Deploy with AWS CloudFormation
This section walks you through the process of executing the AWS CloudFormation template to set up the AWS Observability Solution for a single AWS region and account combination.
If you are ready to deploy the solution to multiple AWS regions and accounts, see Deploy to Multiple Accounts and Regions.
Click here to view a microlesson on deploying the AWS Observability Solution with the AWS CloudFormation template.
Before you start
If you are already collecting AWS metrics, logs, and/or events, we recommend that you override the default settings. By overriding the configuration sources, we prevent them from being re-created in the AWS infrastructure or Sumo Logic.
If this is the first time you've deployed the AWS Observability Solution, read the Before You Deploy topic for information about:
- Prerequisites for installing the solution.
- Things you should keep in mind before you run the CloudFormation template.
- Instructions for setting up Sumo Logic Host Metric Sources on your EC2 hosts.
Review required inputs
The sections below describe the configuration prompts in the CloudFormation template and the information you need to supply. Before you start filling out the template, it’s a good idea to review each section to make sure you know which sections you want to fill out, and that you have the information you need to proceed.
AWS Observability integrates with the AWS Observability view by populating metadata and only shows entities with metrics coming in. If you do not see expected entities, make sure configurations are correct to collect and receive metrics. For example, metrics for Lambda functions must be coming in for those entities to show in the view. If you do not see Lambda functions, verify the CloudFormation stack is correctly configured including the AWS/Lambda namespace to collect metrics.
"AWS Observability Apps-<Version> <Date of installation>" folder of dashboards by default will be created in the personal library and will be shared with the Sumo org of the user that the Sumo Logic Access keys belong to.
Step 1: Open the CloudFormation template
- Sign in to the AWS Management console.
- Choose an option to invoke AWS CloudFormation Template:
- Click this URL to invoke the latest Sumo Logic AWS CloudFormation template.
- Download the AWS Observability Solution template (S3 Link for cloudformation template): https://sumologic-appdev-aws-sam-apps.s3.amazonaws.com/aws-observability-versions/v2.12.0/sumologic_observability.master.template.yaml to invoke the latest Sumo Logic AWS CloudFormation template.
noteDownload this or other versions of this template from Changelog.
noteTo change the Collector Name and Source Categories of Sumo Logic sources, you must download CloudFormation template version 2.1.0 or greater and follow the instructions in the (#modify-the-collector-name-and-source-categories) section.
- Select the AWS Region where you want to deploy the AWS CloudFormation template.
danger
This step is critical: if you do not select the correct region, you will deploy the solution in the wrong region.
- Proceed to Step 2, below.
Step 2: Sumo Logic access configuration
The table below displays the response for each text box in this section.
| Prompt | Guideline |
|---|---|
| Sumo Logic Deployment Name | Enter au, ca, de, eu, jp, us2, fed, kr, or us1. See Sumo Logic Endpoints and Firewall Security for more information on Sumo Logic deployments. |
| Sumo Logic Access ID | Sumo Logic Access ID. See Access Keys for more information. |
| Sumo Logic Access Key | Sumo Logic Access Key. This key is used for Sumo Logic API calls. |
| Sumo Logic Organization ID | You can find your org on the Preferences page in the Sumo Logic UI. Your org ID will be used to configure the IAM Role for Sumo Logic AWS Sources. |
| Delete Sumo Logic Resources when stack is deleted | To delete collectors, sources and apps in Sumo Logic when the stack is deleted, set this parameter to "True". If this is set to "False", Sumo Logic resources are not deleted when the AWS CloudFormation stack is deleted. Deletion of updated resources will be skipped. |
| Send telemetry to Sumo Logic | To send solution telemetry to Sumo Logic. This will help to troubleshoot the issues occurring during solution installation. To Opt-out change this to false, default value is true |
Step 3: AWS account alias
The table below displays the response for each text box in this section.
| Prompt | Guideline |
|---|---|
| Alias for your AWS account | Enter an account alias for the AWS environment from which you are collecting data. This alias should be something that makes it easy for you to identify what this AWS account is being used for (for example, dev, prod, billing, and marketplace). This name will appear in metrics and logs, and can be queried via the “account field”. Important: Account Aliases should be alphanumeric and cannot include special characters such as “-, $, _” etc. Leave this blank If you're using CloudFormation StackSets to deploy the solution in multiple AWS accounts. |
| S3 URL of a CSV file that maps AWS Account IDs to an Account Alias | This parameter is applicable only If you're using CloudFormation StackSets to deploy the solution in multiple AWS accounts. The S3 URL of the CSV file should have public read access when deploying or updating the solution. Enter the S3 URL of a CSV file which contains the mapping of AWS Account IDs to an Account Alias in the following format: accountid,alias For example: 1234567,dev 9876543,prod |
Step 4: Sumo Logic AWS Observability apps and Alerts
You should only install the AWS Observability apps and alerts the first time you run the template.
