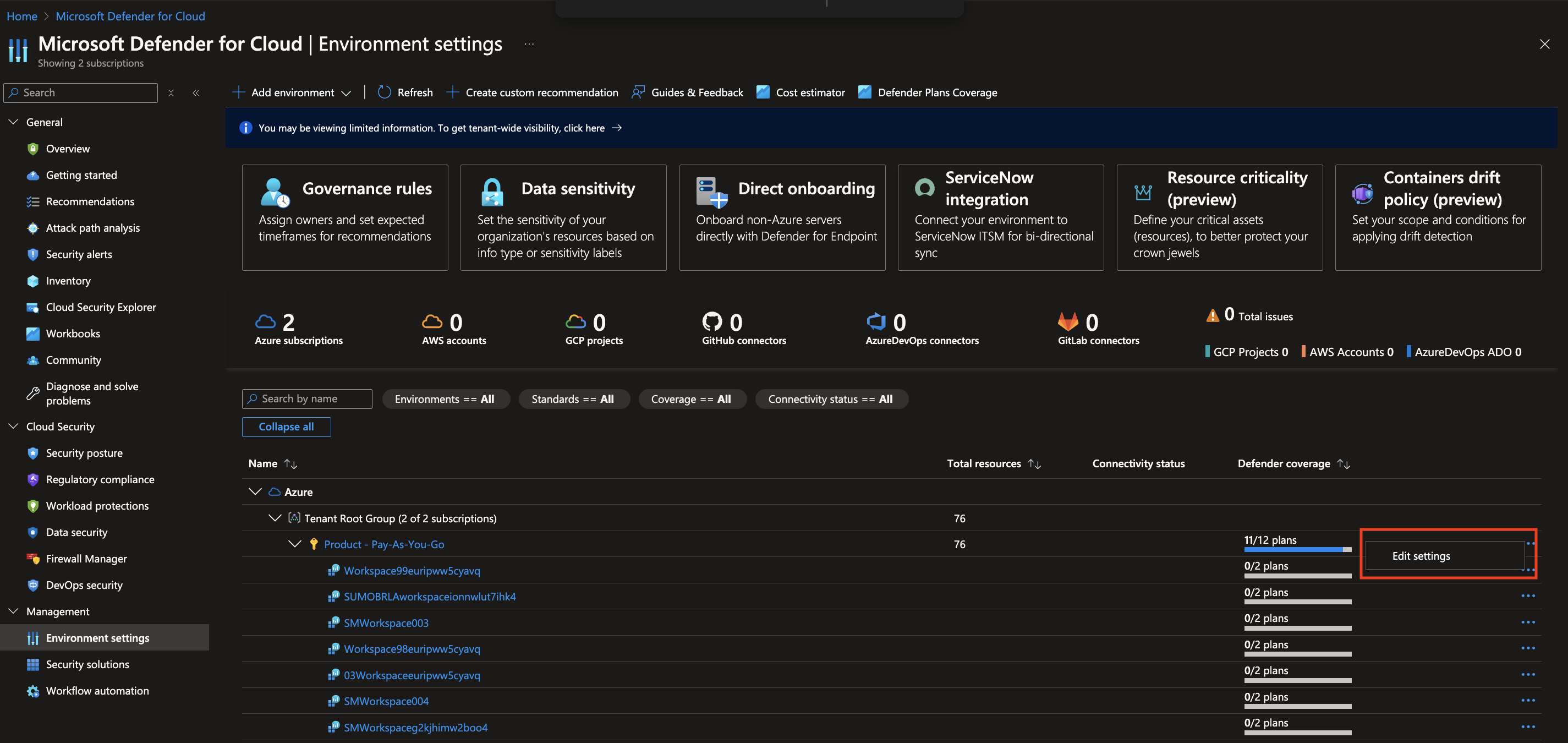
Enabling Microsoft Defender for Cloud
For Security events, make sure you enable Microsoft Defender for Cloud. If you have existing settings, click Edit Settings.
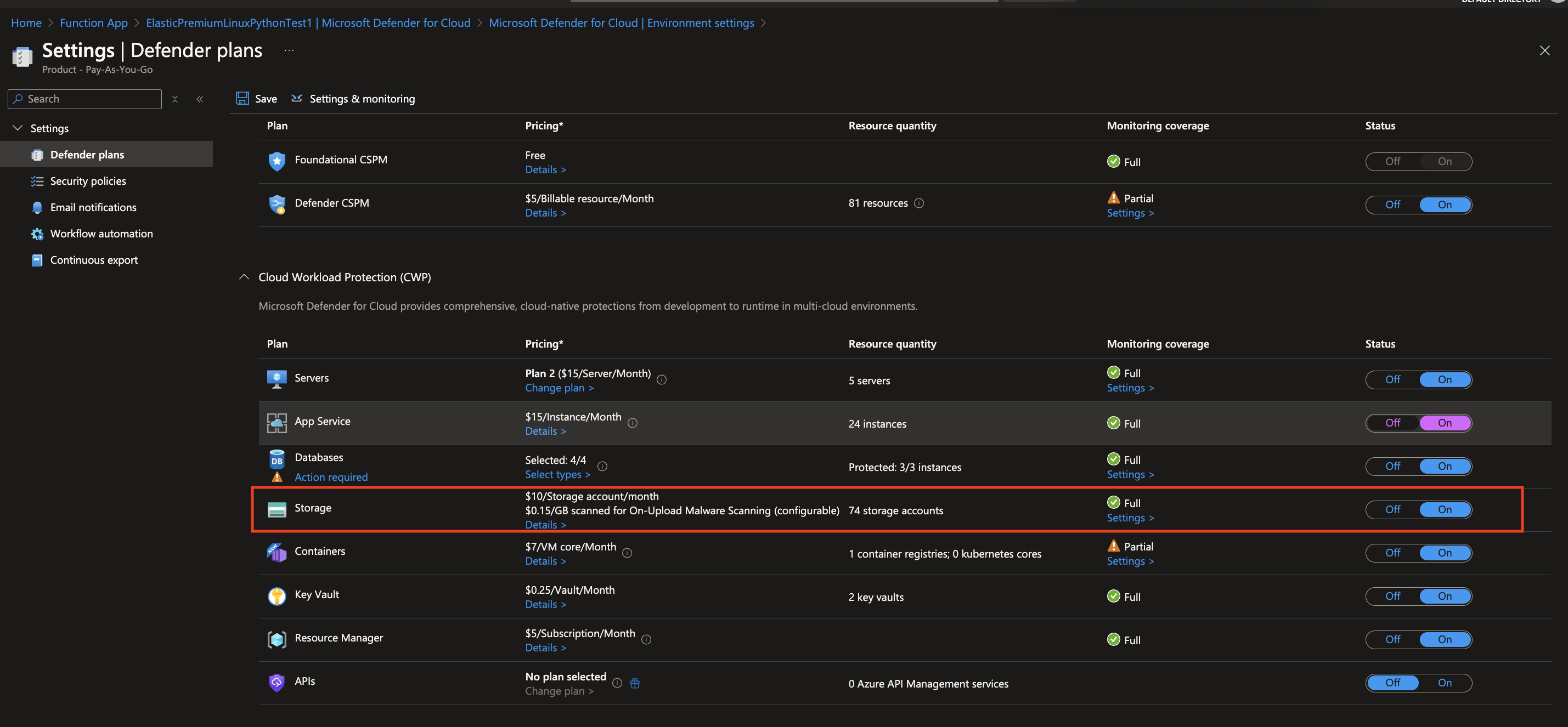
In Defender Plans settings page turn on the Azure Storage status under Cloud Workload Protection section.
Installing the Azure Storage app
Now that you have set up data collection, install the Azure Storage Sumo Logic app to use the pre-configured dashboards that provide visibility into your environment for real-time analysis of overall usage.
To install the app, do the following:
Next-Gen App: To install or update the app, you must be an account administrator or a user with Manage Apps, Manage Monitors, Manage Fields, Manage Metric Rules, and Manage Collectors capabilities depending upon the different content types part of the app.
- Select App Catalog.
- In the 🔎 Search Apps field, run a search for your desired app, then select it.
- Click Install App.
note
Sometimes this button says Add Integration.
- Click Next in the Setup Data section.
- In the Configure App section of your respective app, complete the following field.
- Index. Specify value for _index if the collection is configured with custom partition. Learn more. Default value is set to
sumologic_default(default partition)
- Index. Specify value for _index if the collection is configured with custom partition. Learn more. Default value is set to
- Click Next. You will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
Post-installation
Once your app is installed, it will appear in your Installed Apps folder, and dashboard panels will start to fill automatically.
