Collect AWS ECS Fargate Container Logs
This page describes how to collect application container logs from AWS ECS clusters launched with AWS Fargate using AWS FireLens. This method also works with ECS clusters with EC2 containers. However, the recommended method for collecting EC2 logs is to utilize the Docker logging driver.
- Collect Fargate container logs
- Collect EC2 container logs
- (Optional) Create a centralized fluentd aggregator
- Troubleshooting
Collection process overview
The following diagram illustrates the process for sending container logs from ECS containers running on AWS Fargate or EC2 to Sumo Logic using the FireLens log driver.
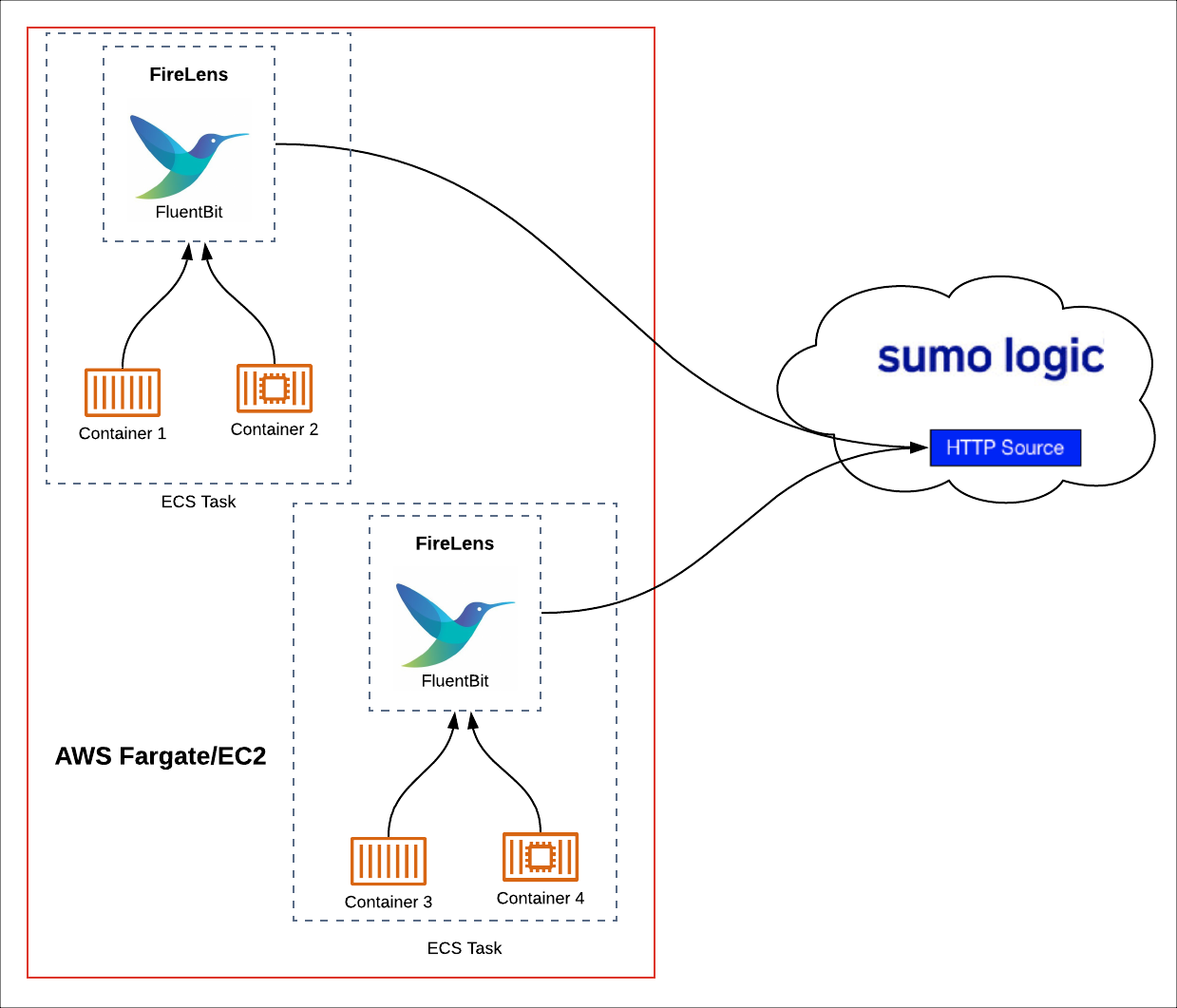
Firelens allows you to configure Fluentd or Fluent Bit output in your Fargate task definition. Fluent Bit is the recommended option because its resource utilization is significantly lower than Fluentd.