The table below displays the response for each text box in this section.
| Prompt | Guideline |
|---|---|
| Install AWS Observability apps and alerts |
|
Step 5: Sumo Logic AWS CloudWatch Metrics Sources
The table below displays the response for each text box in this section.
| Prompt | Guideline |
|---|---|
| Select the kind of CloudWatch Metrics Source to create |
|
| Sumo Logic AWS Metrics Namespaces | Enter a comma-delimited list of the namespaces which will be used for AWS CloudWatch Metrics. The default will be AWS/ApplicationELB, AWS/ApiGateway, AWS/DynamoDB, AWS/Lambda, AWS/RDS, AWS/ECS, AWS/ElastiCache, AWS/ELB, AWS/NetworkELB, AWS/SQS, AWS/SNS, and AWS/EC2. You can provide both AWS as well as custom namespaces. Supported namespaces are based on the type of CloudWatch Metrics Source you have selected above. See the relevant docs for the Kinesis Firehose Metrics Source and the CloudWatch Metrics Source for details on which namespaces they support. |
| Existing Sumo Logic Metrics Source API URL | You must supply this URL if you are already collecting CloudWatch Metrics. Provide the existing Sumo Logic Metrics Source API URL. The account field will be added to the Source. For information on how to determine the URL, see View or Download Source JSON Configuration. |
| Sumo Logic AWS Metrics Tag Filters | Provide JSON format of the namespaces with its tags values to add filters to your metrics. Use semicolons to separate multiple values for the same tag key. AWS Tag Filters will be added to the Source. See JSON format example: json {"AWS/ELB":{"tags":["env=prod;dev"]},"AWS/EC2":{"tags":["env=dev","creator=john"]},"AWS/RDS":{"tags":["env=prod;dev","creator=himan"]},"All":{"tags":["env=dev"]}} .Filters are not supported for custom metrics. |
Step 6: Sumo Logic AWS ALB Log Source
The table below displays the response for each text box in this section.
| Prompt | Guideline |
|---|---|
| Enable ALB Access logging |
|
| Create Sumo Logic ALB Logs Source |
|
| Existing Sumo Logic ALB Logs Source API URL | You must supply this URL if you are already collecting ALB logs. Enter the existing Sumo Logic ALB Source API URL. The account, accountId, and region fields will be added to the Source. For information on how to determine the URL, see View or Download Source JSON Configuration. |
| AWS S3 Bucket Name | If you selected "No" to creating a new source above, skip this step. Provide a name of an existing S3 bucket name where you would like to store ALB logs. If this is empty, a new bucket will be created in the region |
| Path Expression for the Existing ALB logs | This is required in case the above existing bucket is already configured to receive ALB access logs. If this is blank, Sumo Logic will store logs in the path expression: elasticloadbalancing/AWSLogs/* |
Step 7: Sumo Logic AWS CloudTrail Source
The table below displays the response for each text box in this section.
If you are collecting AWS CloudTrail logs from multiple AWS accounts into a common S3 bucket, please run the CloudFormation template in the account that has the S3 bucket and please see the Centralized CloudTrail Log Collection help page.
| Prompt | Guideline |
|---|---|
| Create Sumo Logic CloudTrail Logs Source |
|
| Existing Sumo Logic CloudTrail Logs Source API URL | Required if you are already collecting CloudTrail logs. Provide the existing Sumo Logic CloudTrail Source API URL. The account field will be added to the Source. For information on how to determine the URL, see View or Download Source JSON Configuration. |
| AWS S3 Bucket Name | If you selected "No" to creating a new source above, skip this step. Provide a name of an existing S3 bucket where you would like to store CloudTrail logs. If this is empty, a new bucket will be created in the region. |
| Path Expression to the Existing CloudTrail logs | This is required in case the above existing bucket is already configured to receive CloudTrail logs. If this is blank, Sumo Logic will store logs in the path expression: AWSLogs/*/CloudTrail/*/* |
Step 8: Sumo Logic AWS CloudWatch logs
The table below displays the response for each text box in this section.
| Prompt | Guideline |
|---|---|
| Select the Sumo Logic CloudWatch Logs Sources |
|
| Existing Sumo Logic Lambda CloudWatch Logs Source API URL | Required you already collect AWS Lambda CloudWatch logs. Provide the existing Sumo Logic AWS Lambda CloudWatch Source API URL. The account, region and namespace fields will be added to the Source. For information on how to determine the URL, see View or Download Source JSON Configuration. |
| Subscribe log groups to destination (lambda or kinesis firehose delivery stream) |
|
| Regex for AWS Log Groups | Default Value: aws/(lambda|apigateway|rds) With default value, log group names matching with lambda or rds will be subscribed and ingesting cloudwatch logs into sumo logic. Enter a regex for matching log group names. For more information, see Configuring parameters in the Auto-Subscribe ARN (Amazon Resource Name) Destination topic. |
| Tags for filtering CloudWatch Log Groups | Enter comma separated key value pairs for filtering logGroups using tags. Ex KeyName1=string,KeyName2=string. This is optional leave it blank if tag based filtering is not needed. Visit Configuring parameters. |
- Don't use forward slashes (
/) to encapsulate the regex. While normally they are needed for raw code, it's not necessary here. - Use regex
.*for auto-subscribing all log groups.
Step 9: Sumo Logic AWS ELB Classic Log Source
The table below displays the response for each text box in this section.
| Prompt | Guideline |
|---|---|
| Enable ELB Classic Access logging |
|
| Create Sumo Logic ELB Logs Source |
|
| Existing Sumo Logic ELB Classic Logs Source API URL | You must supply this URL if you are already collecting ELB Classic logs. Enter the existing Sumo Logic ELB Classic Source API URL. The account, and region fields will be added to the Source. For information on how to determine the URL, see View or Download Source JSON Configuration. |
| AWS S3 Bucket Name | If you selected "No" to create a new source above, skip this step. Provide a name of an existing S3 bucket name where you would like to store ELB Classic logs. If this is empty, a new bucket will be created in the region. |
| Path Expression for the Existing ELB Classic logs | This is required in case the above existing bucket is already configured to receive ELB Classic access logs. If this is blank, Sumo Logic will store logs in the path expression: classicloadbalancing/AWSLogs/* |
Step 10: App Installation and Sharing
The table below displays the response for each text box in this section.
| Prompt | Guideline |
|---|---|
| Location where you want the App to be Installed |
|
| Do you want to share App with whole organization |
|
Step 11: Create stack
- Under Capabilities and transforms, click each checkbox.