Each panel slowly fills with data matching the time range query received since the panel was created. Results will not immediately be available but will be updated with full graphs and charts over time.
As part of the app installation process, the following fields will be created by default:
tenant_name. This field is tagged at the collector level. You can get the tenant name using the instructions here.location. The region the resource name belongs to.subscription_id. ID associated with a subscription where the resource is present.resource_group. The resource group name where the Azure resource is present.provider_name. Azure resource provider name (for example, Microsoft.Network).resource_type. Azure resource type (for example, storage accounts).resource_name. The name of the resource (for example, storage account name).service_type. Type of the service that can be accessed with an Azure resource.service_name. Services that can be accessed with an Azure resource (for example, in Azure Container Instances the service is Subscriptions).
Viewing the Azure Storage app dashboards
All dashboards have a set of filters that you can apply to the entire dashboard. Use these filters to drill down and examine the data to a granular level.
- You can change the time range for a dashboard or panel by selecting a predefined interval from a drop-down list, choosing a recently used time range, or specifying custom dates and times. Learn more.
- You can use template variables to drill down and examine the data on a granular level. For more information, see Filtering Dashboards with Template Variables.
- Many of the Next-Gen apps allow you to provide the Index at the installation time and a default value for this key (sumologic_default). Based on your input, the app dashboards will be parameterized with a dashboard variable, allowing you to change the data partition queried by all panels. This restricts the query scope of all the dashboard queries to a specific data partition.
Overview
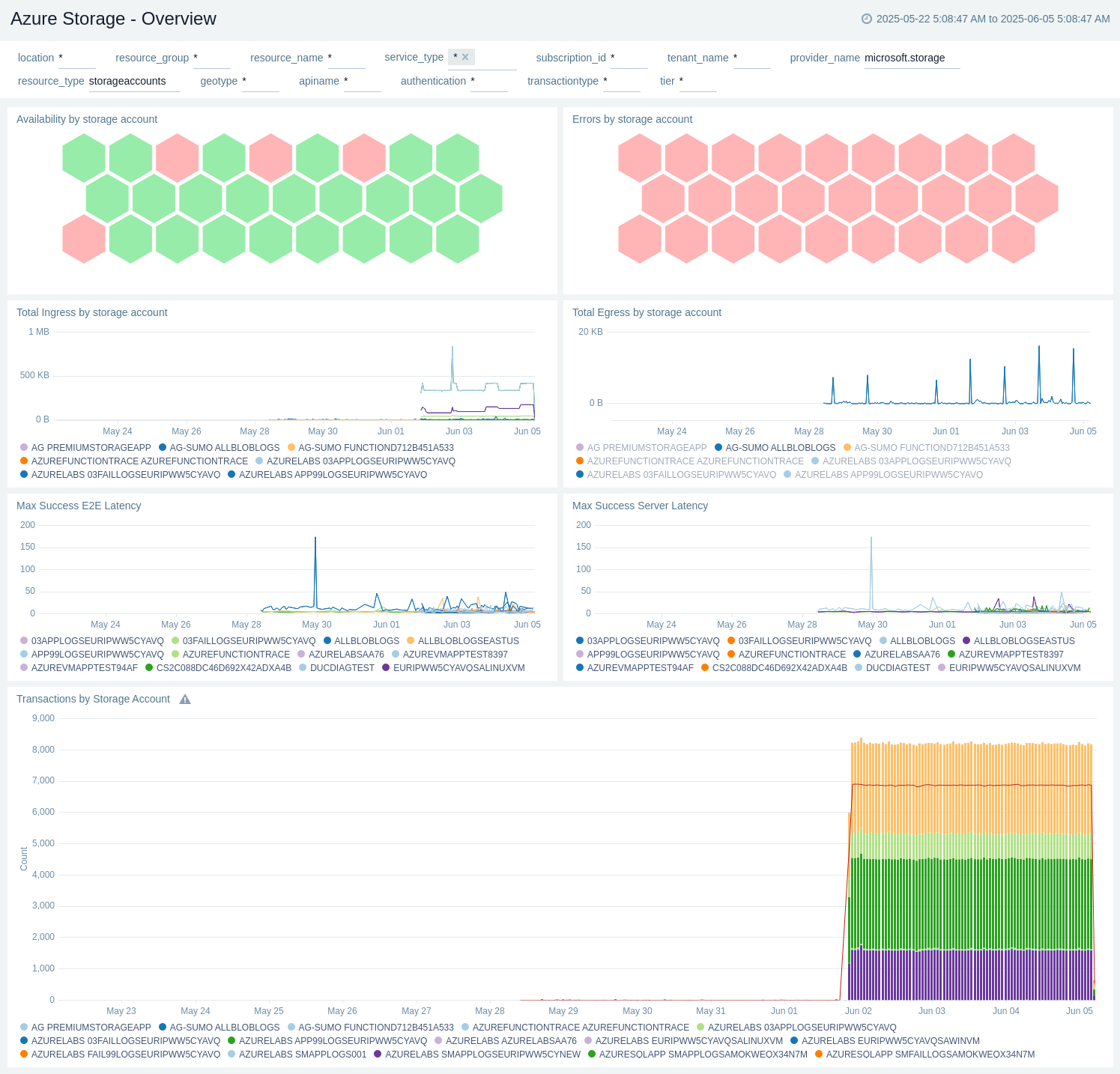
The Azure Storage - Overview dashboard provides insights into transactions by storage account, storage type, and API name.
Use this dashboard to:
- Monitor Availability by storage account.
- Monitor Errors by storage account.
- View Total Ingress by storage account.
- View Total Egress by storage account.
- View Max Success E2E Latency.
- View Max Success Server Latency.
- View transactions by storage account.
Access
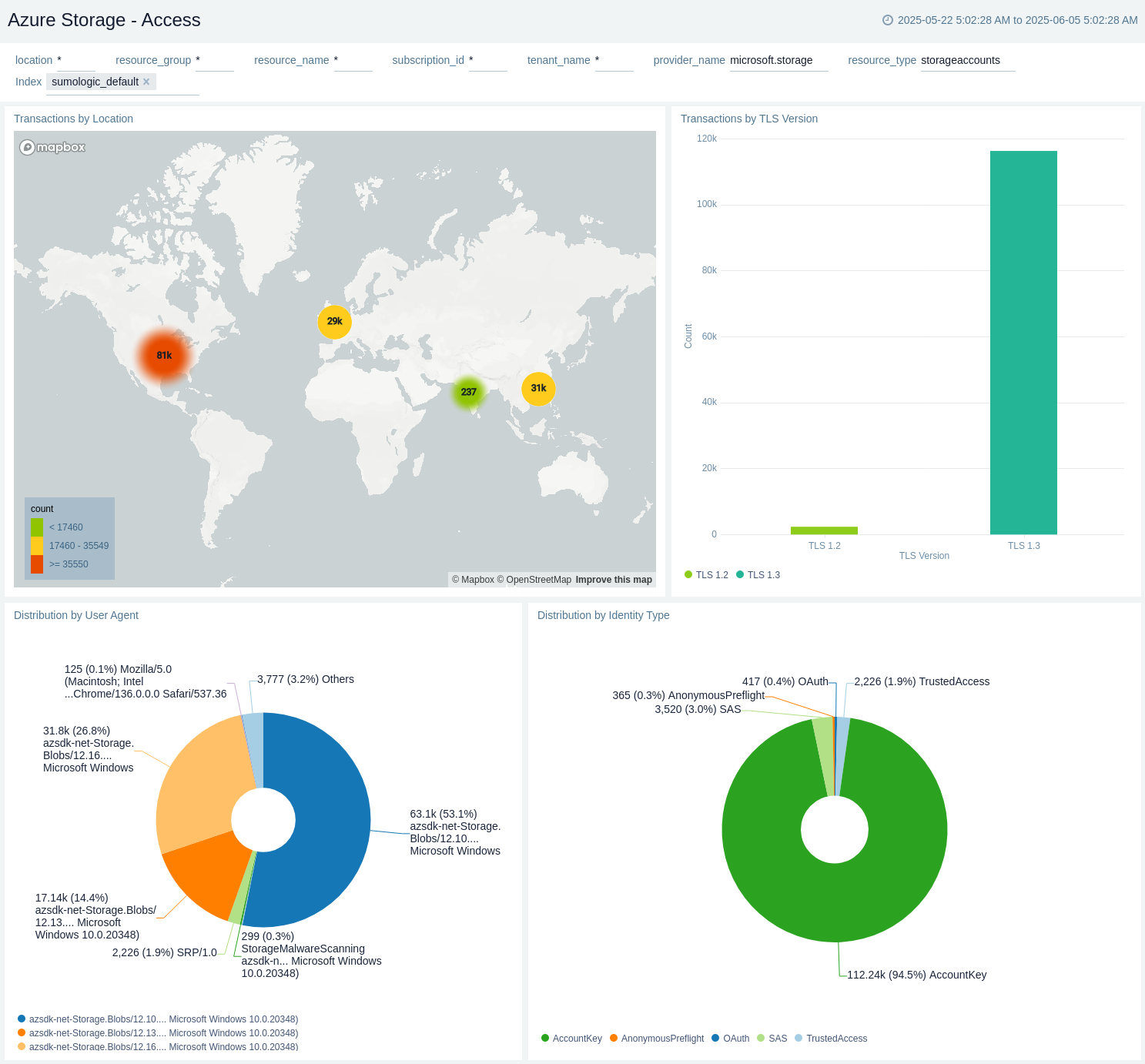
The Azure Storage - Access dashboard provides insights into transactions by location, TLS version, and also shows the distribution by user agent and identity type.
