View Information About Scheduled Views
The page has information about viewing information about the scheduled views configured for your organization.
note
You must have a role that grants you the View Scheduled Views role capability in order to view information about scheduled views.
- New UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu select Data Management, and then under Logs select Scheduled Views. You can also click the Go To... menu at the top of the screen and select Scheduled Views.
Classic UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu, select Manage Data > Logs > Scheduled Views.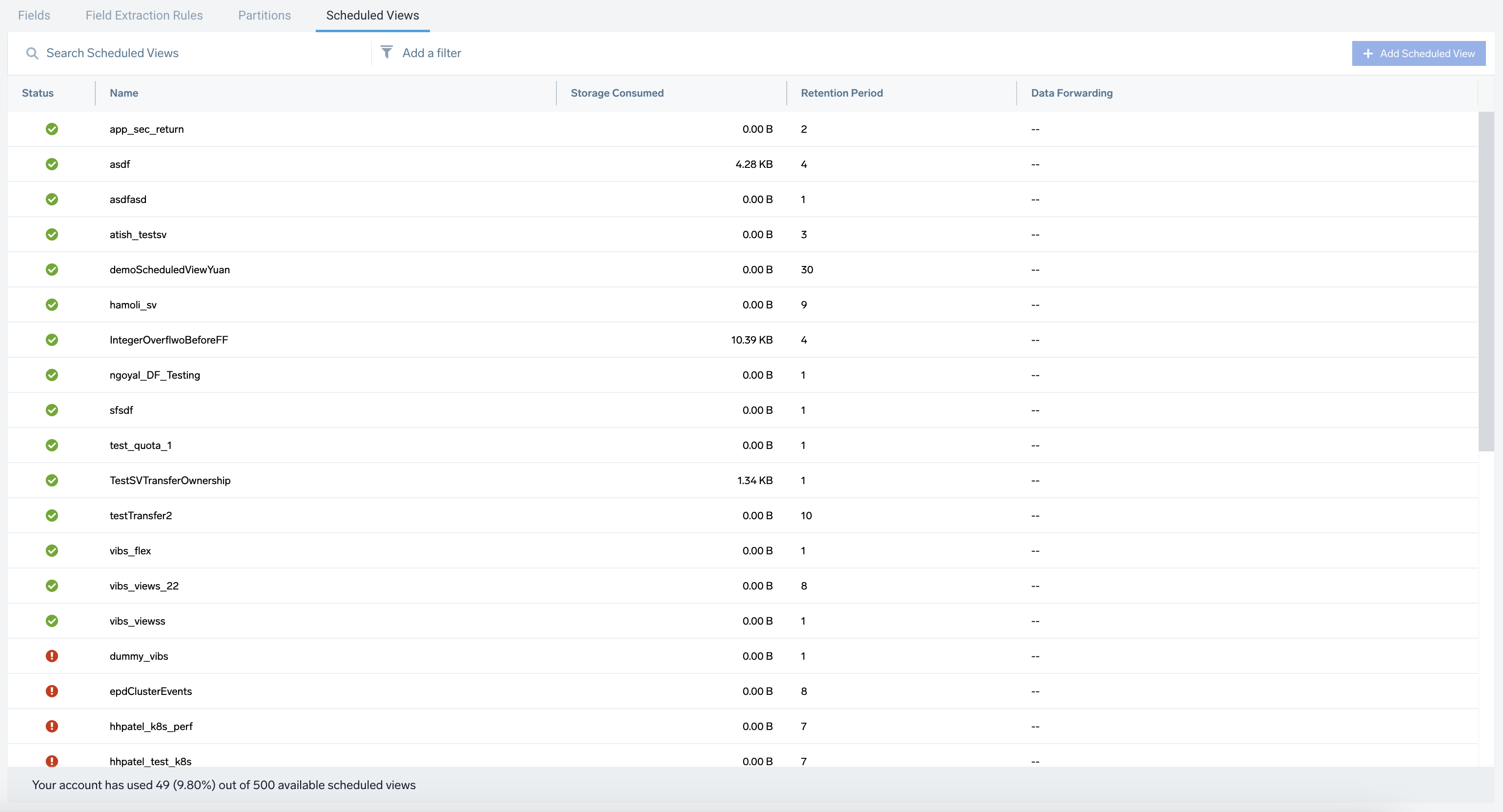
- Add a Filter. To refine the table results, use the Add a filter section located above the table. AND logic is applied when filtering between different sections, while OR logic is applied when filtering within the same section.
note
You can see the suggestions only if there are two or more responses for the same column or section.
- Status. Indicates whether the scheduled view is currently Completed, Failed, Not Started, Filling, or Paused.