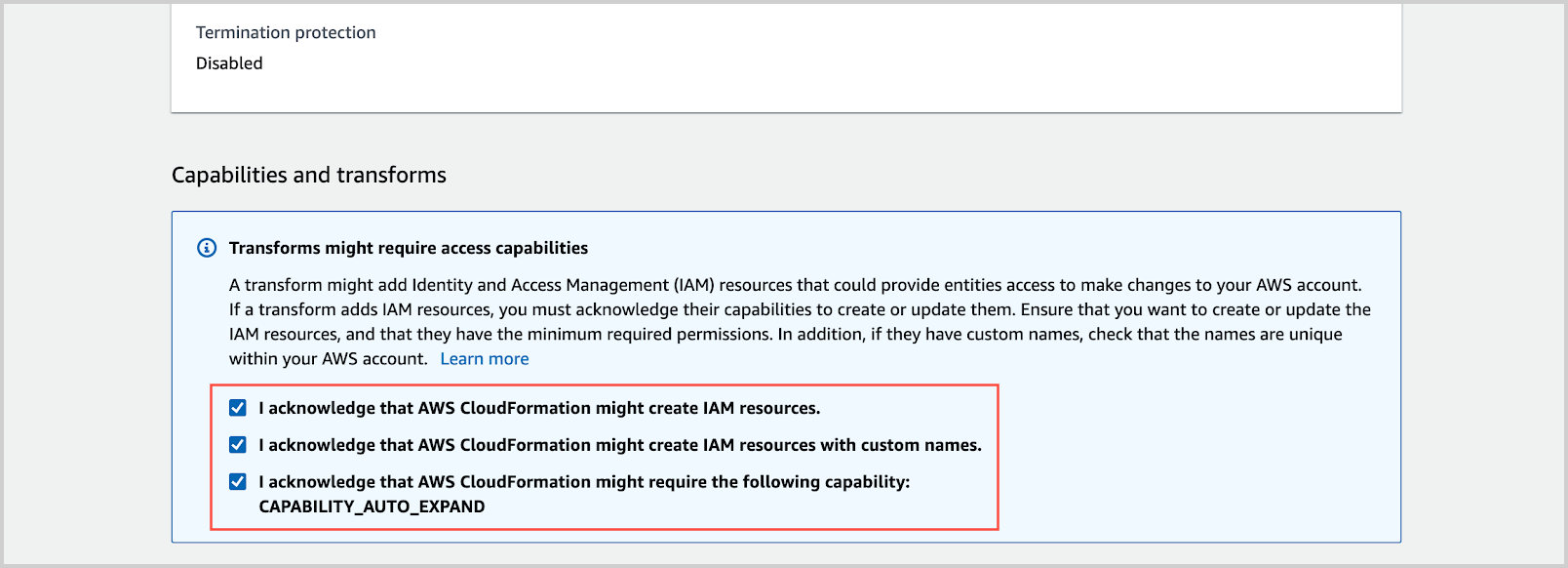
- Click Create Stack.
- Verify that the AWS CloudFormation template has executed successfully in a CREATE_COMPLETE status. This indicates that all the resources have been created successfully in both Sumo Logic and AWS.
- If the AWS CloudFormation template has not run successfully, identify and fix any permission errors till the stack completes with a CREATE_COMPLETE status. See Troubleshooting for assistance with how to resolve these errors.
Modify the source categories
The AWS Observability CloudFormation template creates collector and sources with pre-configured names and source categories. The capability to update the source categories has been added from version v2.1.0 and above.
Do not update the source names as created by CloudFormation template in Sumo Logic. Updating the source name will break the FERs and impact the AWS Observability dashboards.
Follow the steps below to change the default source categories
- Download the template version 2.1.0 or later from the changelog page.
- Modify the source categories in the
Mappingssection of the CloudFormation template.
- Deploy the CloudFormation template.
Troubleshooting
While deploying the template, you may receive error messages such as CREATE_FAILED status or ROLLBACK_COMPLETE status for various reasons. This section provides information on how to troubleshoot such AWS CloudFormation installation failures.
Determine the cause of a CloudFormation installation failure
This section walks you through the process of troubleshooting an AWS CloudFormation installation failure.