Use this dashboard to:
- View transactions by location.
- View transactions by TLS version.
- View distribution by user agent.
- View distribution by identity type.
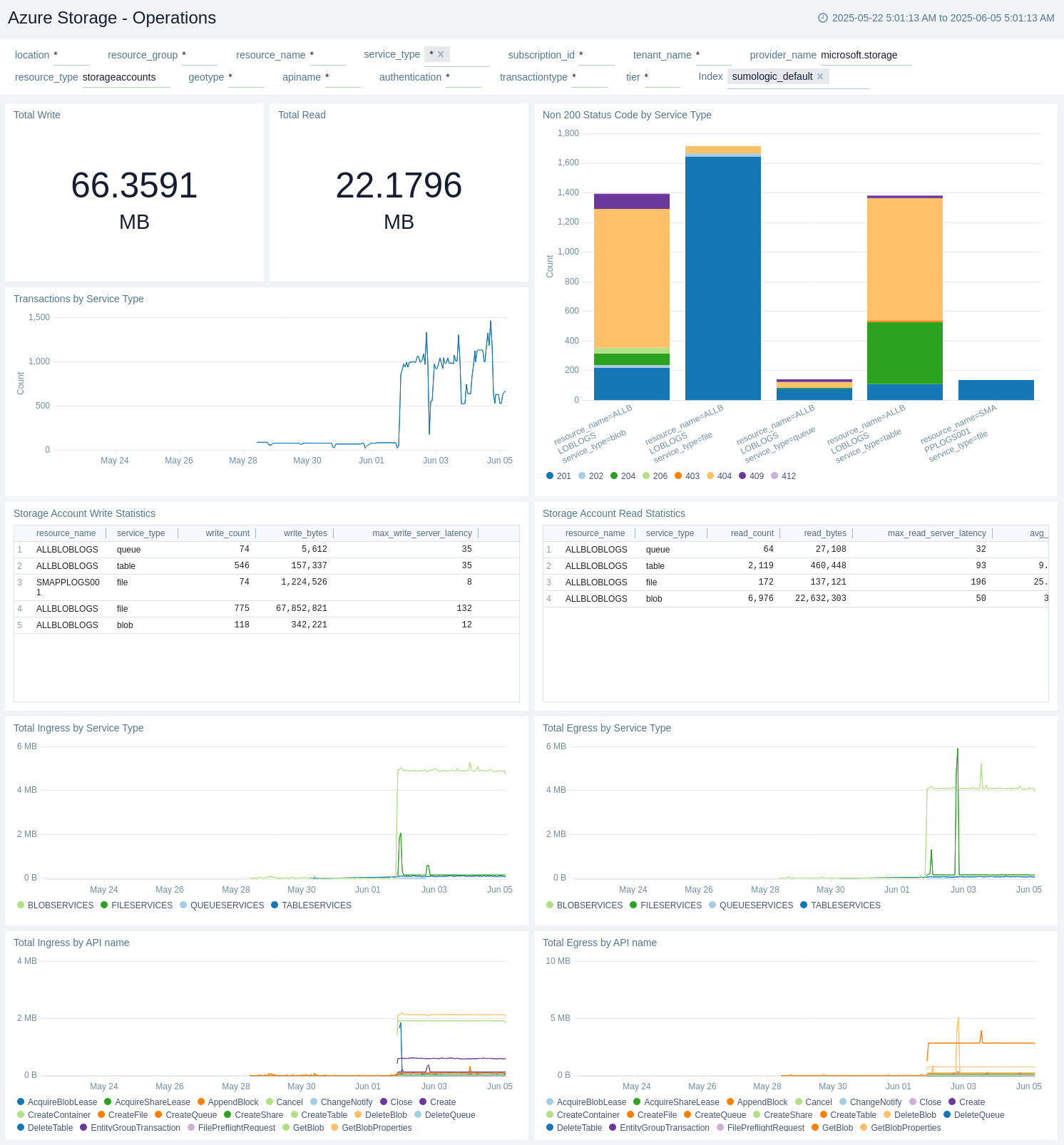
Operations
The Azure Storage - Operations dashboard provides details like total write in bytes, total read, total ingress by storage account, and total egress by storage account. It also provides storage account statistic insights such as total read count, read bytes, max/avg read latency, total write count, write bytes, and max/avg write latency. In addition, it also displays the status code trend.
Use this dashboard to:
- View amount of write data in MB.
- View amount of read data in MB.
- View Non 200 status code by Service Type.
- View Transactions by Service Type.
- View Storage Account Write Statistics.
- View Storage Account Read Statistics.
- Monitor Total Ingress by Service Type.
- Monitor Total Egress by Service Type.
- Monitor Total Ingress by API name.
- Monitor Total Egress by API name.
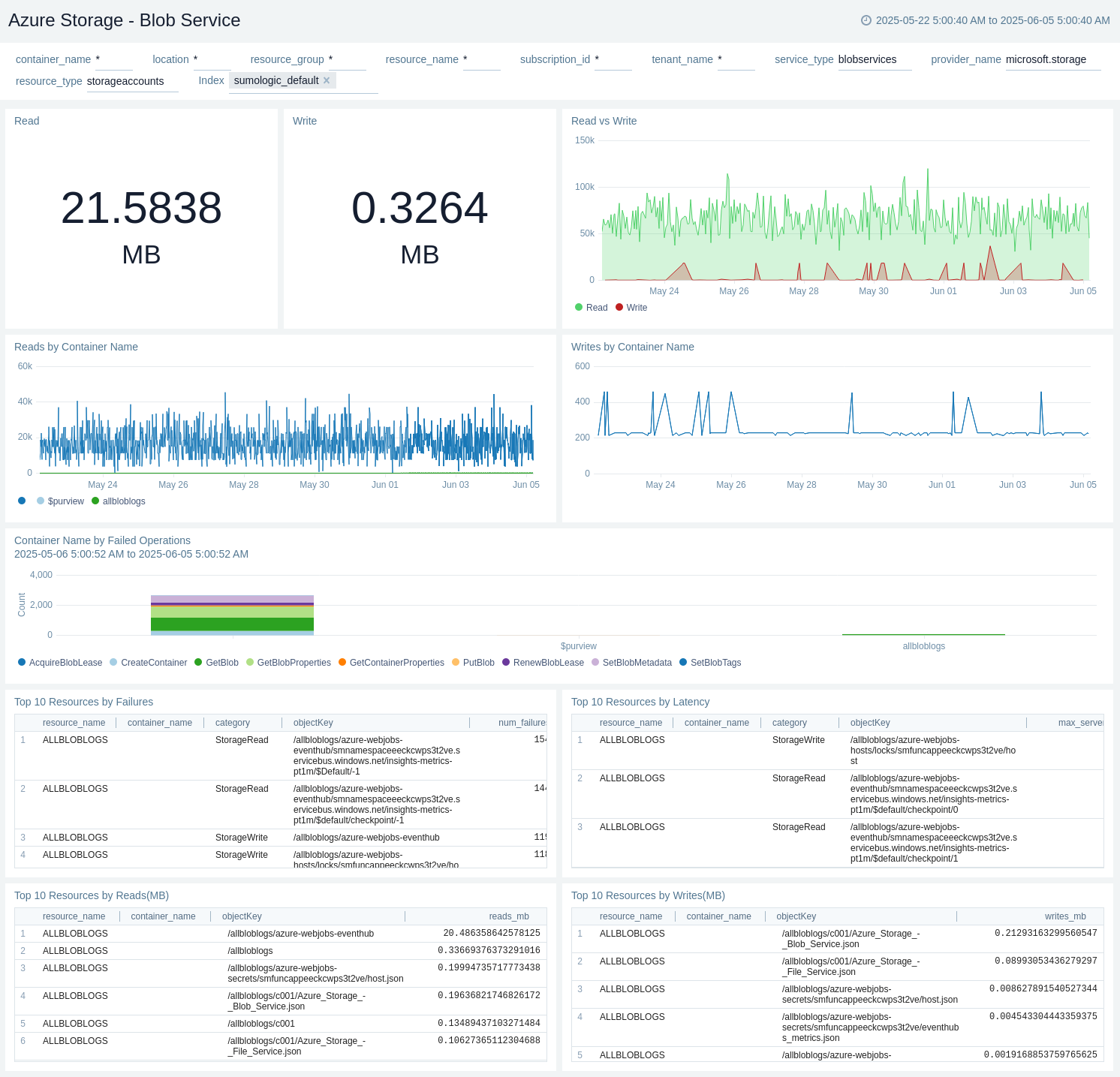
Blob Service
The Azure Storage - Blob Service dashboard provides details like read bytes, write bytes, last 10 operations, read/write trend by service type, and top 10 read/write by resource name.
