Azure Event Hubs Source for Logs
The Azure Event Hubs Source provides a secure endpoint to receive data from Azure Event Hubs. It securely stores the required authentication, scheduling, and state tracking information.
Data collected
The Azure platform can be configured to export logs to one or more Event Hub destinations. Platform logs include:
Third party apps or services can be configured to send event data to Event Hubs as well, including Auth0.
Scaling Event Hubs
There are two factors that influence scaling with Event Hubs:
- Throughput units (standard tier) or Processing units (premium tier). Configured while creating Event hubs namespace.
- Partitions. Configured while creating Event hubs instance in an Event Hubs namespace.
| Expected EPS | Throughput Unit (TU) [Max 40] | Partitions [Max 32] |
|---|---|---|
| 1mb/sec | 1 TU | 1+ |
| 2mb/sec | 2 TU | 2+ |
| 10mb/sec | 10 TU | 10+ |
| 32mb/sec | 32 TU | 32 |
Throughput units (TUs) and Processing units (PUs) are shared across an Event Hub namespace. If you have multiple Event hubs in a name space, consider increasing the TU/PU units. If your volume exceeds 32 mb/sec, consider splitting the data in multiple Event Hubs namespaces.
Setup
Vendor configuration
The Event Hub doesn't have to be in the same subscription as the resource sending logs if the user who configures the setting has appropriate Azure role-based access control access to both subscriptions. By using Azure Lighthouse, it's also possible to have diagnostic settings sent to an event hub in another Azure Active Directory tenant. The event hub namespace needs to be in the same region as the resource being monitored if the resource is regional so you may have to configure multiple Azure Event Hubs Sources. More details about destination limitations and permissions are described here.