To debug an AWS CloudFormation installation failure, do the following:
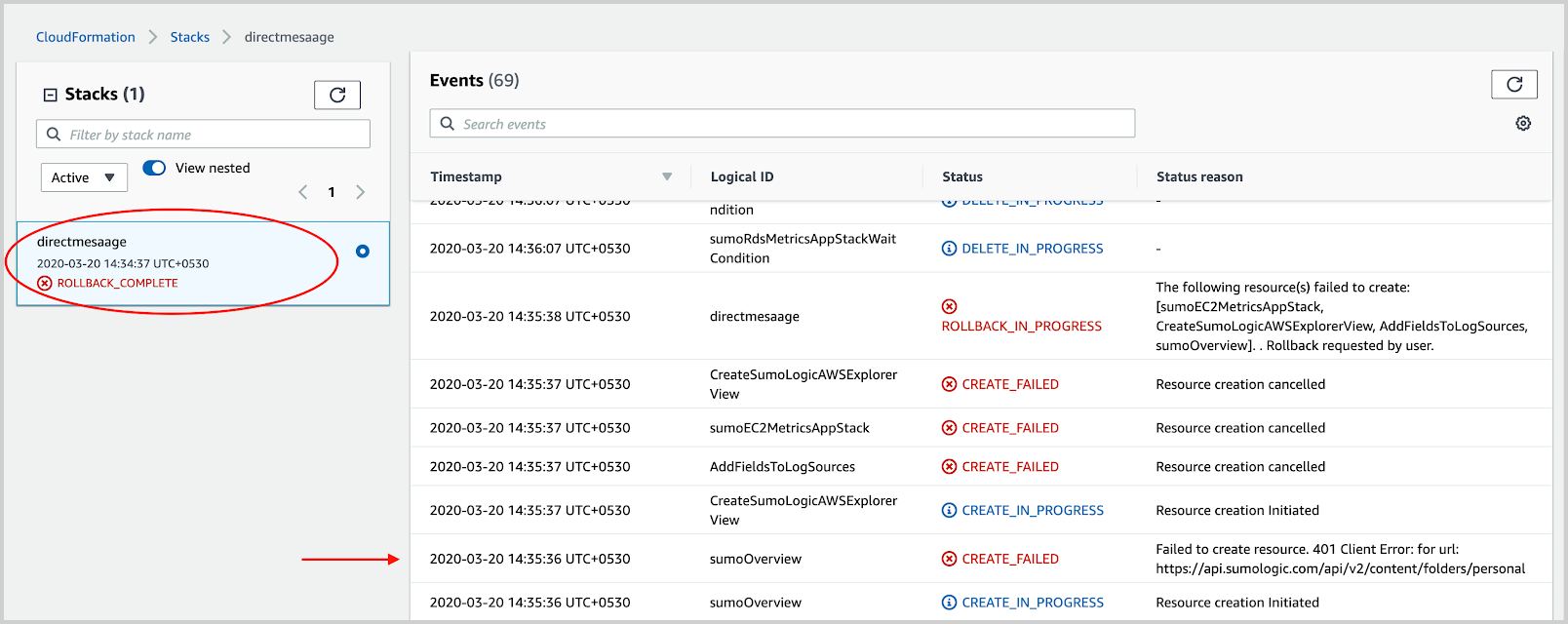
- After the stack rollback is complete and the status is ROLLBACK_COMPLETE, go to the parent stack. In the parent stack, look for the first failure as shown in the following example. The failure can be a direct reason or can point to a nested stack.
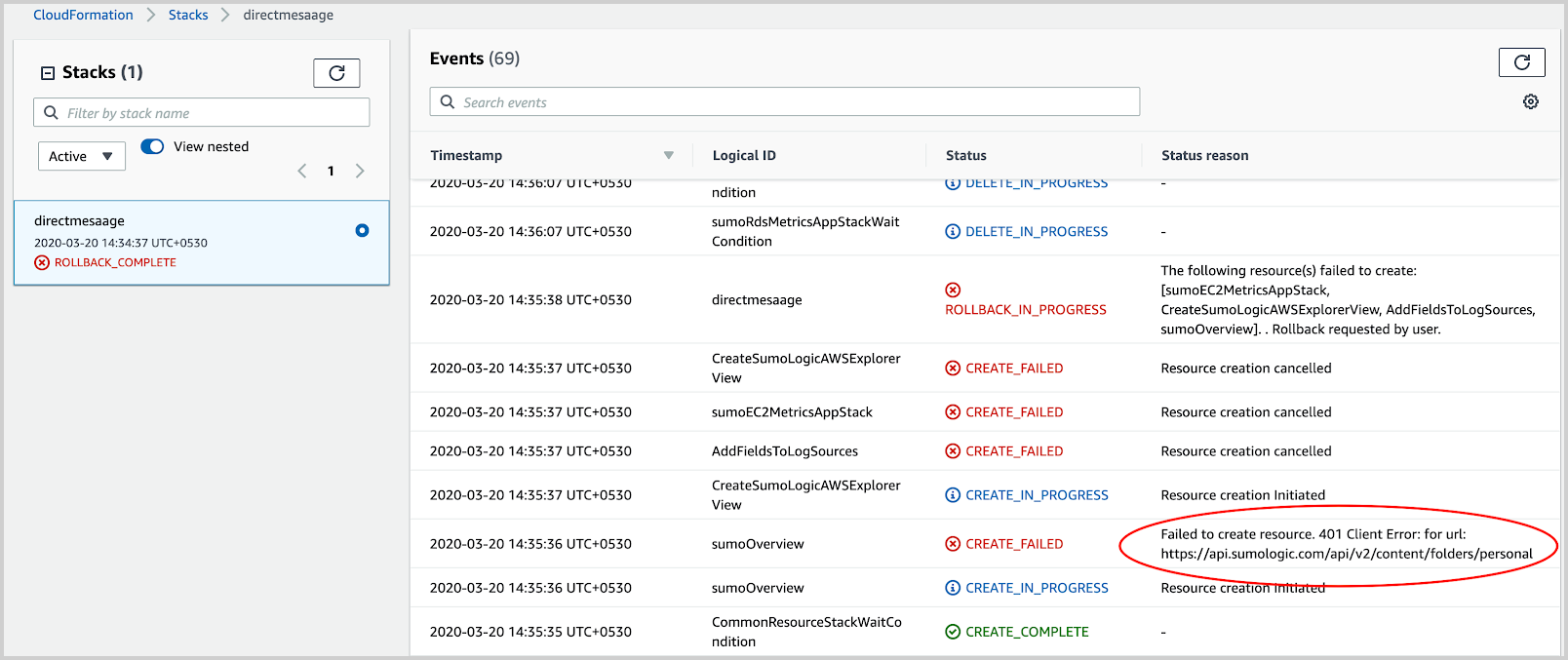
- Look for direct reasons for the failure that is available in the parent stack, as shown in the following example.
