Azure Network Watcher

The Sumo Logic app for Azure Network Watcher leverages Network Security Group (NSG) flow logs to provide real-time visibility and analysis of your Azure Network. This App provides preconfigured Dashboards that allow you to monitor inbound traffic, outliers in traffic flow, and denied traffic flows.
On September 30, 2027, Azure Network Watcher will retire Network Security Group (NSG) flow logs. Starting June 30, 2025, you will no longer be able to create new NSG flow logs. To avoid service disruptions, migrate your existing NSG flow logs configuration to Virtual Network Flow Logs. After migration, configure collection for Virtual Network Flow logs and install the new Sumo Logic app for Azure Virtual Network.
Log types
The Sumo Logic App for Azure Network Watcher uses Network Security Group (NSG) flow logs. NSG flow logs provide ingress and egress IP traffic flow with the following information:
- Inbound and Outbound flows per Rule
- NIC and traffic flow
- 5-tuple information with respect to flow (Source/Destination IP and Port, Protocol)
- Allowed/Denied traffic flow.
Sample log messages
{
"time":"2017-09-27 21:22:33.443+0000",
"sys_id":"4181995a-801f-4075-a56c-30b3671148bf",
"category":"NetworkSecurityGroupFlowEvent",
"resource_id":"/SUBSCRIPTIONS/C088DC46-D692-42AD-A4B6-9A542D28AD2A/RESOURCEGROUPS/AZURELABS/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/NETWORKSECURITYGROUPS/NSG-AZURELABS-03",
"event_name":"NetworkSecurityGroupFlowEvents",
"rule_name":"All_prod_tcp",
"mac":"000D3AF86058",
"src_ip":"51.148.136.204",
"dest_IP":"107.198.121.243",
"src_port":"47676",
"dest_port":"4367",
"protocol":"T",
"traffic_destination":"I",
"traffic_a/d":"D"
}
Sample queries
_sourceCategory="security/flowlogs"
| json field=_raw "rule_name"
| json field=_raw "resource_id"
| json field=_raw "event_name"
| json field=_raw "mac"
| json field=_raw "src_ip"
| json field=_raw "dest_IP"
| json field=_raw "dest_port"
| json field=_raw "protocol"
| json field=_raw "traffic_destination"
| json field=_raw "traffic_a/d" as traffic_a_d
| parse regex field=resource_id"(?<NSG>[\w-_.]+)$"
| json field=_raw "src_port"
| where traffic_a_d = "D"
| lookup latitude, longitude, country_code, country_name, region, city, postal_code, area_code, metro_code from geo://default on ip = src_ip
| count by latitude, longitude, country_code, country_name, region, city, postal_code, area_code, metro_code
| sort _count
Collecting logs for the Azure Network Watcher app
This document provides instructions for configuring the collection of NSG Flow Logs for the Azure Network Watcher App.
Configuration requirements
Before you begin configuring NSG Flow Log collection, make sure the following environment prerequisites are met:
- Your Storage Account must be of type General-purpose v2 or Blob storage.
- Your Network Security Group and Storage Account should be in same resource location.
- You also need to have Microsoft Authorization/role Assignments/write permissions, so they should be a "User Access Administrator" or "Owner".
Resource group names should not contains underscores (_).
Step 1: Configure Azure Storage Account
In this step you configure a storage account to which you will export monitoring data for your Azure service.
The storage account must be a General-purpose v2 (GPv2) storage account
If you have a storage account with a container that you want to use for this purpose, make a note of its resource group, storage account name and container name and proceed to step 2.
To configure an Azure storage account, do the following:
- Create a new storage account General-purpose v2 (GPv2) storage account. For instructions, see Create a storage account in Azure help.
- Create a container(Optional) all services in azure create containers automatically. This step is needed only when you are exporting custom logs in some container.
- In the Azure portal, navigate to the storage account you just created (in the previous step).
- Select Blobs under Blob Service.
- Select + Container,
- Enter the Name
- Select Private for the Public Access Level.
- Click OK.
Make a note of the container name. You will need to supply it later.
And now proceed to step 2. By default, the flow logs are in insights-logs-networksecuritygroupflowevent container.
If you have a storage account that you want to use for this purpose, make a note of its resource group, storage account name, then proceed to step 2. If you want to collect only flow logs from the storage account then you can add the filter /blobServices/default/containers/insights-logs-networksecuritygroupflowevent/.
Step 2: Configure an HTTP Source
This section demonstrates how to configure an HTTP source to receive logs from the Azure function.
To configure an HTTP source for Azure, do the following:
- Select a hosted collector where you want to configure the HTTP source. If desired, create a new hosted collector, as described on Configure a Hosted Collector.