Use this dashboard to:
- View amount of read data in MB.
- View amount of write data in MB.
- View Read vs Write.
- View Reads by Container Name.
- View Writes by Container Name.
- View Container Name by Failed Operations.
- View Top 10 Resources by Failures.
- View Top 10 Resources by Latency.
- View Top 10 Resources by Reads(MB).
- View Top 10 Resources by Writes(MB).
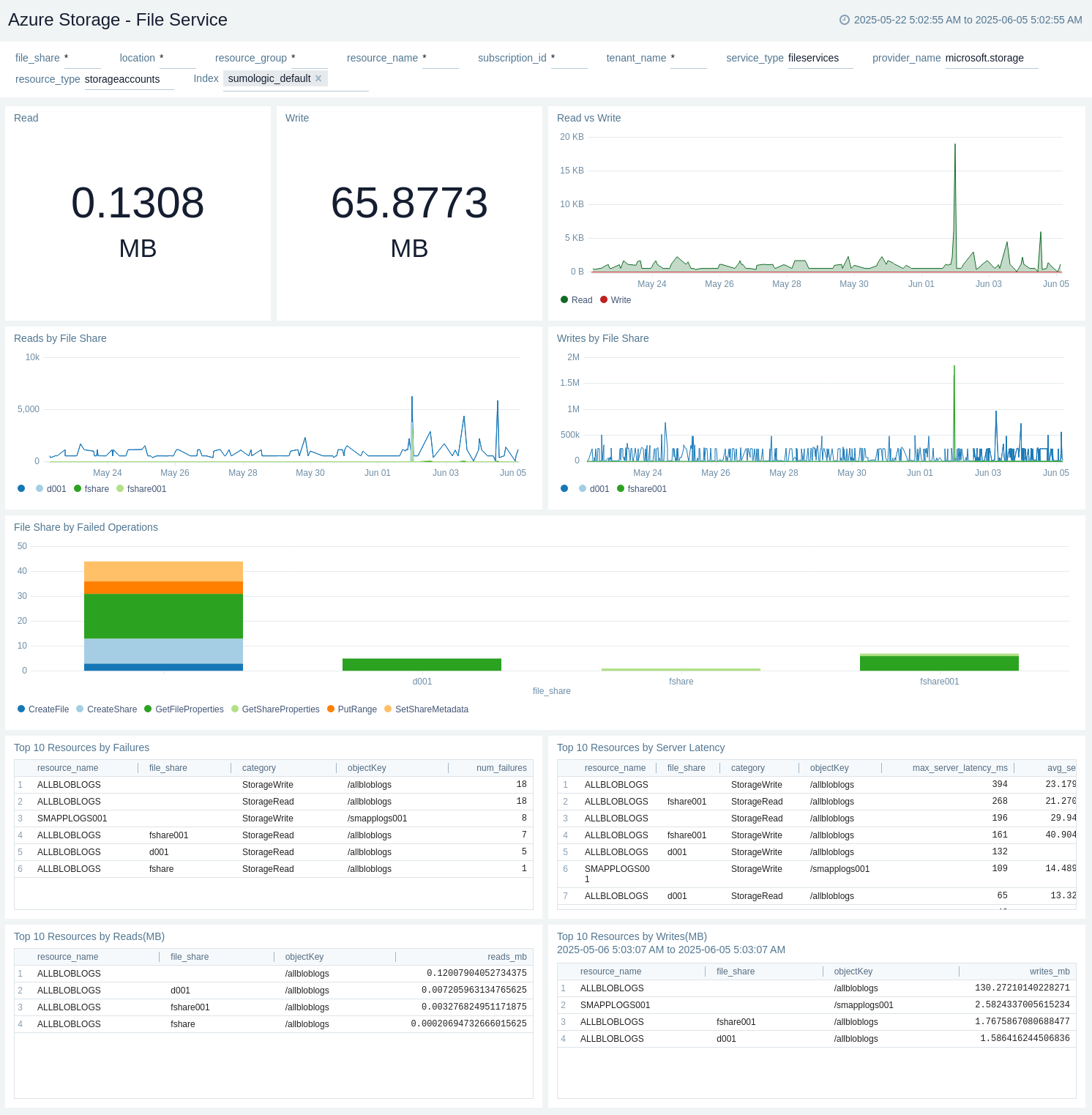
File Service
The Azure Storage - File Service dashboard provides details like read bytes, write bytes, last 10 operations, read/write trend by service type, and top 10 read/write by resource name.
Use this dashboard to:
- View amount of read data in MB.
- View amount of write data in MB.
- View Read vs Write.
- View Reads by File Share.
- View Writes by File Share.
- View File Share by Failed Operations.
- View Top 10 Resources by Failures.
- View Top 10 Resources by Latency.
- View Top 10 Resources by Reads(MB).
- View Top 10 Resources by Writes(MB).
Queue Service
The Azure Storage - Queue Service dashboard provides details like read bytes, write bytes, last 10 operations, read/write trend by service type, and top 10 read/write by resource name.
Use this dashboard to:
- View amount of read data in MB.
- View amount of write data in MB.
- View Read vs Write.
- View Reads by Queue Service.
- View Writes by Queue Service.
- View Queue Service by Failed Operations.
- View Top 10 Resources by Failures.
- View Top 10 Resources by Latency.
- View Top 10 Resources by Reads(MB).
- View Top 10 Resources by Writes(MB).