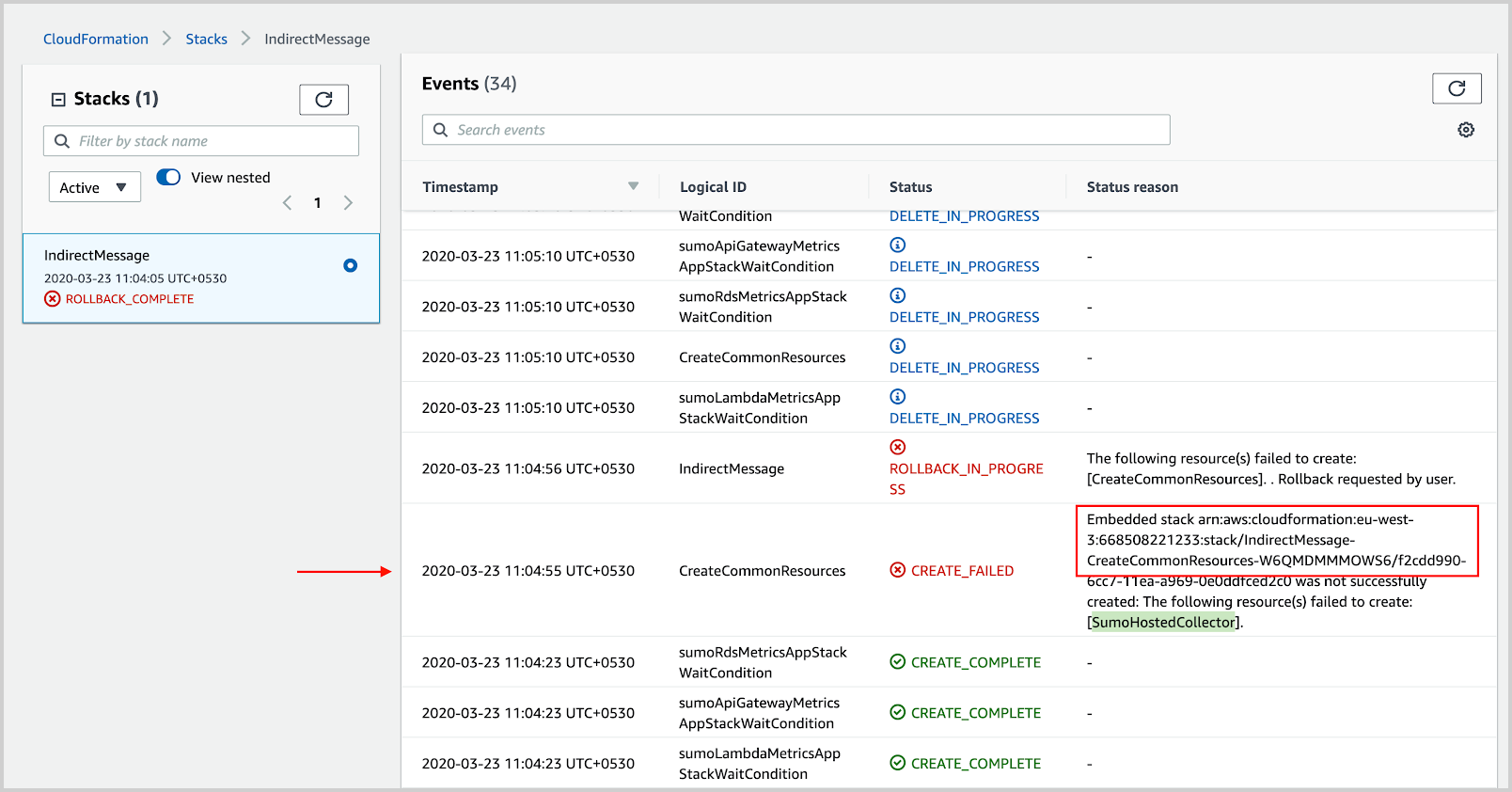
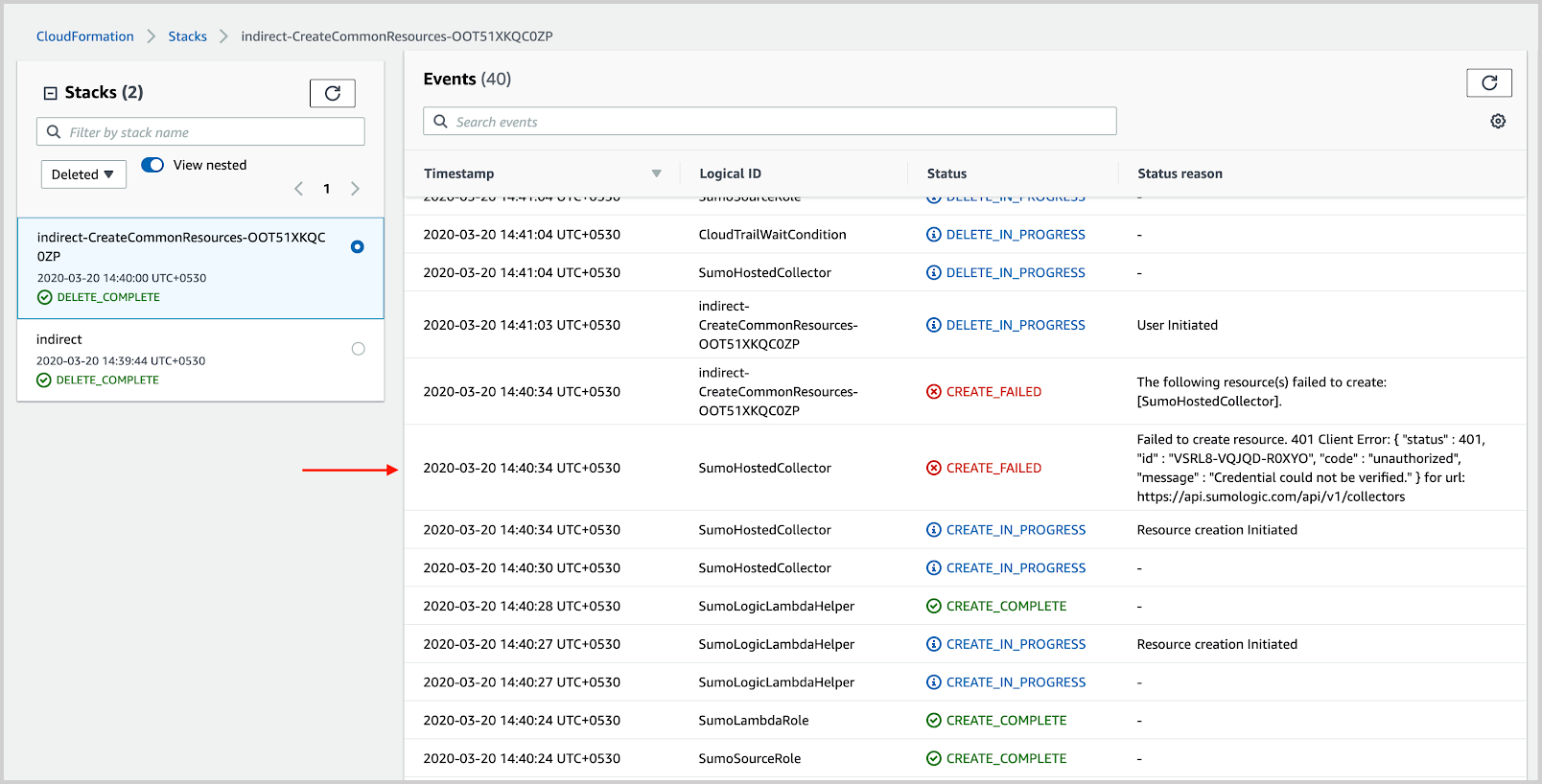
- To find indirect reasons for the failure, go to the nested stack mentioned in the status reason, as shown in the following example. Take a note of the resources mentioned in the reason.
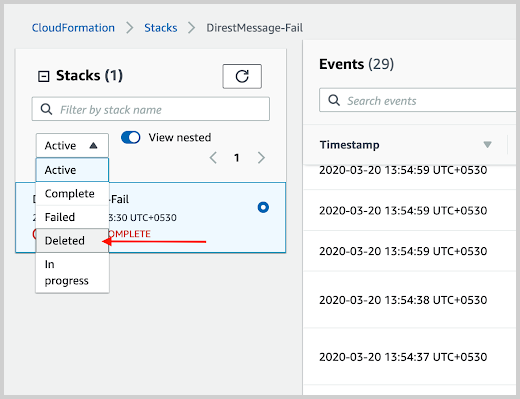
- Select the deleted option to find the nested stacks, as shown in the following example.
- Go to the nested stack and look for the resource mentioned in the previous step to identify the reason, as shown in the following example.
Optimize CloudTrail log ingest
By default, the AWS Observability solution collects AWS CloudTrail logs for all AWS services. To reduce ingestion volume, you can define processing rules that limit log collection to only the logs that are relevant to dashboards provided by the AWS Observability solution.
Define the processing rules for the Sumo Logic AWS CloudTrail Source that was created when you ran the CloudFormation template.
For instructions, see Create a Processing Rule. Create the following rules, selecting Include messages that match as the rule type, using these regular expressions:
.*\"eventSource\":\"elasticloadbalancing\.amazonaws\.com\".*
.*\"eventSource\":\"dynamodb\.amazonaws\.com\".*
.*\"eventSource\":\"ec2\.amazonaws\.com\".*
.*\"eventSource\":\"rds\.amazonaws\.com\".*
.*\"eventSource\":\"lambda\.amazonaws\.com\".*
.*\"eventSource\":\"apigateway\.amazonaws\.com\".*
.*\"eventSource\":\"ecs\.amazonaws\.com\".*
.*\"eventSource\":\"elasticache\.amazonaws\.com\".*
.*\"eventsource\":\"sns\.amazonaws\.com\".*
.*\"eventsource\":\"sqs\.amazonaws\.com\".*
Common errors
Below are some common errors that can occur while using the CloudFormation template.