You can forward from Fluent Bit to Fluentd, and vice versa. For example, you could use FireLens to forward logs from a Fargate/EC2 task to a Centralized Fluentd Aggregator and then to Sumo Logic.
Collect Fargate container logs
This section show you how to create AWS resources and Sumo Logic resources for Fargate container log collection.
Step 1: Add a hosted collector and HTTP source
A hosted collector allows you to upload data stored in the cloud to Sumo Logic, and an HTTP Source is an endpoint for receiving logs and metrics uploaded via a URL.
When you configure the HTTP Source, make sure to save the HTTP Source Address URL. You will need this URL to configure the task definition.
To add a hosted collection and HTTP source, do the following:
- In Sumo Logic, configure a Hosted Collector.
- In Sumo Logic, configure an HTTP Source.
Step 2: Create an AWS task definition and service
A task definition is required to run Docker containers in Amazon ECS. You can define multiple containers in a task definition. The parameters that you use for the task definition depend on the launch type for the task. For more information about available parameters and the launch types they are valid for in a task definition, see the Amazon ECS Task Definition Parameters documentation.
ECS allows for two launch types, Fargate and EC2. Create the launch type that best suits your environment.
The AWS CLI and ECS CLI must be installed and configured before you create the task definition.
You need to create a new task definition with a Log Router based on a *FluentBit *image and a container for your application using this JSON.
Prerequisites
Before creating the task definition, replace the following values in the sample JSON:
- ECS Task IAM Role: Create a new role called ecs_task_iam_role.
- AWS Fluent Bit Image: The default image is amazon/aws-for-fluent-bit:latest. The default image is hosted on Docker Hub. We recommend that you use this image but in case you want to use another, we recommend using the region specific Amazon ECR image repositories, as they provide higher availability.
- Sumo Logic
<endpoint>and<token>: The endpoint and token need to be extracted from the HTTP Source Address URL you generated in Step 1.
For example, for the URL:
https://endpoint3.collection.us2.sumologic.com/receiver/v1/http/ExampleToken5UilxWIRSnHhU6-L_CCbuFDkc9j0l74XvUiFrmESfdsSFDsfsdQ5vYYYEu2HFuQArdsfsdfsdSaaaskNSn-VPkWsdfdWt4A==
endpoint3.collection.us2.sumologic.com will be the endpoint, and what comes after the path /receiver/v1/http/ is the token. In the sample JSON file, replace the bold variables as shown in the following snippet:
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver":"awsfirelens",
"options": {
"Name":"http",
"Host": "<endpoint>",
"URI": "/receiver/v1/http/<token>",
"Port": "443",
"tls": "on",
"tls.verify": "off",
"Format": "json_lines" }
Source category
You can add a source category or a source name by passing the Header parameters inside logConfiguration options, as shown in the following example:
"options": {
"Name":"http",
"Header": "X-Sumo-Category ECS/FireLens/Fargate",
Currently, FireLens supports only one header. If you need to add multiple headers, you can create a custom fluent bit image and specify a custom fluent bit configuration.