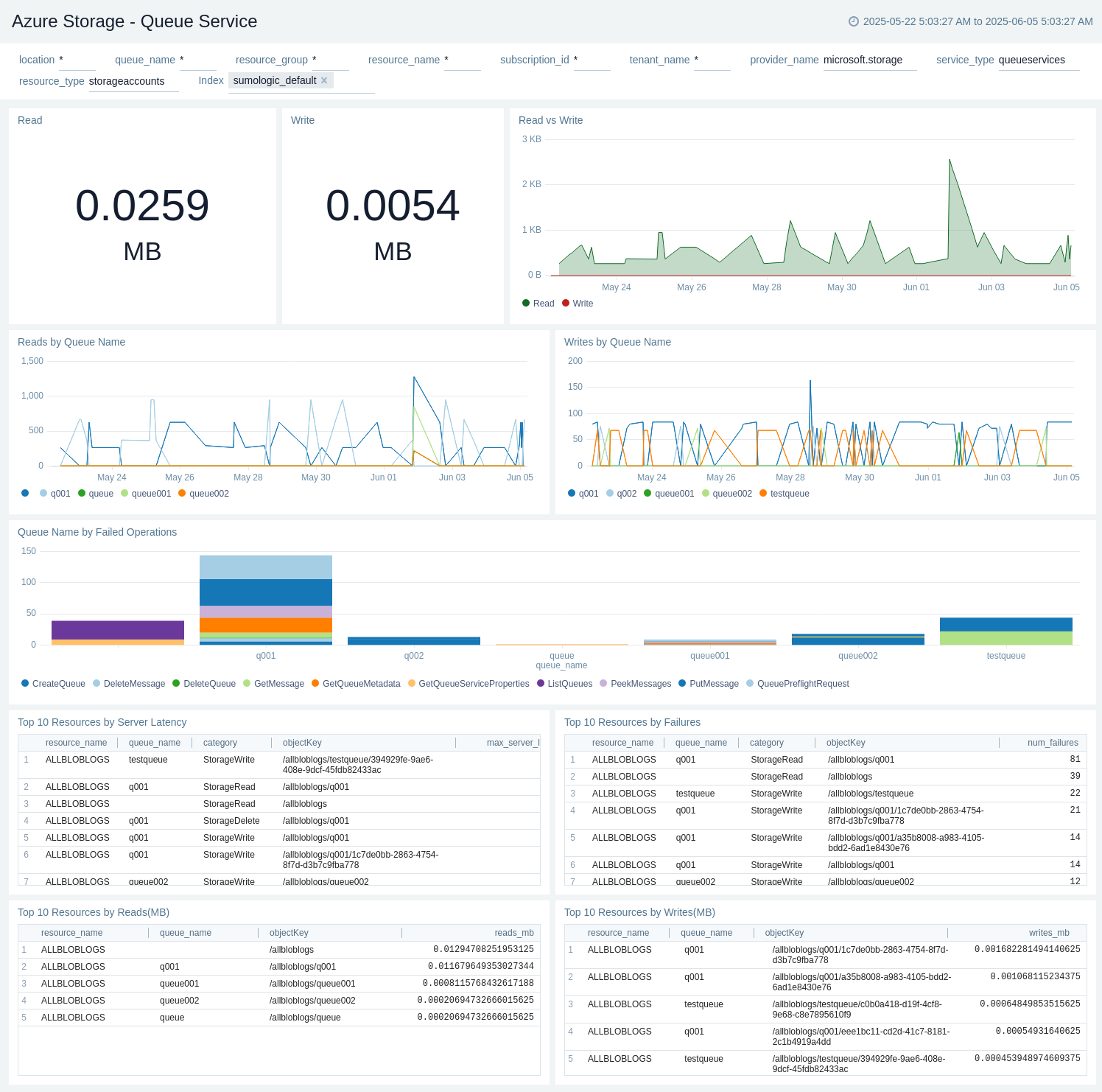
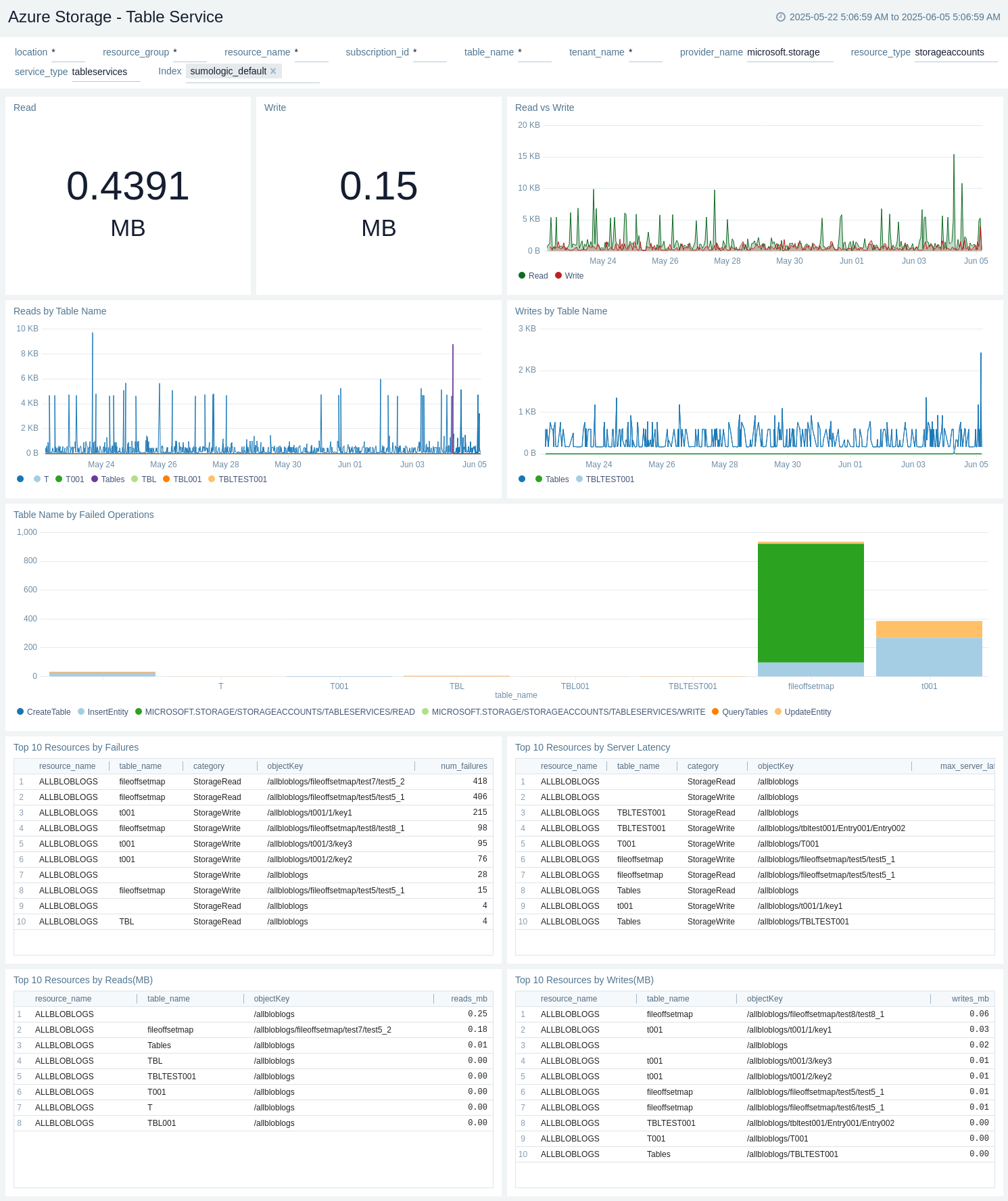
Table Service
The Azure Storage - Table Service dashboard provides details like read bytes, write bytes, last 10 operations, read/write trend by service type, and top 10 read/write by resource name.
Use this dashboard to:
- View amount of read data in MB.
- View amount of write data in MB.
- View Read vs Write.
- View Reads by Table Service.
- View Writes by Table Service.
- View Table Service by Failed Operations.
- View Top 10 Resources by Failures.
- View Top 10 Resources by Latency.
- View Top 10 Resources by Reads(MB).
- View Top 10 Resources by Writes(MB).
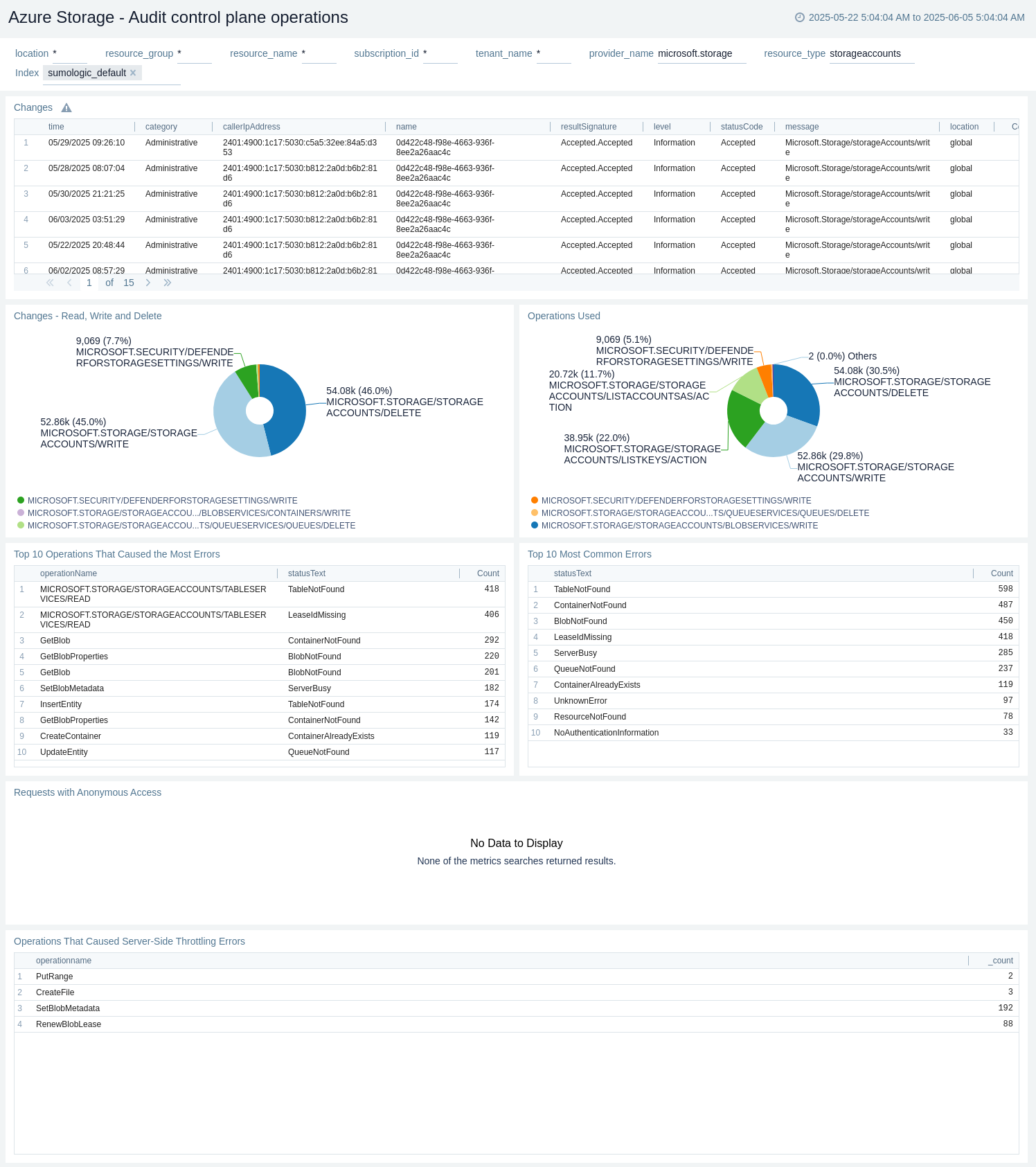
Audit control plane operations
The Azure Storage - Audit control plane operations dashboard provides details like changes, read/write/delete specific changes, different operations used, top 10 operations that caused most errors, and most common errors.