- Configure an HTTP source, as described on HTTP Logs and Metrics Source. Make a note of the URL for the source, you will need it in the next step.
- In Advanced Options for Logs, under Timestamp Format, click Specify a format and enter the following:
- Specify Format as epoch
- Specify Timestamp locator as
\"time\": (.*),
Step 3: Configure Azure Resources using ARM template
To deploy the ARM template-based Blob Storage collection, refer to step 3 of Collect Logs from Azure Blob Storage.
Step 4: Enable NSG flow logs via the Azure Portal
In this step, you enable NSG flow logs with the Azure portal.
- Follow the steps detailed in the Microsoft Azure Network Watcher documentation to enable the flow logs to point to the storage account you configured in the Configure Azure Storage Account section.
Troubleshooting
If logs do not start flowing into Sumo Logic after you perform the configuration above, see Troubleshoot Azure Blob Storage Log Collection.
Installing the Azure Network Watcher app
Now that you have configured Azure Network Watcher, install the Sumo Logic app for Azure Network Watcher to take advantage of the preconfigured searches and dashboards to analyze your data.
To install the app, do the following:
Next-Gen App: To install or update the app, you must be an account administrator or a user with Manage Apps, Manage Monitors, Manage Fields, Manage Metric Rules, and Manage Collectors capabilities depending upon the different content types part of the app.
- Select App Catalog.
- In the 🔎 Search Apps field, run a search for your desired app, then select it.
- Click Install App.
note
Sometimes this button says Add Integration.
- Click Next in the Setup Data section.
- In the Configure section of your respective app, complete the following fields.
- Field Name. If you already have collectors and sources set up, select the configured metadata field name (eg _sourcecategory) or specify other custom metadata (eg: _collector) along with its metadata Field Value.
- Click Next. You will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
Post-installation
Once your app is installed, it will appear in your Installed Apps folder, and dashboard panels will start to fill automatically.
Each panel slowly fills with data matching the time range query received since the panel was created. Results will not immediately be available but will be updated with full graphs and charts over time.
Viewing Azure Network Watcher dashboards