| Error | Description | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| The API rate limit for this user has been exceeded. | This error indicates that AWS CloudFormation execution has exceeded the API rate limit set on the Sumo Logic side. It can occur if you install the AWS CloudFormation template in multiple regions or accounts using the same Access Key and Access ID. | - Re-deploy the deployment stack without updating the stack in the template. Re-running will detect the drift and create remaining resources. - If the throttling problem persists, try to break down the multi-region deployment into parts and use distinct access IDs and access keys for each part. |
| S3 Bucket already exists. | The error can occur if: - An S3 bucket with the same name exists in S3, or - The S3 Bucket is not present in S3 but is referenced by some other AWS CloudFormation stack which created it. | - Remove the S3 bucket from S3 or select “No” in the AWS Cloudformation template for S3 bucket creation. - Remove the AWS CloudFormation Stack which references the S3 bucket. |
| The S3 bucket you tried to delete is not empty. | The error can occur when deleting the stack with a non-empty S3 bucket. | Delete the S3 bucket manually if you do not need the bucket or its content in the future. |
| Invalid IAM role OR AccessDenied | This error can occur when Sumo Logic access keys are disabled or do not have the required permissions. | - Refer to Edit, activate/deactivate, rotate, or delete access keys for access keys activation. - Refer to Role capabilities for permissions related issues. |
Rolling back the AWS Observability Solution
When you roll back the AWS Observability Solution, all the resources that were created with the AWS CloudFormation stack are deleted. The resources deleted with a rollback include AWS Observability Solution apps, collectors, sources, S3 buckets, Lambda functions, IAM roles, bucket policy, SNS topic, and SNS subscriptions.
Rolling back the AWS Observability Solution deletes the main AWS CloudFormation stack, including the nested stack and associated Sumo Logic and AWS resources. The following rollback guidelines apply:
- Sumo Logic resources are deleted based on the “Delete Sumo Logic Resources when the stack is deleted” flag provided during the AWS CloudFormation configuration. These resources include apps, collectors, and sources.
- AWS resources are deleted by default, regardless of the flag provided. These resources include S3 buckets, Lambda functions, IAM roles, bucket policy, SNS topic, and SNS subscription.
To uninstall the AWS Observability Solution:
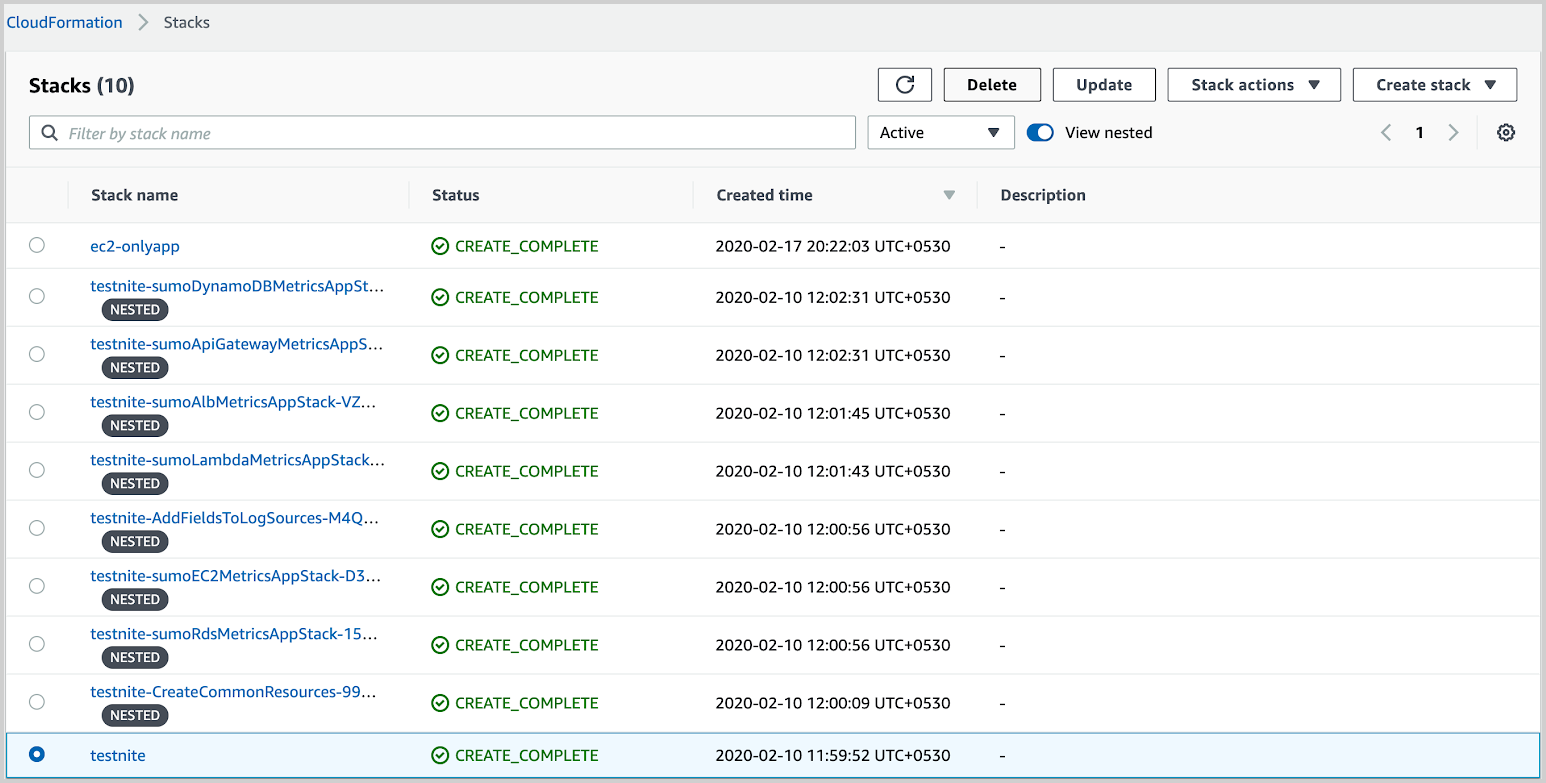
- Log in to your AWS account and go to CloudFormation.