- Create an Event Hub using the Azure portal by navigating to Event Hubs in the Azure Portal.
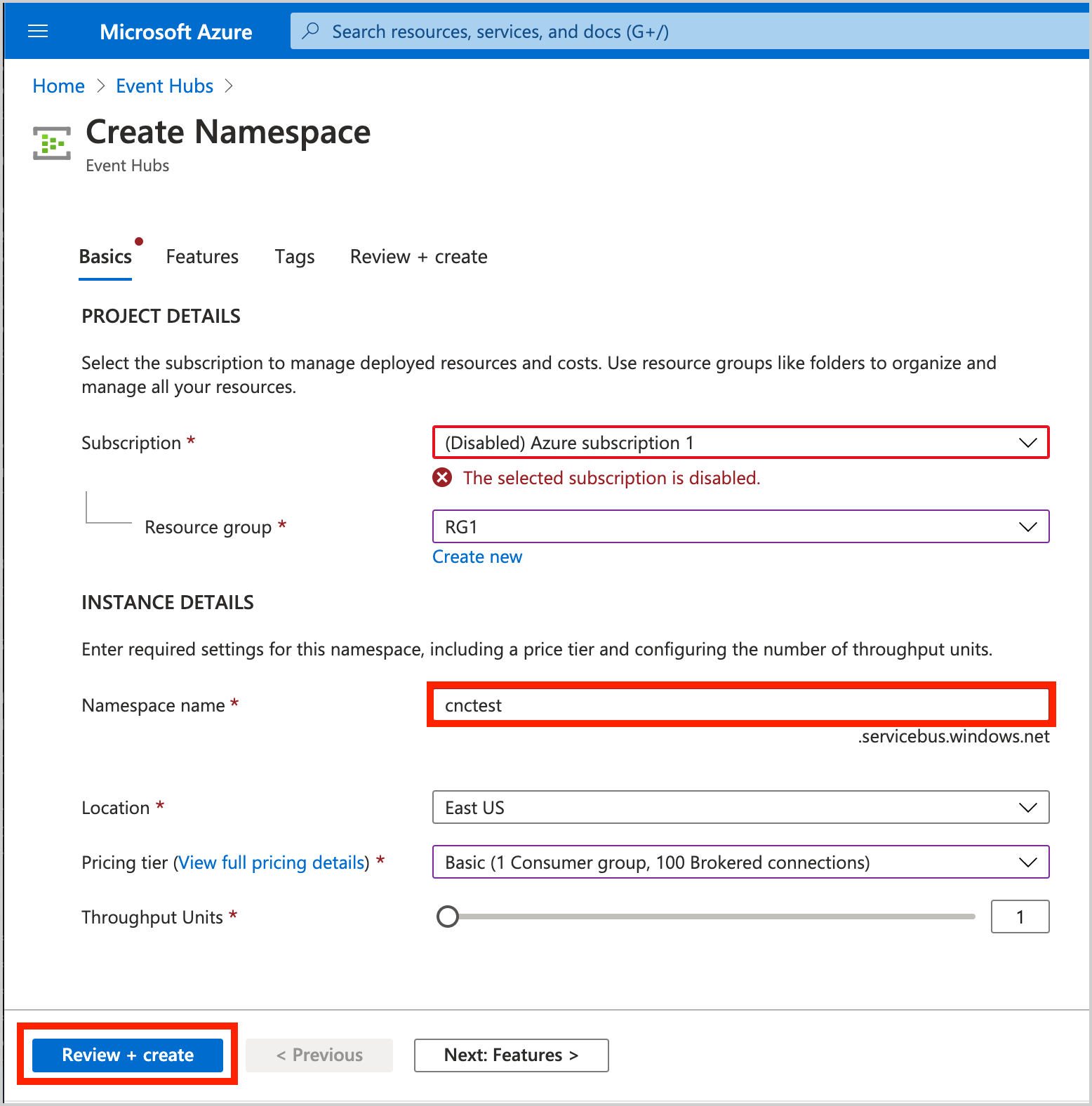
- Create an Event Hubs namespace. In this example, Namespace is set to
cnctest:
- Create an Event Hub Instance.
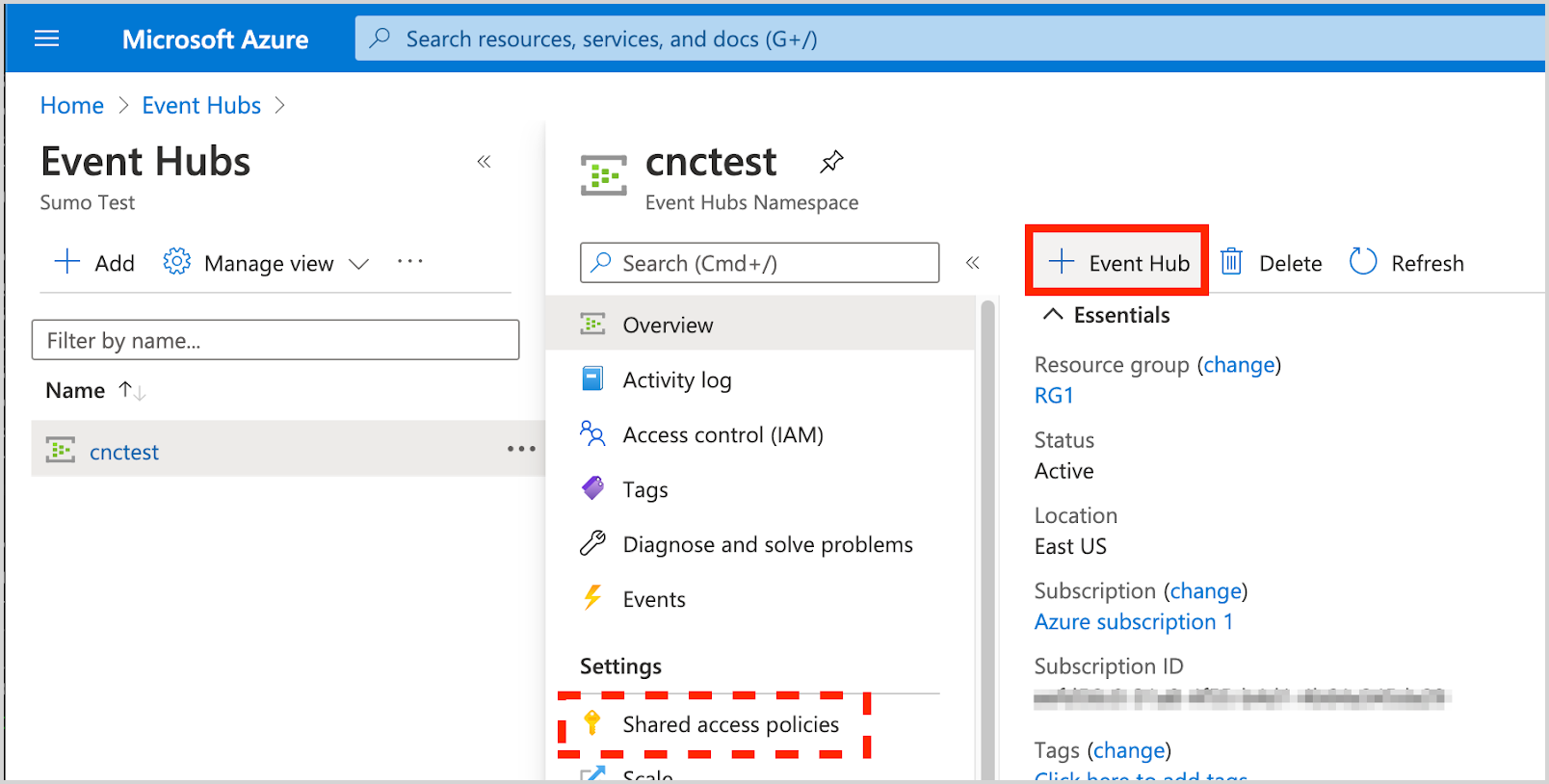
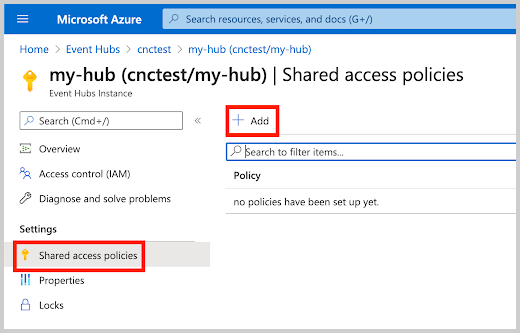
- Shared Access Policies can be set up for the entire namespace. These policies can be used to access/manage all hubs in the namespace. A policy for the namespace is created by default:
RootManageSharedAccessKey. In this example, Event Hub Instance is set tomy-hub.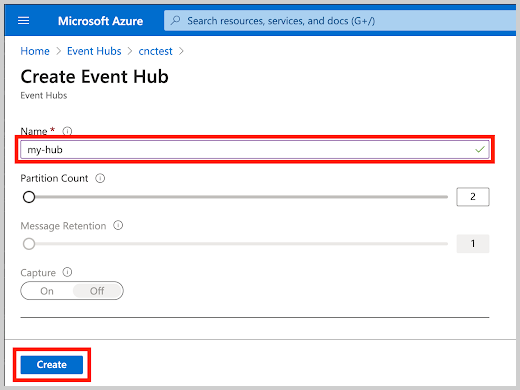