All dashboards have a set of filters that you can apply to the entire dashboard. Use these filters to drill down and examine the data to a granular level.
- You can change the time range for a dashboard or panel by selecting a predefined interval from a drop-down list, choosing a recently used time range, or specifying custom dates and times. Learn more.
- You can use template variables to drill down and examine the data on a granular level. For more information, see Filtering Dashboards with Template Variables.
- Most Next-Gen apps allow you to provide the scope at the installation time and are comprised of a key (
_sourceCategoryby default) and a default value for this key. Based on your input, the app dashboards will be parameterized with a dashboard variable, allowing you to change the dataset queried by all panels. This eliminates the need to create multiple copies of the same dashboard with different queries.
Overview
The Network Watcher - Overview dashboard provides general information of the NSG flow logs, including panels that drill-down into queries with NIC, tuple, and traffic flow information. This dashboard gives a good starting point for detecting outlier in denied traffic and geographic hotspots for inbound traffic. In addition, this dashboard allows you to filter data by rule name, source/destination IP and port, and other metadata fields.
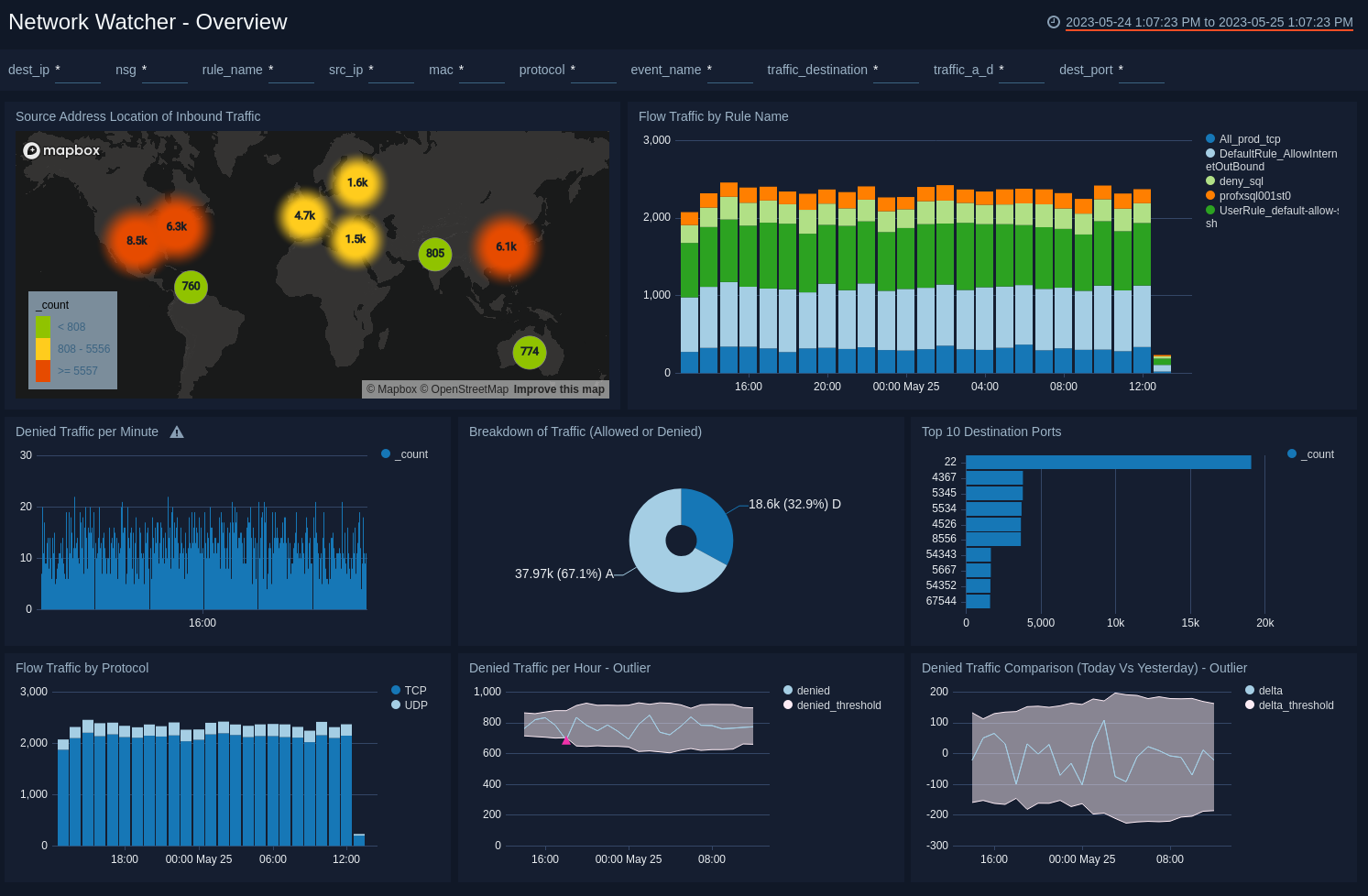
Source Address Location of Inbound Traffic. Displays geo-location of Inbound Traffic.
Flow Traffic by Rule Name. Shows breakdown of all traffic, by Security Rule name, set up at NSG level.
Denied Traffic per Minute. Shows trend in Denied Inbound traffic flow per minute.
Breakdown of Traffic (Allowed or Denied). Displays traffic breakdown by Allowed or Denied flow.
Top 10 Destination Ports. Shows top 10 destination ports in last 24 hours.
Flow Traffic by Protocol. Displays trend of traffic by protocol (TCP/UDP).
Denied Traffic per Hour - Outlier. Using Sumo Logic machine learning Outlier operator, shows any unexpected sequence in denied traffic.
Denied Traffic Comparison (Today Vs Yesterday) - Outlier. Compares denied traffic of last 24 hours with previous 24 hours and shows any unexpected difference between two time periods.
Denied Traffic Flow
The Network Watcher - Denied Traffic Flow dashboard drills down on denied traffic flow logs, shows geographic hotspots of denied traffic, top denied IPs and ports, and denied traffic trends by rule name.