Use this dashboard to:
- View last 24 hours changes.
- View changes - read, write, and delete.
- View operations used.
- View Top 10 operations that caused the most errors.
- View Top 10 most common errors.
- View requests with anonymous access.
- view Operations that caused server-side throttling errors.
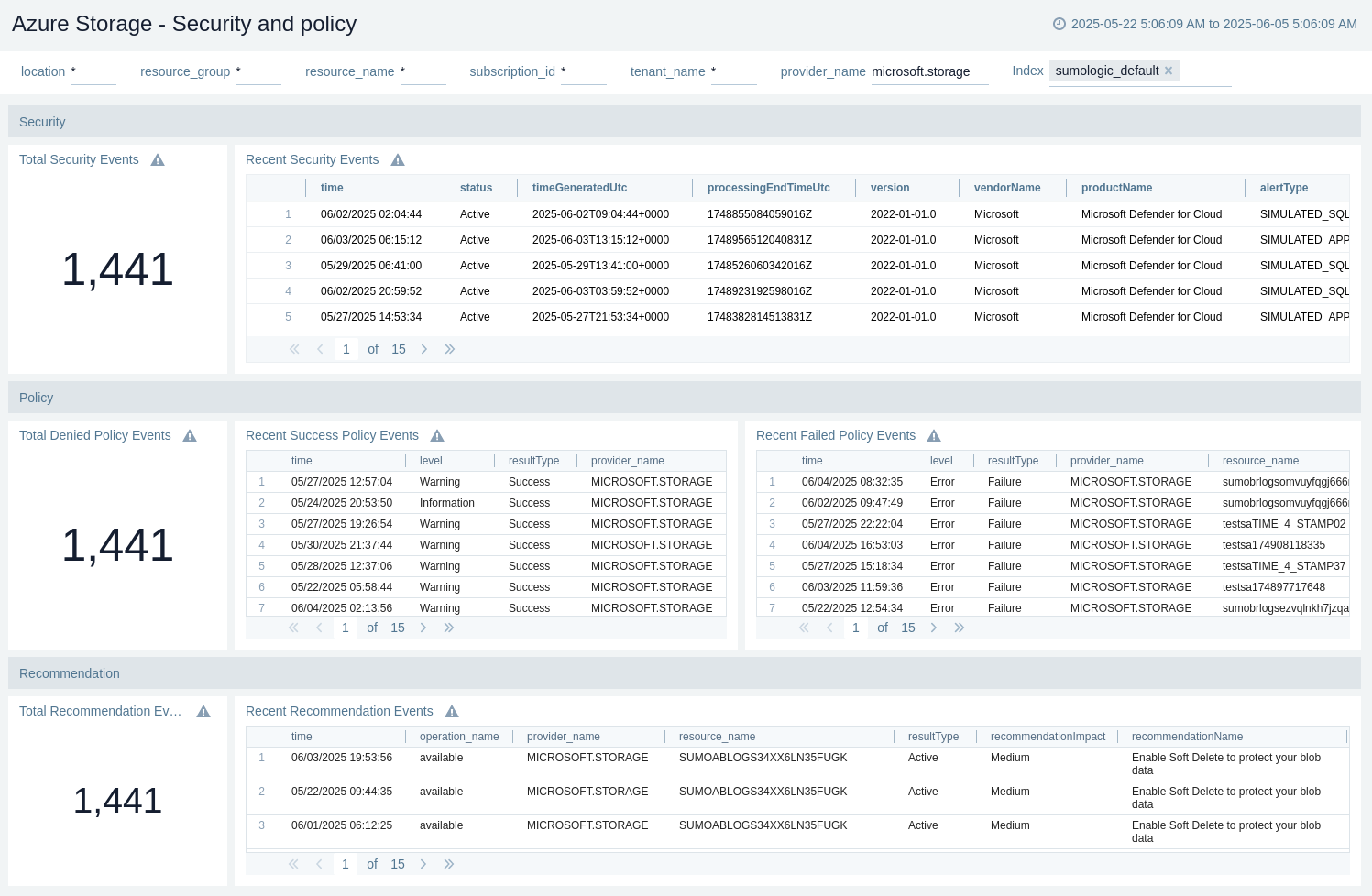
Security and policy
The Azure Storage - Security and Policy dashboard provides security, policy, and recommendation details.
Use this dashboard to:
- View recent security events.
- View total security events.
- View total denied policy events.
- View recent failed policy events.
- View recent success policy events.
- View total recommendation events.
- View recent recommendation events.
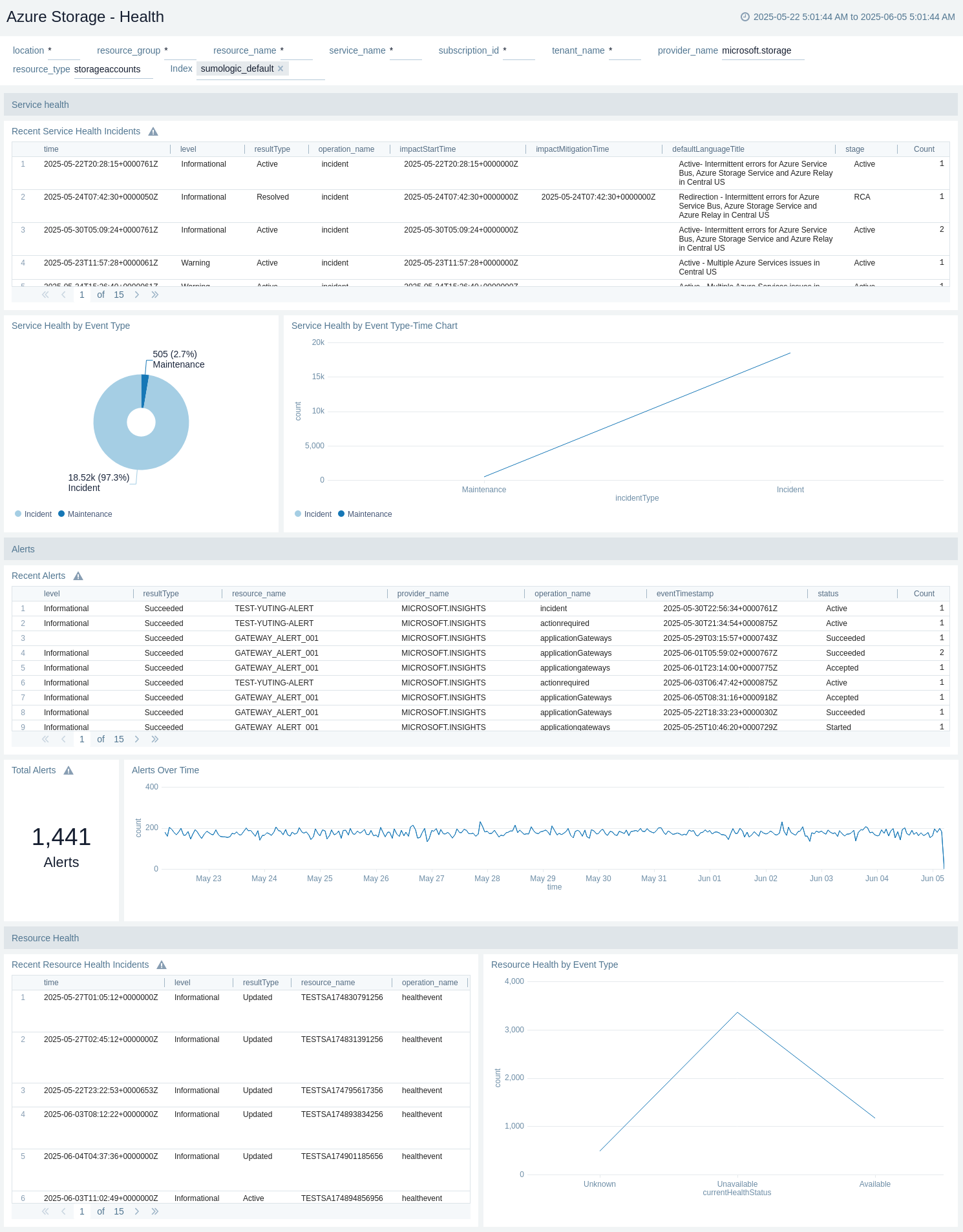
Health
The Azure Storage health dashboard provides information about the service health and alerts.