Application container
The sample JSON creates an httpd application container. In the image parameter, you can replace httpd with the application you are deploying, as shown in the following example:
"essential": true,
"image": "your_application",
"name": "app",
"logConfiguration": {
CloudWatch group
In the sample JSON we've provided, the FireLens Log Router container is configured to send its own logs to the CloudWatch group "awslogs-ecs-fargate-sumo”. We recommended you send the FireLens logs to CloudWatch to debug Fluent Bit Issues.
If you would like to keep this configuration, then create a log group named “awslogs-ecs-fargate-sumo” in us-west-1. Also replace the task execution role if it is named other than the default “executionRoleArn” and populate the account id shown in bold in the following example:
"executionRoleArn":
"arn:aws:iam::<account_id>:role/ecsTaskExecutionRole"
You can also create a log group with a different name. To do this, update the task definition JSON with the new CloudWatch group name as shown in bold in the following example:
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awslogs",
"options": {
"awslogs-group": "awslogs-ecs-fargate-sumo",
"awslogs-region": "us-west-1",
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "awslogs-ecs-fargate-sumo"
}
}
You can choose not to send the FireLens container logs to CloudWatch by deleting the entire options block shown from the JSON; this will not impact your ability to send logs to Sumo Logic. The task execution role executionRoleArn is also required for the awslogs logdriver. This can also be removed if this logdriver is not used.
Other properties
You can modify other properties as desired, such as CPU, RAM, and the like. For more information, see the Amazon ECS Task Definition Parameters documentation.
Create the task definition
To create the Fargate task definition, use the following command:
aws ecs register-task-definition --region us-west-1 --cli-input-json file://httpd_fargate_sumologic.json
Launch the service
You will use the following command syntax to launch the service. The command requires subnets and the security groups for the service. You will need to substitute the cluster VPC, subnet, and security group variables with real values for your environment. You can determine your cluster VPC, subnets, and associated security group from the AWS console.
aws ecs create-service --cluster fargate-ecs-firelens-cluster
--service-name firelens-sumologic-fargate --task-definition firelens-sumologic-fargate:1
--desired-count 1 --region us-west-1 --launch-type "FARGATE" --network-configuration
"awsvpcConfiguration={subnets=[subnet-1,subnet-2],securityGroups=[sg-1],assignPublicIp=ENABLED}"
You can use the following command to determine the security group for the VPC ID:
aws ec2 describe-security-groups --filters Name=vpc-id,Values=VPC_ID --region us-west-1
Step 3: Verify logs in Sumo Logic
The previous steps showed you how to configure container log collection. This section shows you how to verify the logs are appearing in Sumo Logic.
To verify your container logs are coming into Sumo Logic, run an interactive search such as shown in the following example:
_sourceCategory=ECS/Fargate
Collect EC2 container logs
This method also works with ECS clusters with EC2 containers however, the recommended method for collecting EC2 logs is to utilize the Docker logging driver.
Follow the steps in this procedure to configure EC2 container log collection using the sample EC2 task definition file.
Step 1: Add a hosted collector and HTTP source
A hosted collector allows you to upload data stored in the cloud to Sumo Logic, and an HTTP Source is an endpoint for receiving logs and metrics uploaded via a URL.
When you configure the HTTP Source, make sure to save the HTTP Source Address URL. You will need this URL to configure the task definition.
To add a hosted collection and HTTP source, do the following:
- In Sumo Logic, configure a Hosted Collector.
- In Sumo Logic, configure an HTTP Source.
Step 2: Create the task definition
Replace <account_id>, <endpoint>, <token> and AWS Fluent Bit Image in the sample JSON as done previously for Fargate.
Use the following command to create the task definition.
aws ecs register-task-definition --region us-west-1 --cli-input-json file://httpd_ec2_sumologic.json
Step 3: Create the service
Use the following command to create the service.
aws ecs create-service --cluster ec2-ecs-firelens-cluster --service-name firelens-sumologic-ec2
--task-definition firelens-sumologic-ec2:1 --desired-count 1 --region us-west-1 --launch-type "EC2"
(Optional): Create a centralized Fluentd aggregator
This task is optional. If you want to create a centralized Fluentd aggregator for log collection across all your containers, complete the steps outlined in this section.