- Shared Access Policies can be set up for the entire namespace. These policies can be used to access/manage all hubs in the namespace. A policy for the namespace is created by default:
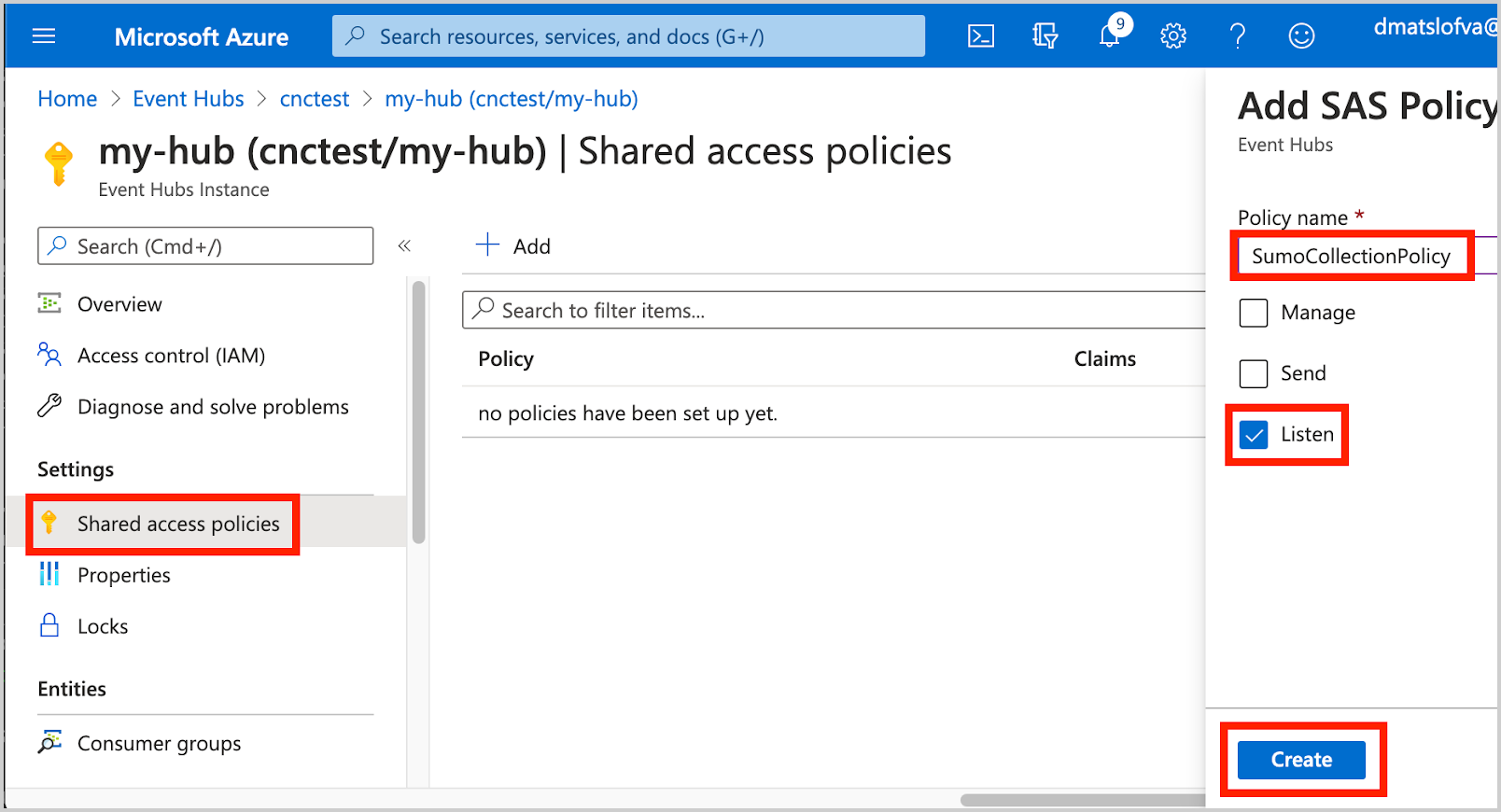
- Create a Shared Access Policy with the Listen claim to the newly created Event Hub Instance. In this example, Event Hub Instance is set to
SumoCollectionPolicy.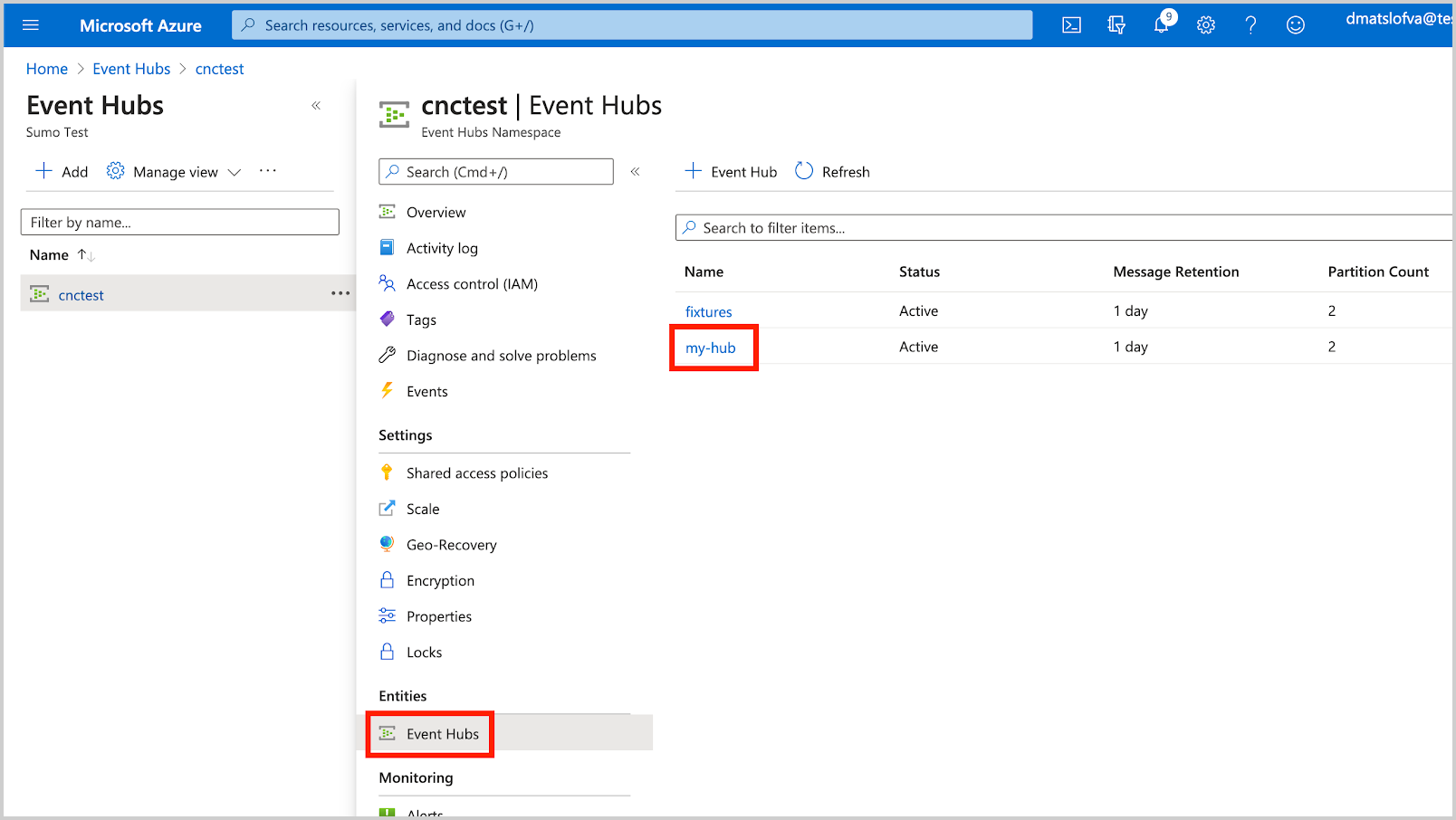
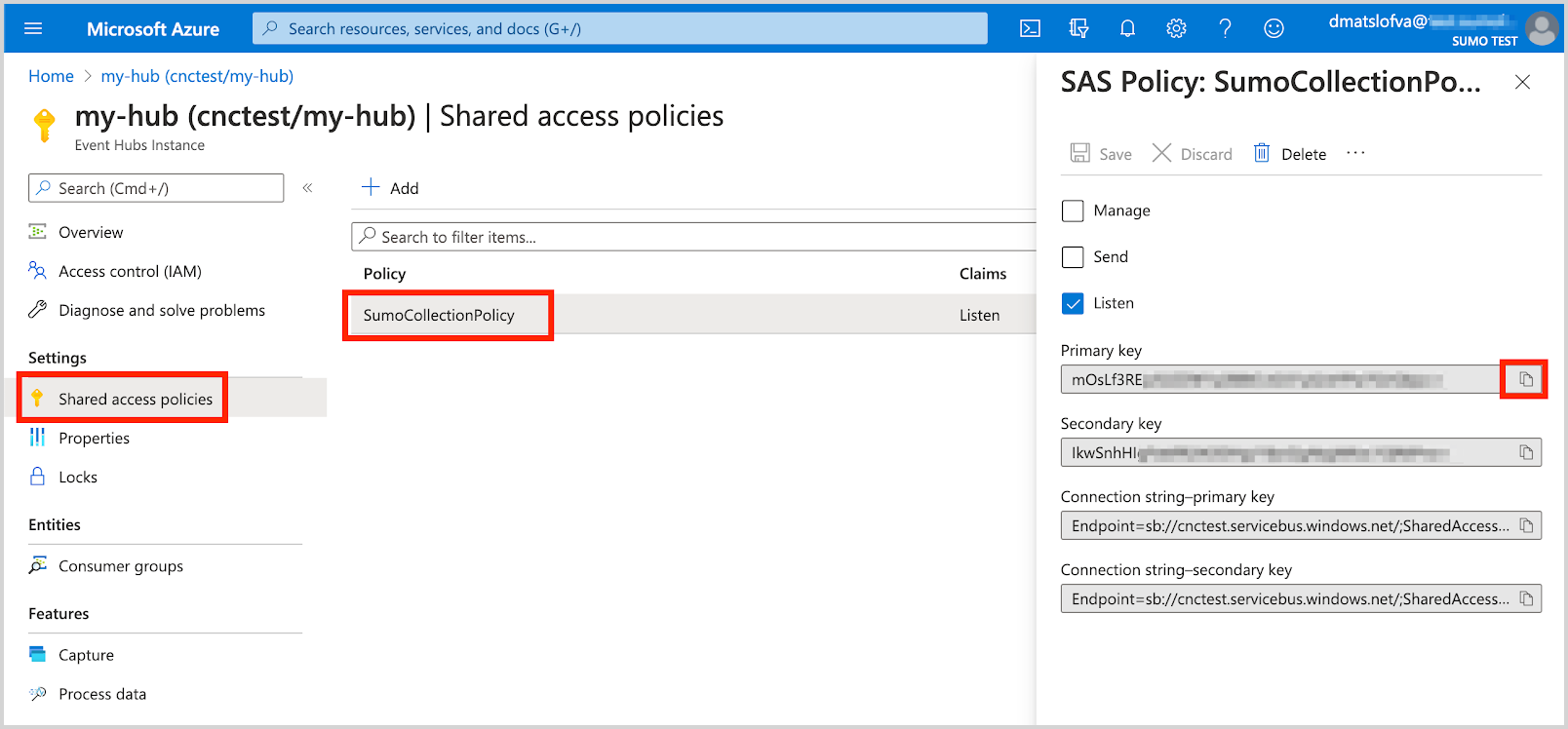
- Copy the Shared access policies Key. Copy the Primary key associated with this policy.
- When configuring the Azure Event Hubs Source in Sumo Logic, our input fields might be:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Azure Event Hubs Namespace | cnctest |
| Event Hubs Instance Name | my-hub |
| Shared Access Policy Name | SumoCollectionPolicy |
| Shared Access Policy Key (use primary key) | mOsLf3RE... |
Source configuration
When you create an Azure Event Hubs Source, you add it to a Hosted Collector. Before creating the Source, identify the Hosted Collector you want to use or create a new Hosted Collector. For instructions, see Configure a Hosted Collector.