Use this dashboard to:
- View recent service health incidents.
- Monitor service health by event type.
- View service health by event type-Time chart.
- View recent alerts.
- View total alerts.
- View alerts over time.
- View recent resource health incidents.
- Monitor resource health by event type.
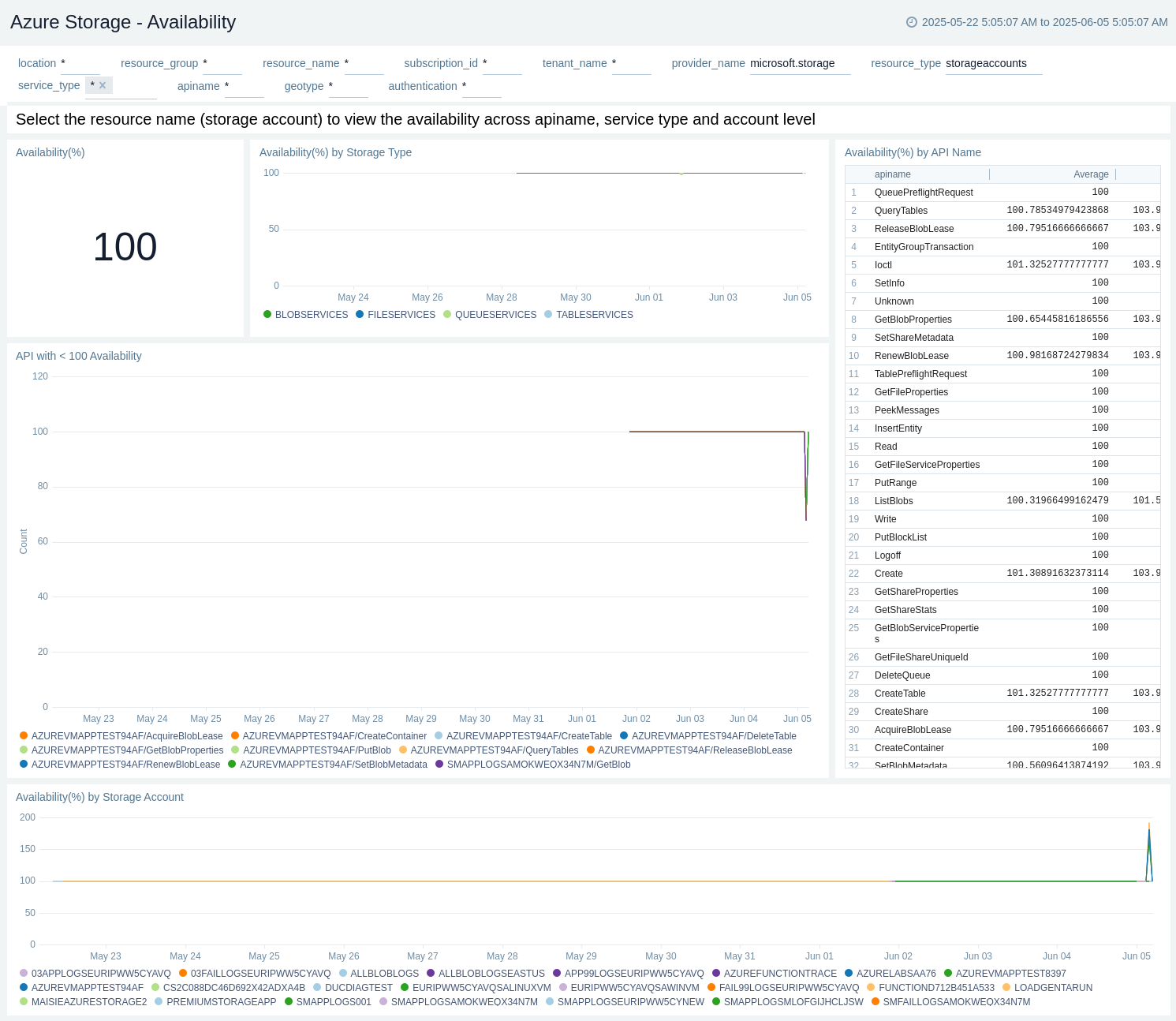
Availability
The Azure Storage - Availability metrics dashboard provides details like availability in percentage, availability by API name, and trend by API name and by storage type.
Use this dashboard to:
- Monitor availability percentage.
- Monitor availability percentage trend by Storage Type.
- View API with < 100 availability.
- Monitor availability percentage by API name.
- Monitor availability percentage trend by Storage Account.
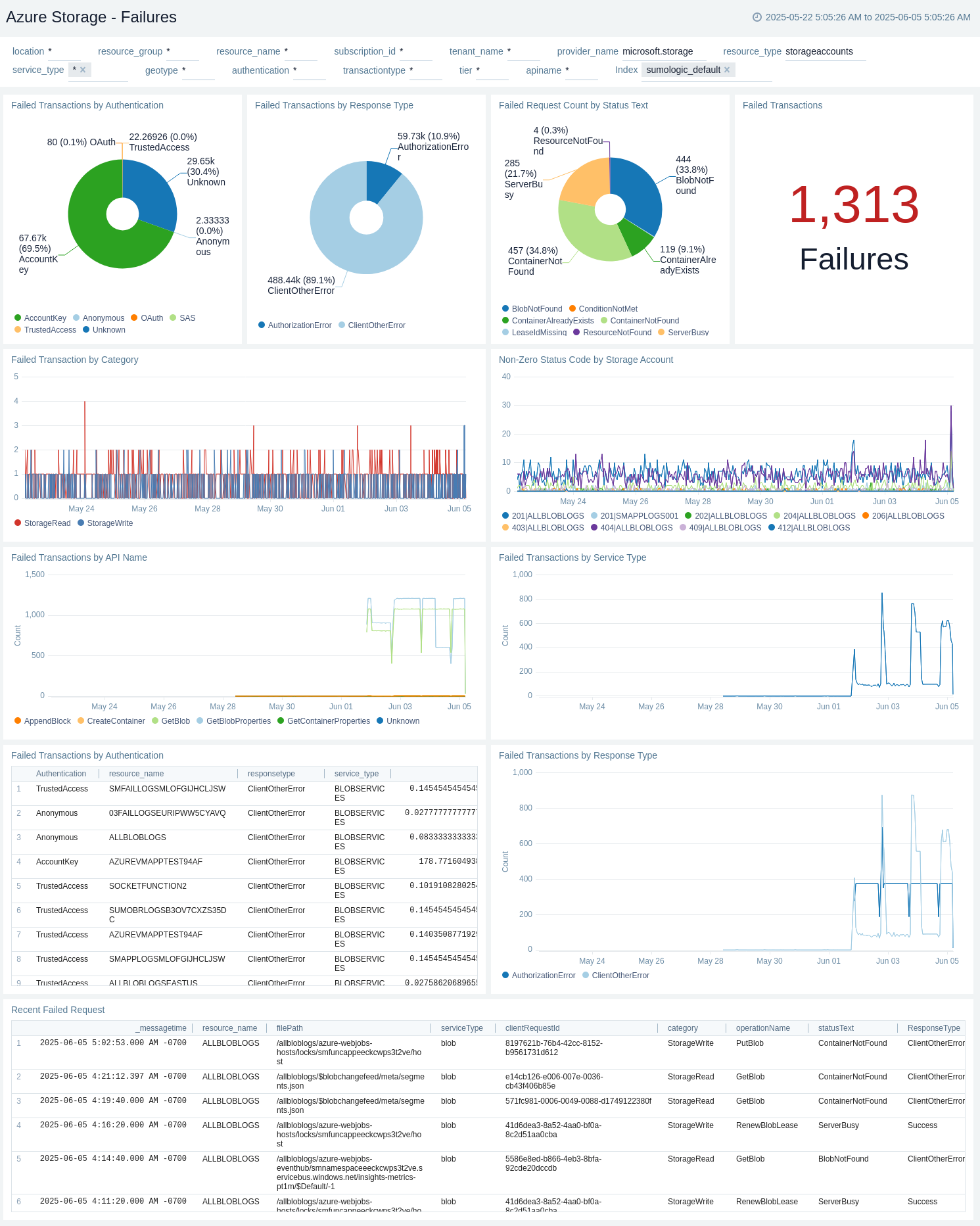
Failures
The Azure Storage - Failures metrics dashboard provides details like failing transactions by API name, response type, storage account, and storage type.