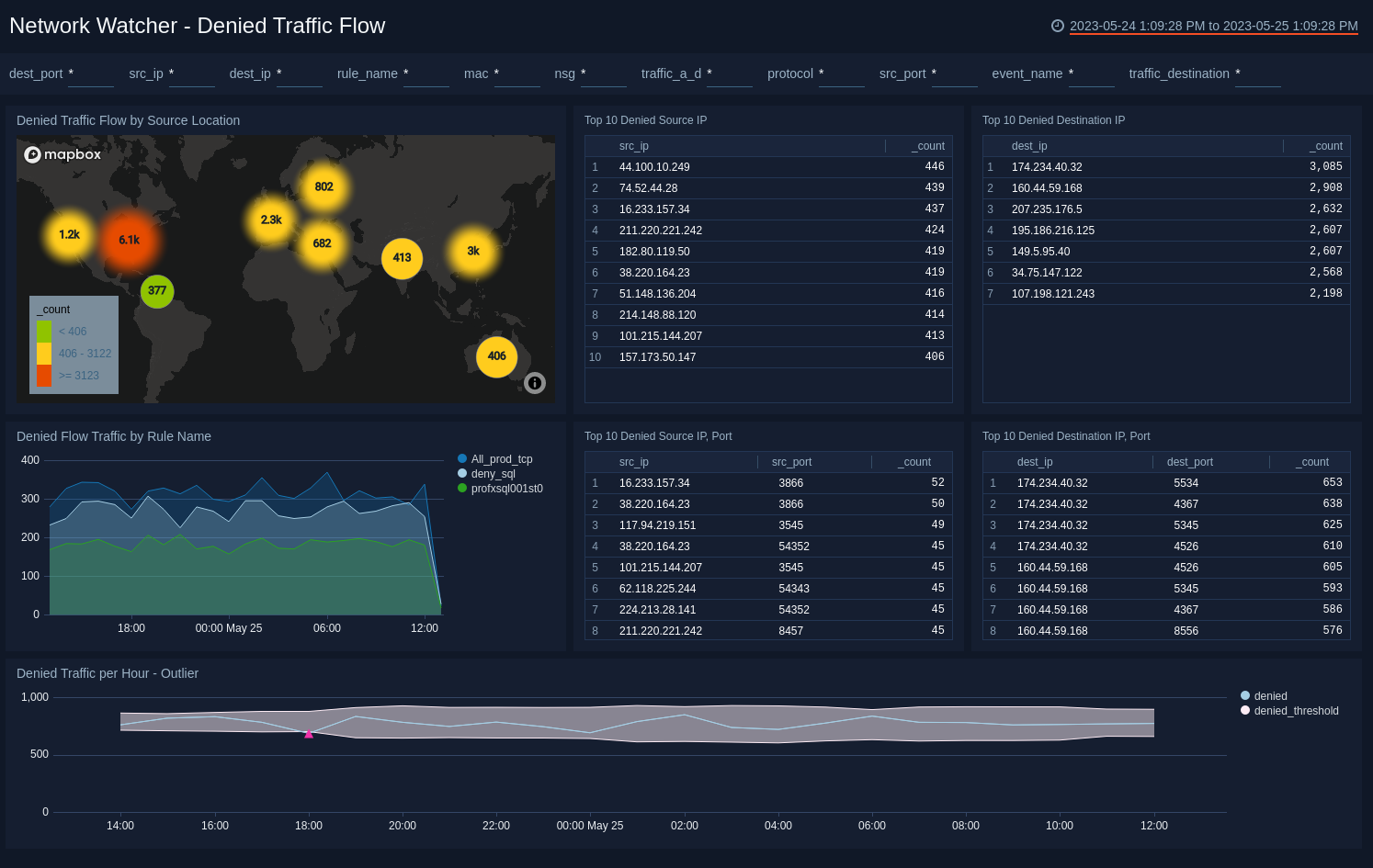
Denied Traffic Flow by Source Location. Shows geographic hotspots of denied traffic flow.
Top 10 Denied Source IP. Displays a table of source IP addresses with denied traffic flow.
Top 10 Denied Destination IP. Displays a table of destination IP addresses with denied traffic flow.
Denied Flow Traffic by Rule Name. Shows trends in denied traffic flow with rule name over last 24 hours.
Top 10 Denied Source IP, Port. Displays a table of source IP addresses and ports with denied traffic flow.
Top 10 Denied Destination IP, Port. Displays a table of destination IP addresses and ports with denied traffic flow.
Denied Traffic per Hour - Outlier. Using Sumo Logic machine learning Outlier operator, shows any unexpected sequence in denied traffic.
Upgrade/Downgrade the Azure Network Watcher app (Optional)
To update the app, do the following:
Next-Gen App: To install or update the app, you must be an account administrator or a user with Manage Apps, Manage Monitors, Manage Fields, Manage Metric Rules, and Manage Collectors capabilities depending upon the different content types part of the app.
- Select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
Optionally, you can identify apps that can be upgraded in the Upgrade available section. - To upgrade the app, select Upgrade from the Manage dropdown.
- If the upgrade does not have any configuration or property changes, you will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
- If the upgrade has any configuration or property changes, you will be redirected to the Setup Data page.
- In the Configure section of your respective app, complete the following fields.
- Field Name. If you already have collectors and sources set up, select the configured metadata field name (eg _sourcecategory) or specify other custom metadata (eg: _collector) along with its metadata Field Value.
- Click Next. You will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
Post-update
Your upgraded app will be installed in the Installed Apps folder and dashboard panels will start to fill automatically.
See our Release Notes changelog for new updates in the app.
To revert the app to a previous version, do the following:
- Select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
- To version down the app, select Revert to < previous version of your app > from the Manage dropdown.
Uninstalling the Azure Network Watcher app (Optional)
To uninstall the app, do the following:
- Select App Catalog.
- In the 🔎 Search Apps field, run a search for your desired app, then select it.
- Click Uninstall.