The following diagram illustrates the centralized Fluentd collection process.
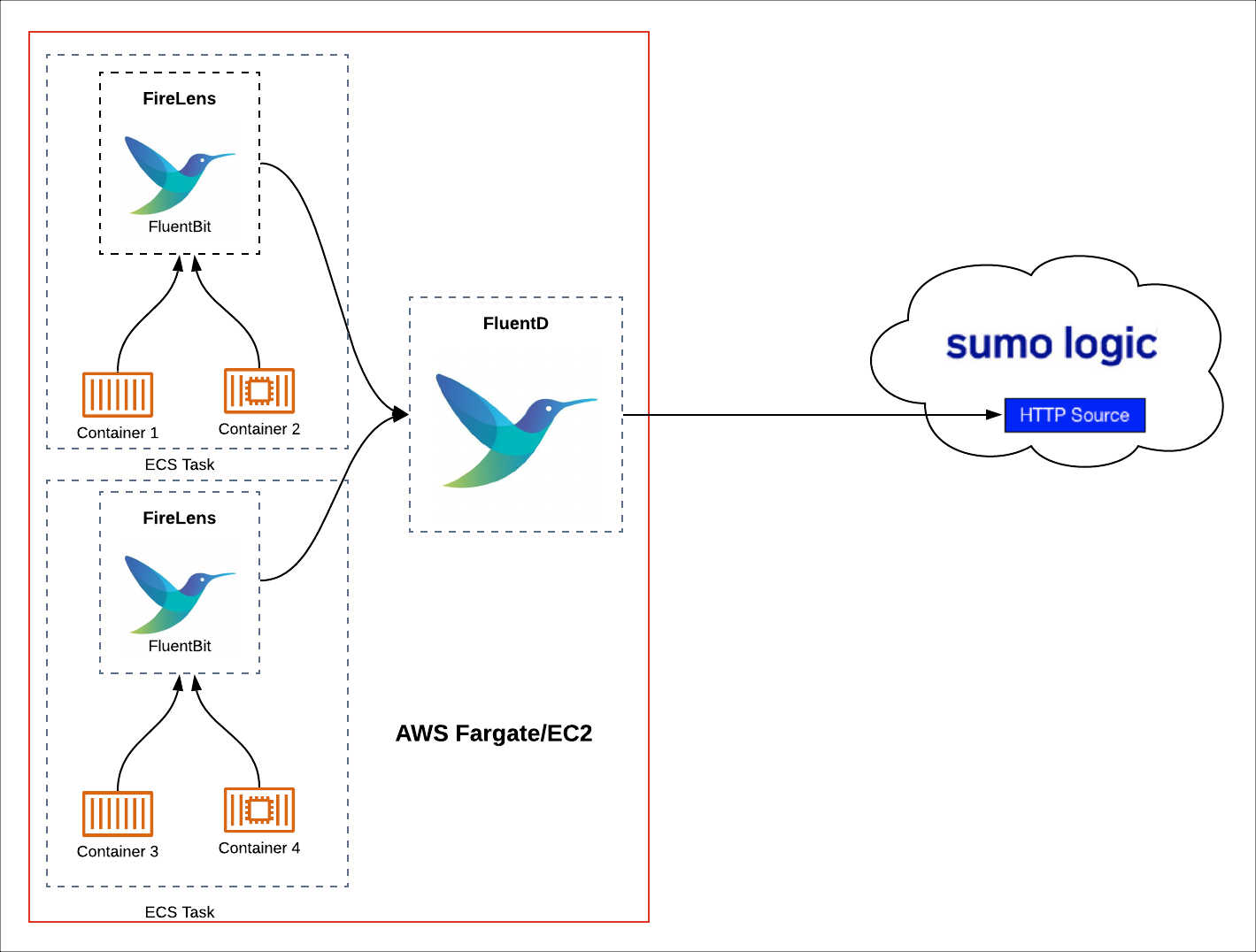
To create a centralized Fluentd aggregator, do the following:
- Create a Fluentd deployment as described in this document.