- Name. The name assigned to the scheduled view.
- Storage Consumed. The total volume of uncompressed data ingested across the duration of the retention period.
- Retention Period. The number of days configured as the retention period.
- Data Forwarding. Indicates the name of the data forwarding destination if the scheduled view is configured to forward data to an S3 or GCS bucket.
- Add a Filter. To refine the table results, use the Add a filter section located above the table. AND logic is applied when filtering between different sections, while OR logic is applied when filtering within the same section.
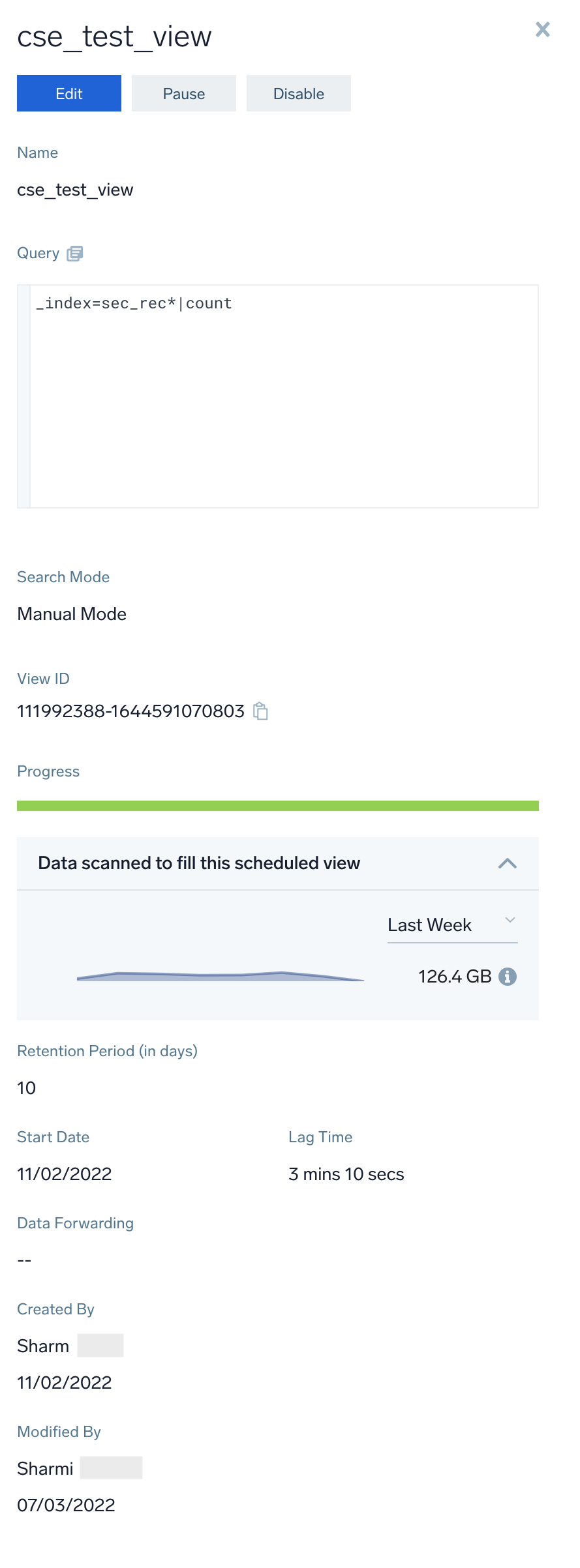
- To view details of a scheduled view configuration, click the row containing the view. A pane will appear on the right side of the page with the following information.
- Name. Displays the name of the scheduled view.
- Query. The query that returns the data for the scheduled view.
- Search Mode. Indicates the type of search mode, such as Manual Mode or Auto Parse Mode.
- View ID. Unique ID for each scheduled view, used for faster debugging and improved internal operation efficiency. With the view ID, you can collect the details and update the scheduled view directly using the API.
- Progress. Indicates how up-to-date the scheduled view is.
- Data scanned to fill this scheduled view. Provides trend information about the data scanned over time and displays the total data scanned for the selected time to run the query.
- Retention Period. The period of time data in the scheduled view is retained.
- Start Date. Date when data was first added to the scheduled view.
- Lag Time. If the scheduled view is not up-to-date, Lag Time contains the actual lag time. For more information, see Scheduled View Lag Time.
- Timezone. Displays the selected time zone or the default timezone of your browser while creating the scheduled view.
- Query. The query that returns that data to be written to the scheduled view.
- Data Forwarding. If the scheduled view is configured to forward data to an S3 or GCS bucket, the name of the data forwarding destination.
- Created by and Modified by. The user that created the view, and the user that most recently modified the view.