To configure an Azure Event Hubs Source:
- Classic UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu, select Manage Data > Collection > Collection.
New UI. In the Sumo Logic top menu select Configuration, and then under Data Collection select Collection. You can also click the Go To... menu at the top of the screen and select Collection. - On the Collectors page, click Add Source next to a HostedCollector.
note
Make sure the hosted collector is tagged with tenant_name field for the out of the box Azure apps to work. You can get the tenant name using the instructions here.
- Select the Azure Event Hubs for Logs app.
- Enter a Name for the Source. The description is optional.

- (Optional) For Source Category, enter any string to tag the output collected from the Source. Category metadata is stored in a searchable field called
_sourceCategory. - Forward to SIEM. Check the checkbox to forward your data to Cloud SIEM. note
Select Forward to SIEM only if you have Cloud SIEM installed.
- (Optional) Fields. Click the +Add Field link to define the fields you want to associate, each field needs a name (key) and value.
- A green circle with a check mark is shown when the field exists in the Fields table schema.
- An orange triangle with an exclamation point is shown when the field doesn't exist in the Fields table schema. In this case, an option to automatically add the nonexistent fields to the Fields table schema is provided. If a field is sent to Sumo that does not exist in the Fields schema it is ignored, known as dropped.
- Azure Event Hubs Namespace. Enter your Azure Event Hubs Namespace name.
- Event Hubs Instance Name. Enter the Azure Event Hubs Instance Name.
- Shared Access Policy. Enter your Shared Access Policy Name and Key. The Shared Access Policy requires the Listen claim.
- Consumer Group Name. If needed, specify a custom consumer group name. When using a custom Consumer Group make sure that it exists for the Event Hub instance.
- Start collecting data field to state the start of data ingestion. Choose one of the following options:
- Now
- 24h ago
- 72h ago
- 7 days ago
- Processing Rules for Logs. Configure any desired filters, such as allowlist, denylist, hash, or mask, as described in Create a Processing Rule.
- Advanced Options for Logs.
- Timestamp Parsing. This option is selected by default. If it's deselected, no timestamp information is parsed at all.
- Time Zone. There are two options for Time Zone. You can use the time zone present in your log files, and then choose an option in case time zone information is missing from a log message. Or, you can have Sumo Logic completely disregard any time zone information present in logs by forcing a time zone. It's very important to have the proper time zone set, no matter which option you choose. If the time zone of logs cannot be determined, Sumo Logic assigns logs UTC; if the rest of your logs are from another time zone your search results will be affected.
- Timestamp Format. By default, Sumo Logic will automatically detect the timestamp format of your logs. However, you can manually specify a timestamp format for a Source. See Timestamps, Time Zones, Time Ranges, and Date Formats for more information.
- When you're finished configuring the Source, click Submit.
Metadata fields
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
_siemVendor | Microsoft | Set when Forward To SIEM is checked. |
_siemProduct | Azure | Set when Forward To SIEM is checked. |
_siemFormat | JSON | Set when Forward To SIEM is checked. |
_siemEventID | <metadata.eventType> | Where metadata.eventType is populated from the field in the event JSON, such as Administrative or Resource Health. See more information about the available event types for the Azure platform in Activity Log Categories and Resource Log Categories. Logs that do not contain a category field are assigned category UNKNOWN. |
Exporting Platform Logs to Event Hub using Diagnostic settings
To create the diagnostic settings in Azure portal, refer to the documentation and choose Stream to an event hub as the destination. Use the event hub namespace and event hub name configured in the Prerequisites section in the destination details section. You can use the default policy RootManageSharedAccessKey as the policy name.
Troubleshooting
For common error messages, refer Event Hub export error messages section.