- Configure Fluentd to send the logs to Sumo Logic, using the Sumo Logic FluentD plugin.
- Create FireLens, Fluent Bit, and application containers as described in the previous section.
- Forward the logs to the Fluentd aggregator using the following application container log driver configuration. Replace "fluentdhost" (shown in bold in the following example) with the actual name of your Fluentd host.
"logConfiguration":
{
"logDriver":"awsfirelens",
"options": {
"Name": "forward",
"Host": "fluentdhost",
"Port": "24224"
}
}
(Optional) Support for Multiple HTTP Headers
At present, FireLens supports only one header in the task definition. If you need to add multiple headers, for EC2 you can store the fluent bit configuration on S3, however S3 config doesn’t work for Fargate. For Fargate you can create a custom fluent bit image and specify custom fluent bit configuration in an external configuration file.
For EC2, to store the fluent configuration on S3, do the following:
- Set the following as the log configuration:
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awsfirelens",
} - Set the following in your firelens configuration:
"firelensConfiguration": {
"type": "fluentbit",
"options": {
"config-file-type": "s3",
"config-file-value": "arn:aws:s3:::yourbucket/yourdirectory/extra.conf"
}
},
For Fargate, to create, deploy, and use custom fluent bit image, do the following:
-
Clone the AWS Fluent Bit Image available here.
-
Add a new file with custom configuration at the root folder, fluent-bit-custom.conf.
[OUTPUT]
Name http
Match *
Host <endpoint>
URI /receiver/v1/http/<token>
Port 443
Header X-Sumo-Category ECS/FireLens/Custom/Fargate
Header X-Sumo-Name ECS FireLens Custom
tls on
tls.verify off
Format json_lines -
Replace endpoint and token as described in the Prerequisites section.
-
Modify the Docker file by doing the following:
-
Add the custom directory to store the fluent-bit-custom.conf in image, /fluent-bit/etc/custom, using the following command:
RUN mkdir -p /fluent-bit/bin /fluent-bit/etc /fluent-bit/log /tmp/fluent-bit-master/ /fluent-bit/etc/custom -
Add following line to copy fluent-bit-custom.conf to the custom directory:
COPY fluent-bit-custom.conf /fluent-bit/etc/custom/fluent-bit-custom.conf
-
-
Modify the name of the Makefile, following a standard convention such as: sumologic/aws:latest
-
Create the image with the command: make release
-
Upload the image to a public repository with the command: docker push sumologic/aws:latest
-
Modify the task definition to use the newly created image and set options to use the custom configuration, as follows:
"firelensConfiguration": {
"type": "fluentbit",
"options": {
"enable-ecs-log-metadata": "true",
"config-file-type": "file",
"config-file-value": "/fluent-bit/etc/custom/fluent-bit-custom.conf"
}
}noteIn this case, the application container doesn’t need the following options:
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awsfirelens",
} -
Create a new task definition using the sample JSON, and update account ID and Image name, then run the following command.
aws ecs register-task-definition --region us-west-1 --cli-input-json file://httpd_fargate_sumologic_external_config.json -
Create the service by running the following command. You will need to substitute the subnet, and security group variables with real values for your environment. You can determine your cluster subnets and associated security group from the AWS console.
aws ecs create-service --cluster fargate-cluster --service-name firelens-sumologic-fargate-ext-image
--task-definition firelens-sumo-fargate-external-config-custom-image:1 --desired-count 1
--region us-west-1 --launch-type "FARGATE" --network-configuration
"awsvpcConfiguration={subnets=[subnet-1,subnet-2],securityGroups=[security group],assignPublicIp=ENABLED}"
Troubleshooting
- Make sure cluster has access to the internet to allow it to send logs to Sumo Logic.
- For FireLens troubleshooting and log parsing examples, please refer to this link.