- Select the main stack you want to delete.
- Select Delete.
Remove the account from AWS Observability hierarchy
AWS Observability hierarchy is auto-populated based on the metrics ingested into Sumo Logic with an account tag on the metric source. To remove any AWS account from the AWS Observability hierarchy, you need to remove the data sources ingesting metrics data or remove the account tag from the same metric source. After this, the account will be removed automatically in the next 24 hours. Follow the below the steps to remove the account from the AWS Observability hierarchy:
- Identify the account that you want to remove from the AWS Observability hierarchy. For example, let's assume you want to remove
mobilebankingprodfrom the hierarchy.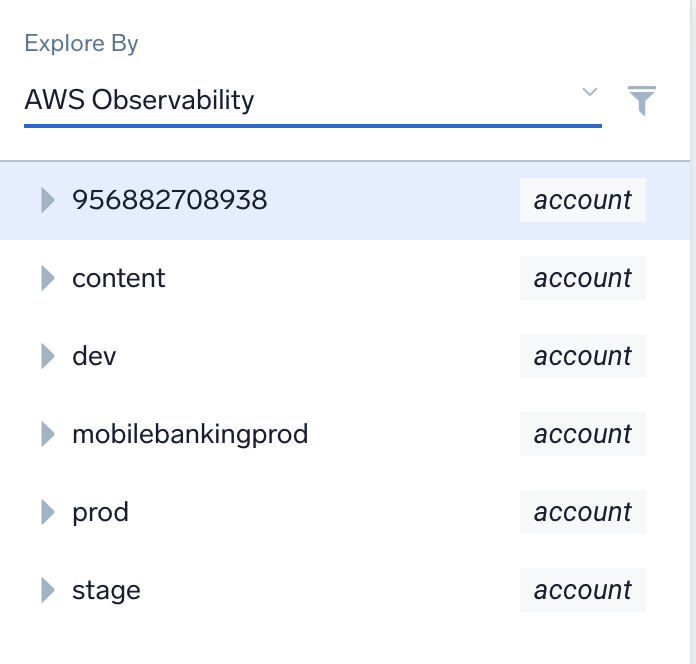
- Run the required metric query to identify from which source and collector data is getting ingested. For this example, enter the below metric query:
account= mobilebankingprod | count by _collector , _source
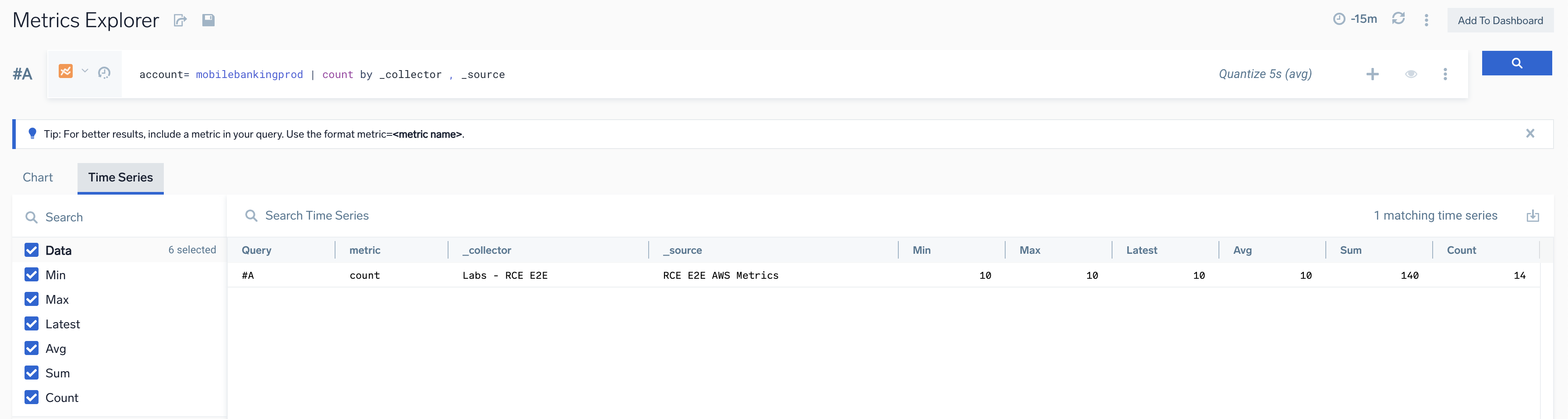
- Delete the source or remove the account tag from the same metric source. After this, the account will be automatically removed from the AWS Observability hierarchy in the next 24 hours.
note
Removing the account tag will not stop the metrics ingestion.
Redeploying the AWS Observability CloudFormation template with existing Sumo Logic resources from a previous deployment
Ensure that you delete the Sumo Logic resources completely prior to redeployment. If you have Delete Sumo Logic Resources when stack is deleted set to "True", then the Sumo Logic resources will automatically be removed while deleting the AWS Observability CloudFormation template. If you have Delete Sumo Logic Resources when stack is deleted set to "False", then the Sumo Logic resources will not be removed while deleting the AWS Observability CloudFormation template. If you do not delete the Sumo Logic resources prior to redeployment (that is, collectors and sources), then subsequent deployments may attempt to use the existing resources, which can result in collection issues. This is not recommended.