Use this dashboard to:
- Monitor Failed transactions by authentication.
- Monitor Failed transactions by response type.
- Monitor Failed request count by status text.
- Monitor Failed Transactions.
- Monitor Failed Transaction by Category.
- Monitor Non-zero status code by storage account.
- Monitor Failed transactions by API name.
- Monitor Failed transactions by service type.
- Monitor Failed transactions by authentication.
- Monitor Failed transactions by response type.
- Monitor Recent failed request.
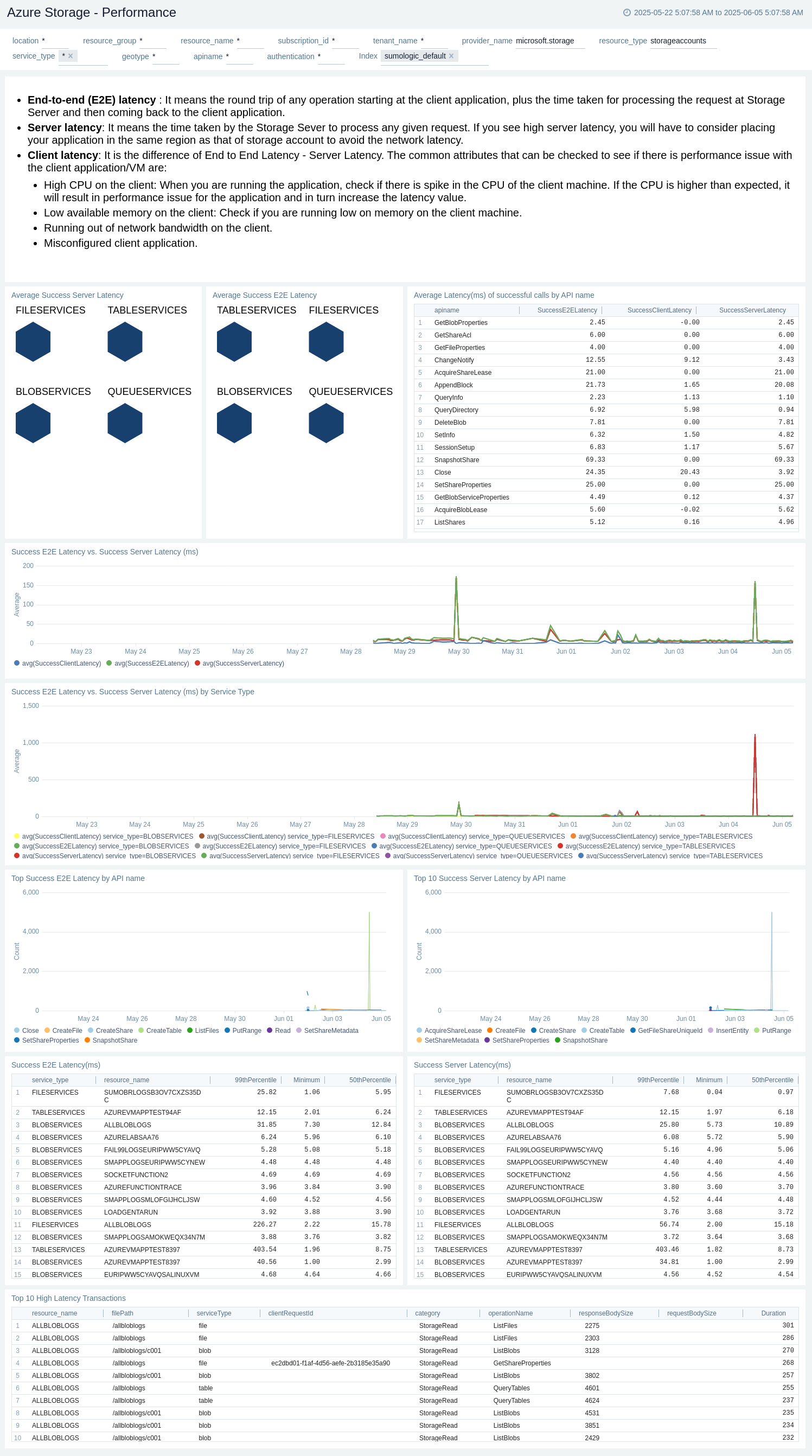
Performance
The Azure Storage - Performance metrics dashboard provides details like failing transactions by API name, response type, storage account, and storage type.
Use this dashboard to:
- Monitor Average Success Server Latency.
- Monitor average success E2E latency.
- View Average Latency(ms) of successful calls by API name.
- View Success E2E Latency vs. Success Server Latency (ms).
- View Success E2E Latency vs. Success Server Latency (ms) by Service Type.
- View Top 10 Success Server Latency by API name.
- View SuccessE2ELatency(ms).
- View SuccessServerLatency(ms).
- View Top 10 high latency transactions.
Upgrade/Downgrade the Azure Storage app (optional)
To update the app, do the following:
Next-Gen App: To install or update the app, you must be an account administrator or a user with Manage Apps, Manage Monitors, Manage Fields, Manage Metric Rules, and Manage Collectors capabilities depending upon the different content types part of the app.
- Select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
Optionally, you can identify apps that can be upgraded in the Upgrade available section. - To upgrade the app, select Upgrade from the Manage dropdown.
- If the upgrade does not have any configuration or property changes, you will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
- If the upgrade has any configuration or property changes, you will be redirected to the Setup Data page.
- In the Configure section of your respective app, complete the following fields.
- Field Name. If you already have collectors and sources set up, select the configured metadata field name (eg _sourcecategory) or specify other custom metadata (eg: _collector) along with its metadata Field Value.
- Click Next. You will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
Post-update
Your upgraded app will be installed in the Installed Apps folder and dashboard panels will start to fill automatically.
See our Release Notes changelog for new updates in the app.
To revert the app to a previous version, do the following:
- Select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
- To version down the app, select Revert to < previous version of your app > from the Manage dropdown.
Uninstalling the Azure Storage app (optional)
To uninstall the app, do the following:
- Select App Catalog.
- In the 🔎 Search Apps field, run a search for your desired app, then select it.
- Click Uninstall.
Azure Storage alerts
These alerts are metric based and will work for all Azure Storage.
| Alert Name | Alert Description and Conditions | Alert Condition | Recover Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
Azure Storage - Availability | This alert is triggered when average Availability is less than 90%. Also, a warning type alert will be triggered when average Availability is less than 95%. | Percentage < = 90 | Percentage > 90 |
Azure Storage - Success E2E Latency | This alert is triggered when Success E2E Latency is greater than 1000 MilliSeconds. | MilliSeconds > = 1000 | MilliSeconds < 1000 |
Azure Storage - Success Server Latency | This alert is triggered when Success Server Latency greater than 1000. | MilliSeconds > = 1000 | MilliSeconds < 1000 |
Azure Storage - Transactions | This alert is triggered when Transactions count greater than 500. | Count > = 500 | Count < 500 |
Azure Storage - Used Capacity(GB) | This alert is triggered when Used Capacity(GB) greater than 100. | Byted(GB) > = 100 | Byted(GB) < 100 |
Troubleshooting
HTTP Logs and Metrics Source used by Azure Functions
To troubleshoot metrics collection, follow the instructions in Collect Metrics from Azure Monitor > Troubleshooting metrics collection.